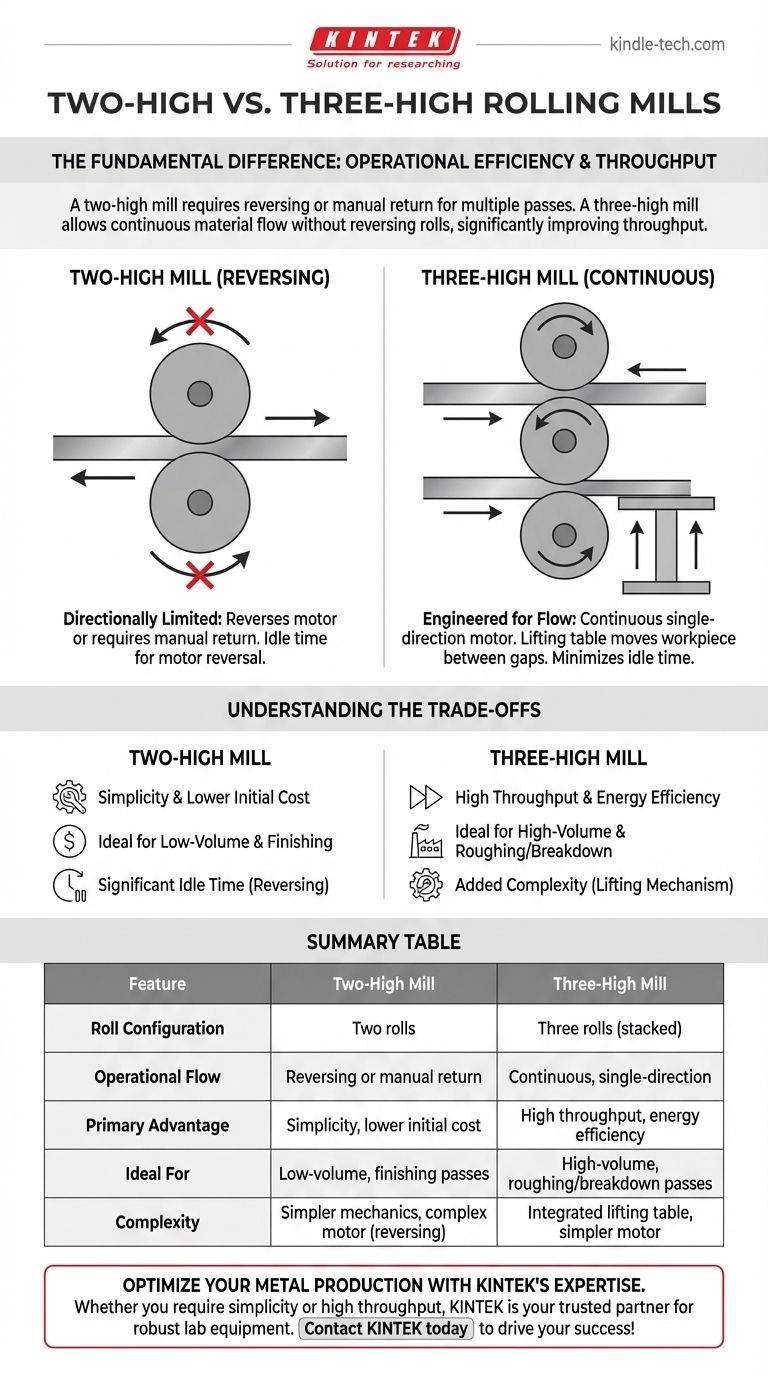
The fundamental difference between two-high and three-high rolling mills lies in their operational efficiency and how they handle multiple passes. A two-high mill uses two rollers and requires either reversing the entire drive motor or manually passing the workpiece back over the top for another pass. A three-high mill uses a stack of three rollers, which allows the material to be passed back and forth continuously without ever reversing the direction of the rolls, significantly improving throughput.
The choice between a two-high and three-high configuration is not just about the number of rolls; it's a strategic decision balancing mechanical simplicity against operational efficiency. The three-high mill's design is purpose-built to eliminate the idle time inherent in reversing mills.

Deconstructing the Mill Designs
To grasp the implications, we must first visualize how each configuration works. The arrangement of the rolls directly dictates the flow of material and the overall efficiency of the process.
The Two-High Mill: Simple but Directionally Limited
A two-high mill is the most basic rolling configuration, consisting of two large rollers rotating in opposite directions. The workpiece is drawn through the gap between them to reduce its thickness.
There are two primary variants of this design:
- Non-Reversing: The simplest type, where the rolls spin in a fixed direction. To make another pass, the workpiece must be lifted and passed back over the top of the mill, an inefficient and time-consuming process.
- Reversing: The motor driving the rolls can change direction, allowing the workpiece to be passed back and forth through the same set of rolls. This is more efficient than a non-reversing mill but requires a robust, specialized motor and control system.
The Three-High Mill: Engineered for Continuous Flow
A three-high mill features three rolls stacked vertically. The top and bottom rolls rotate in the same direction, while the middle roll rotates in the opposite direction.
This clever arrangement creates two distinct rolling gaps. The workpiece is passed through the gap between the bottom and middle rolls in one direction. Then, a lifting table raises the workpiece to pass it back through the gap between the middle and top rolls.
The key advantage is that the drive motor runs continuously in one direction. There is no lost time or energy waiting for a massive motor to reverse its rotation.
Comparing Operational Efficiency
The design differences directly translate into performance metrics. The primary distinction is how each mill handles the time between compressive passes.
Throughput and Idle Time
In a production environment, idle time is the enemy of efficiency. The three-high mill is designed specifically to minimize it. As soon as the workpiece completes one pass, it is immediately positioned for the return pass.
A two-high reversing mill, by contrast, introduces a mandatory pause as the powerful motor stops and reverses direction. A non-reversing two-high mill has the most significant idle time, as the workpiece must be physically transported back to the entry side.
Mechanical and Control Complexity
Efficiency comes at the cost of complexity. The three-high mill, while mechanically elegant, requires an integrated lifting mechanism to move the workpiece between the lower and upper rolling gaps. This adds another system to build, operate, and maintain.
The two-high reversing mill has simpler workpiece handling but requires a more complex and expensive electrical system capable of handling the immense torque and energy demands of frequent reversals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither design is universally superior. The correct choice depends entirely on the specific application, required production volume, and budget.
Two-High Mill: Simplicity and Lower Initial Cost
The primary advantage of a two-high mill is its relative simplicity and lower capital cost. Its construction is straightforward, and maintenance is less demanding.
This makes it an ideal choice for lower-volume applications, finishing passes where only one or two passes are needed, or for smaller-scale operations where initial cost is a major driver. The trade-off is significantly lower throughput.
Three-High Mill: Throughput and Energy Efficiency
The core strength of the three-high mill is its high production rate. By eliminating reversal time, it achieves a more continuous and efficient workflow, making it a workhorse for the initial breakdown of ingots and blooms (roughing passes).
Its continuous, single-direction motor operation is also more energy-efficient than the constant start-stop-reverse cycle of a two-high reversing mill. The main disadvantage is the higher initial investment and the added complexity of the workpiece lifting table.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the proper mill configuration requires a clear understanding of your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is low-volume production or mechanical simplicity: A two-high mill offers the most straightforward, lowest-cost entry point for rolling operations.
- If your primary focus is high-volume throughput and energy efficiency: A three-high mill is the superior choice for continuous roughing and breakdown passes, as it is engineered to minimize idle time.
- If you are performing initial breakdown of heavy ingots: The robust, high-throughput nature of a three-high mill almost always makes it the preferred configuration for this demanding stage.
Ultimately, understanding this core operational difference empowers you to select the mill configuration that best aligns with your specific production goals and economic constraints.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Two-High Mill | Three-High Mill |
|---|---|---|
| Roll Configuration | Two rolls | Three rolls (stacked) |
| Operational Flow | Reversing or manual return | Continuous, single-direction |
| Primary Advantage | Simplicity, lower initial cost | High throughput, energy efficiency |
| Ideal For | Low-volume, finishing passes | High-volume, roughing/breakdown passes |
| Complexity | Simpler mechanics, complex motor (reversing) | Integrated lifting table, simpler motor |
Optimize Your Metal Production with KINTEK's Expertise
Choosing the right rolling mill is critical for your lab or production facility's efficiency and output. Whether you require the simplicity of a two-high mill or the high-throughput capabilities of a three-high mill, KINTEK is your trusted partner. We specialize in providing robust lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific metalworking and research needs.
Our experts can help you select the perfect configuration to enhance your operational workflow and achieve superior results. Don't let equipment limitations hinder your progress.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your requirements and discover how our solutions can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
People Also Ask
- Is co-extrusion the same as dual extrusion? Unlock the Power of Multi-Material Plastic Profiles
- What is the difference between Banbury and internal mixer? Understanding Rotor Design for Better Mixing
- What are the disadvantages of single screw extruders? Key Limitations for Complex Materials
- What is the process of twin screw granulation? Achieve Superior Consistency in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- What is pyrolysis of rubber? Transform Waste Tires into Oil, Carbon & Gas
- What is the meaning of blowing film? A Guide to Biaxial Orientation and Stronger Plastic Films
- What are the two basic types of extrusion? Hot vs. Cold Extrusion Explained
- What are the advantages of a two-high rolling mill? Cost-Effective Durability for Heavy Reduction



















