At its core, the term "ceramic" is a broad category of materials, and zirconia is a specific type of advanced ceramic. The common confusion arises because in dentistry, "ceramic" is often used as shorthand for more traditional porcelain-based materials, especially those fused to a metal base (PFM). Zirconia, composed of zirconium dioxide, is a monolithic (single-material) ceramic that is significantly stronger and more fracture-resistant than traditional porcelain.
The essential difference isn't between zirconia and ceramic, but between zirconia and other types of dental ceramics. Zirconia offers superior strength ideal for high-pressure areas, while other ceramics can sometimes provide more nuanced aesthetics for highly visible teeth.
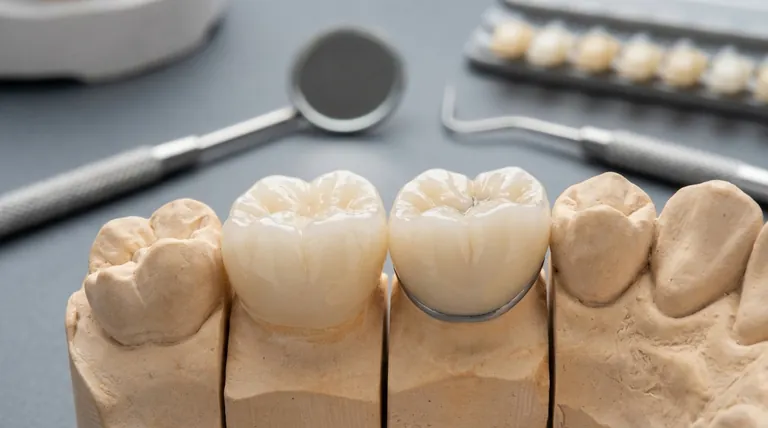
Understanding the Material Landscape
To make an informed decision, you must first understand the main players in dental restorations. "Ceramic" is a class, not a single material.
Defining Dental Ceramics
A ceramic is an inorganic, non-metallic solid prepared by the action of heat and subsequent cooling. In dentistry, this class of materials is prized for its hardness, wear resistance, and natural appearance.
The Three Main Contenders
When discussing crowns or bridges, the choice is typically between three types of restorations:
- Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM): A metal alloy substructure with a layer of tooth-colored porcelain baked on top.
- Zirconia: A monolithic material made from incredibly strong zirconium dioxide crystals.
- Lithium Disilicate: Another type of all-ceramic material (brand name E-max) known for its excellent aesthetics.
Zirconia vs. PFM: A Head-to-Head Comparison
The most common comparison is between the modern standard, zirconia, and the former gold standard, PFM.
Material Composition
A PFM crown is a hybrid. It has a hidden metal core for strength and an outer porcelain layer for aesthetics.
A zirconia crown is monolithic, meaning it's crafted from a single, solid block of zirconium dioxide. This eliminates the need for a metal base.
Strength and Durability
Zirconia is the clear winner in strength. It is exceptionally resistant to chipping and fracturing, making it the premier choice for molars and patients who grind their teeth (bruxism).
PFM crowns derive strength from their metal core, but the porcelain layer is their weak point. This layer can chip or fracture, exposing the metal underneath.
Aesthetics and Appearance
Modern zirconia has made huge strides. Newer "high-translucency" zirconia mimics the look of natural teeth very well, making it suitable for front teeth.
PFM can look very natural initially. However, it often creates a dark or gray line at the gumline where the metal edge of the crown becomes visible, a significant aesthetic drawback.
Biocompatibility
Both materials are generally well-tolerated. However, zirconia is an all-ceramic, inert material, eliminating any risk of metal allergies or sensitivities that some patients may experience with the alloys used in PFM crowns.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. Understanding their limitations is key to making the right choice.
The Strength vs. Aesthetics Dilemma
While modern zirconia is highly aesthetic, some dental professionals argue that lithium disilicate or expertly layered porcelain can achieve a slightly higher level of translucency and vitality, sometimes making it the preferred choice for a single front tooth that must perfectly match its neighbors.
PFM's Structural Weakness
The primary trade-off with a PFM crown is the risk of the porcelain layer chipping away from the metal substructure. This is the most common mode of failure for these restorations.
Zirconia's Preparation Requirements
Because zirconia is so strong, it can be made thinner than PFM crowns. This often means your dentist can preserve more of your natural tooth structure when preparing the tooth for the crown, which is always a clinical advantage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Restoration
Your final decision should be made in consultation with your dentist, based on the tooth's location and your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is durability (e.g., a molar): Zirconia is the undisputed champion due to its immense strength and fracture resistance.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics for a front tooth: High-translucency zirconia and lithium disilicate are both premier choices that balance a natural look with excellent strength.
- If you are concerned about metal allergies: Any all-ceramic option like zirconia or lithium disilicate is superior to a PFM restoration.
Understanding these material properties empowers you to have a more informed discussion with your dentist about the ideal long-term solution for your health and smile.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Zirconia | Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Monolithic zirconium dioxide | Metal core with porcelain layer |
| Strength | Excellent, ideal for molars | Good, but porcelain can chip |
| Aesthetics | High-translucency options available | Can show a dark gumline |
| Biocompatibility | Hypoallergenic, no metal | Risk of metal allergies |
Equip your lab with the right tools for dental restoration research and development. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for testing and developing advanced dental materials like zirconia and ceramics. Whether you're researching material strength, aesthetics, or biocompatibility, our reliable equipment helps you achieve precise, consistent results. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's dental material innovations and ensure you have the right technology for your needs.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of biomass conversion? High Costs, Logistical Hurdles, and Environmental Trade-offs
- What is the sputtering voltage of a magnetron? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- What would be an advantage of biomass over the use of coal? A Cleaner, Carbon-Neutral Energy Source
- What are the key differences between incineration and gasification? Explore Waste Management Solutions
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy













