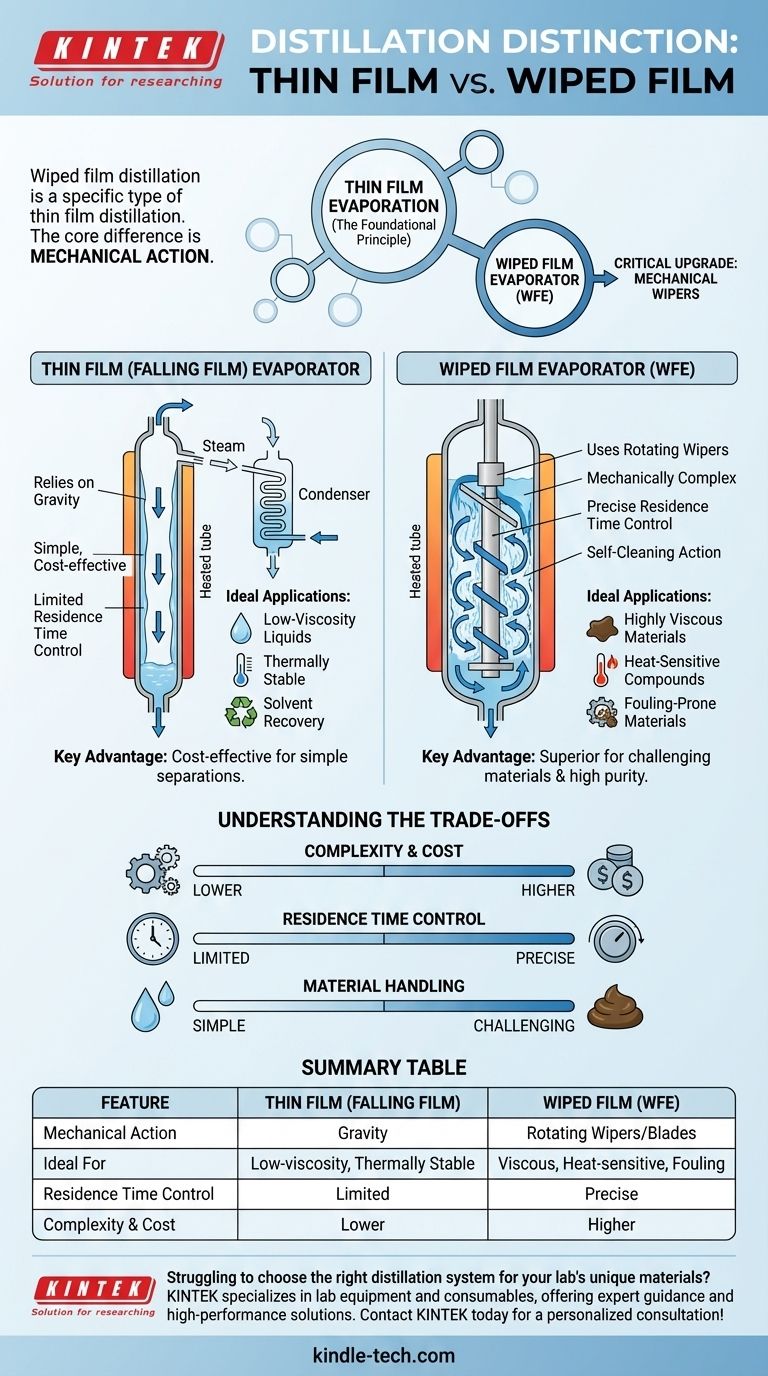
In the world of distillation, the terms 'thin film' and 'wiped film' are a common source of confusion, often used interchangeably. The critical distinction is that wiped film distillation (also called a wiped film evaporator or WFE) is a specific type of thin film distillation. All wiped film systems are thin film systems, but the reverse is not true, and the difference lies in the use of mechanical agitation.
The core difference is mechanical action. A standard thin film evaporator relies on gravity to pull liquid down a heated surface, while a wiped film evaporator uses rotating blades (wipers) to actively spread, mix, and accelerate this process. This mechanical wiping action makes it far superior for processing viscous, heat-sensitive, or fouling materials.

The Foundational Principle: Thin Film Evaporation
All thin film evaporation technologies share a common goal: to separate compounds by boiling them under vacuum. The "thin film" is the key to making this process efficient and gentle.
Why Create a Thin Film?
Distilling under a deep vacuum lowers the boiling point of compounds, which is essential for protecting thermally sensitive molecules from degrading. Creating a thin film of the feed material on a heated surface maximizes the surface area-to-volume ratio.
This allows for extremely rapid and efficient heat transfer into the liquid, causing the more volatile compounds to evaporate almost instantly. The short residence time on the heated surface is what minimizes thermal stress on the product.
The Basic Model: Falling Film Evaporators
The simplest type of thin film evaporator is a falling film evaporator. In this design, liquid is introduced at the top of a heated vertical tube or column.
Gravity pulls the liquid down the interior wall, forming a "falling film." As it flows, the volatile components evaporate and are collected on a separate condenser, while the less volatile residue is collected at the bottom. This is a thin film evaporator in its most basic form.
The Critical Upgrade: Introducing the Wipers
Wiped film distillation takes the core principle of a thin film and enhances it with a crucial mechanical component. This fundamentally changes its capabilities and ideal applications.
What is a Wiped Film Evaporator?
A wiped film evaporator (WFE), sometimes called a short path evaporator, includes an internal rotating assembly fitted with blades or rollers. These wipers are positioned with a very tight clearance to the heated wall.
As the feed material is introduced, these wipers physically spread it into a highly turbulent, ultra-thin film across the entire heated surface.
The Advantage of Mechanical Agitation
This mechanical wiping action provides two critical advantages over a simple gravity-driven falling film:
- Forced Turbulence: The wipers continuously mix the film, ensuring uniform temperature distribution and preventing localized overheating (hot spots) that can degrade the product.
- Surface Renewal: The wipers constantly expose new material to the heated surface, ensuring that evaporation is as fast and complete as possible.
Handling Viscosity and Fouling
The wipers are indispensable when working with challenging materials. For highly viscous liquids (like honey or thick oils), gravity alone is insufficient to create a uniform film. The wipers physically force the material into the required thin layer.
Furthermore, if a material is prone to fouling (leaving solid deposits on the heated surface), the wiping action acts as a self-cleaning mechanism, keeping the heat transfer surface clear and efficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a simple falling film and a wiped film system involves evaluating complexity, cost, and the specific nature of your material.
Complexity and Cost
Wiped film systems are more mechanically complex. They have a rotating drive shaft, a motor, and precision internal seals that must maintain a deep vacuum. This engineering adds to the initial purchase price and long-term maintenance requirements.
When a Simple Thin Film Is Enough
For applications involving low-viscosity, thermally stable liquids (like solvent recovery), a falling film evaporator is often sufficient. It is a simpler, more cost-effective solution when the advanced capabilities of a WFE are not required.
Residence Time and Process Control
A WFE offers superior control over residence time—the duration the material is exposed to heat. By adjusting the wiper speed and feed rate, an operator can precisely dial in the process for optimal separation and minimal degradation, a level of control not possible in a gravity-fed system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision is not about which technology is "better" in the abstract, but which is the correct tool for your specific separation goal.
- If your material is highly viscous, heat-sensitive, or prone to fouling: A wiped film evaporator is the necessary and superior choice for ensuring product quality, yield, and process stability.
- If your material is a low-viscosity liquid with good thermal stability: A simpler falling film evaporator is a more cost-effective and perfectly adequate solution.
- If you need precise control over a very short residence time for maximum purity: The mechanical wipers provide an essential control parameter that is absent in gravity-driven systems.
Ultimately, understanding this distinction moves you from comparing terms to strategically selecting the right tool for your specific separation challenge.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Thin Film (Falling Film) Evaporator | Wiped Film Evaporator (WFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Action | Relies on gravity | Uses rotating wipers/blades |
| Ideal For | Low-viscosity, thermally stable liquids | Viscous, heat-sensitive, or fouling materials |
| Residence Time Control | Limited | Precise control via wiper speed and feed rate |
| Complexity & Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Key Advantage | Cost-effective for simple separations | Superior for challenging materials and purity |
Struggling to choose the right distillation system for your lab's unique materials? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance and high-performance solutions for all your laboratory needs. Whether you're processing heat-sensitive compounds or viscous liquids, our team can help you select the ideal evaporator to maximize yield, purity, and efficiency. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and unlock the full potential of your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the drawbacks of PECVD? Understanding the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing



















