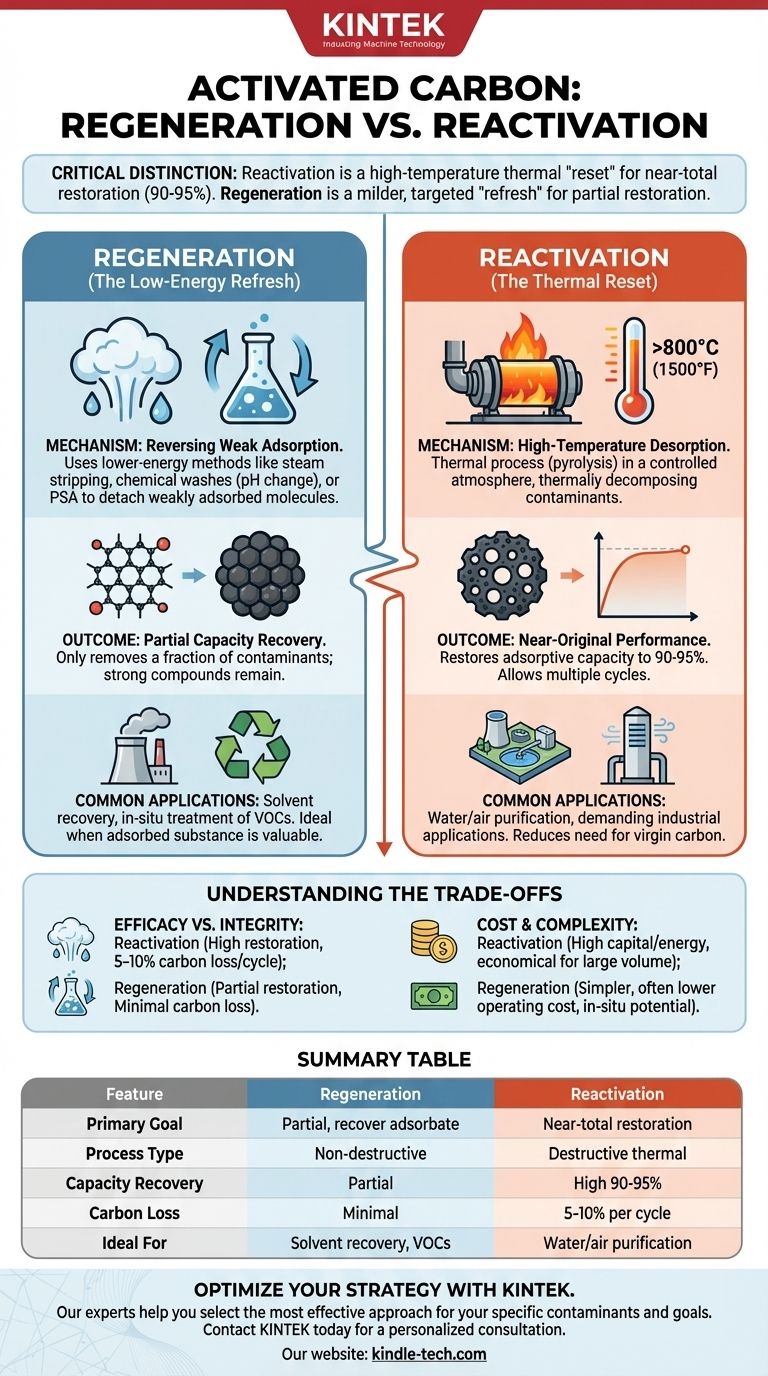
In the context of activated carbon treatment, the terms regeneration and reactivation are not interchangeable. Reactivation is an intensive, high-temperature thermal process designed to destroy adsorbed contaminants and almost fully restore the carbon's original capacity. In contrast, regeneration is a milder process that uses chemical or physical methods to only partially restore the carbon by removing more weakly adsorbed compounds.
The critical distinction lies in the method and the outcome. Reactivation is a destructive, thermal "reset" that recovers most of the carbon's performance but incurs some material loss. Regeneration is a non-destructive, targeted "refresh" that is less effective but preserves both the carbon and the adsorbed substance.

What is Regeneration? The Low-Energy Refresh
Regeneration is best understood as a process of reversing the adsorption of specific contaminants, typically those that are bound with less energy. It is not intended to be a complete restoration.
The Mechanism: Reversing Weak Adsorption
Regeneration uses lower-energy methods to encourage adsorbed molecules to detach from the carbon surface.
This is often achieved through steam stripping, chemical washes (changing pH), or pressure swing adsorption (PSA), where a change in pressure causes the compound to desorb.
These methods are only effective for volatile compounds or those that are weakly held by the carbon.
The Outcome: Partial Capacity Recovery
Because regeneration is a mild process, it only removes a fraction of the adsorbed contaminants.
Any strongly adsorbed compounds, heavy organics, or inorganic materials will be left behind, meaning the carbon's capacity is only partially restored.
Common Applications
Regeneration is most common in applications where the adsorbed substance is valuable and needs to be recovered, such as solvent recovery from industrial air streams.
What is Reactivation? The Thermal Reset
Reactivation is a far more aggressive, brute-force approach. Its goal is to return the spent carbon to a state as close to its original, virgin condition as possible.
The Mechanism: High-Temperature Desorption
Reactivation is a thermal process that occurs in a controlled atmosphere at very high temperatures, typically exceeding 800°C (1500°F).
This process first dries the carbon and then pyrolyzes, or thermally decomposes, the adsorbed organic contaminants, clearing out the intricate pore structure.
This is an industrial process that requires specialized equipment like a rotary kiln and is often performed at an off-site facility.
The Outcome: Near-Original Performance
By essentially incinerating the adsorbates, reactivation can restore the carbon's adsorptive capacity to 90-95% of its original state.
This allows the activated carbon media to be used for multiple cycles in demanding applications, significantly reducing the need to purchase virgin carbon.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these methods requires a clear understanding of the compromises involved in terms of cost, effectiveness, and the impact on the carbon media itself.
Efficacy vs. Carbon Integrity
Reactivation is highly effective at restoring performance but is also a destructive process. Each thermal cycle results in a 5-10% loss of carbon material due to burn-off and physical degradation (abrasion).
Regeneration is much gentler on the carbon structure, but its effectiveness is limited to a narrow range of contaminants and it cannot restore the high performance needed for many critical applications.
Cost and Complexity
While reactivation has a high capital cost and is energy-intensive, it is often more economical over the long term for large-volume applications (like municipal water treatment) compared to repeated disposal and replacement with virgin carbon.
Regeneration systems can often be simpler and less expensive to operate per cycle, and can sometimes be performed in-situ, avoiding transportation costs.
Contaminant Compatibility
The choice is often dictated by the contaminant. Regeneration is only viable for specific, weakly adsorbed substances that can be coaxed off the carbon.
Reactivation is a robust, non-selective solution capable of destroying a wide spectrum of complex organic compounds that are impossible to remove through regeneration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be based on the specific contaminant you are targeting, your operational budget, and your performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is recovering a valuable adsorbed solvent: Regeneration is the only method that preserves the contaminant for reuse.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the lifespan of carbon in a demanding application like water or air purification: Reactivation is the industry standard for restoring high performance over multiple cycles.
- If your primary focus is simple, in-place removal of specific volatile organic compounds (VOCs): An in-situ regeneration system may be the most efficient and cost-effective choice.
Ultimately, understanding this distinction empowers you to select a carbon treatment strategy that aligns perfectly with your operational and financial goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Regeneration | Reactivation |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Partial restoration; recover valuable adsorbate | Near-total restoration of carbon capacity |
| Process Type | Non-destructive (chemical, steam, pressure swing) | Destructive thermal process (>800°C / 1500°F) |
| Capacity Recovery | Partial (only removes weakly adsorbed compounds) | High (90-95% of original capacity) |
| Carbon Loss | Minimal to none | 5-10% material loss per cycle |
| Ideal For | Solvent recovery, in-situ treatment of VOCs | Water/air purification, demanding applications |
Optimize your activated carbon strategy with KINTEK
Understanding the right process for your spent carbon is crucial for efficiency and cost control. Whether your priority is solvent recovery through gentle regeneration or maximizing media lifespan with high-performance reactivation, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your laboratory or industrial needs.
We specialize in providing solutions for laboratories that rely on activated carbon for purification, analysis, and treatment processes. Let our experts help you select the most effective and economical approach for your specific contaminants and operational goals.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover how we can enhance your carbon treatment lifecycle.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How to regenerate activated carbon? Master the 3-Stage Thermal Process for Cost Savings
- What temperature is needed for porcelain? A Guide to Cone 6 and Cone 10 Firing
- What is the temperature of a carbon regeneration kiln? Mastering the 750-800°C Reactivation Process
- Can you restore activated carbon? Understanding the Industrial Reactivation Process
- What temperature is a carbon regeneration kiln? Master the 650°C-800°C Range for Optimal Results



















