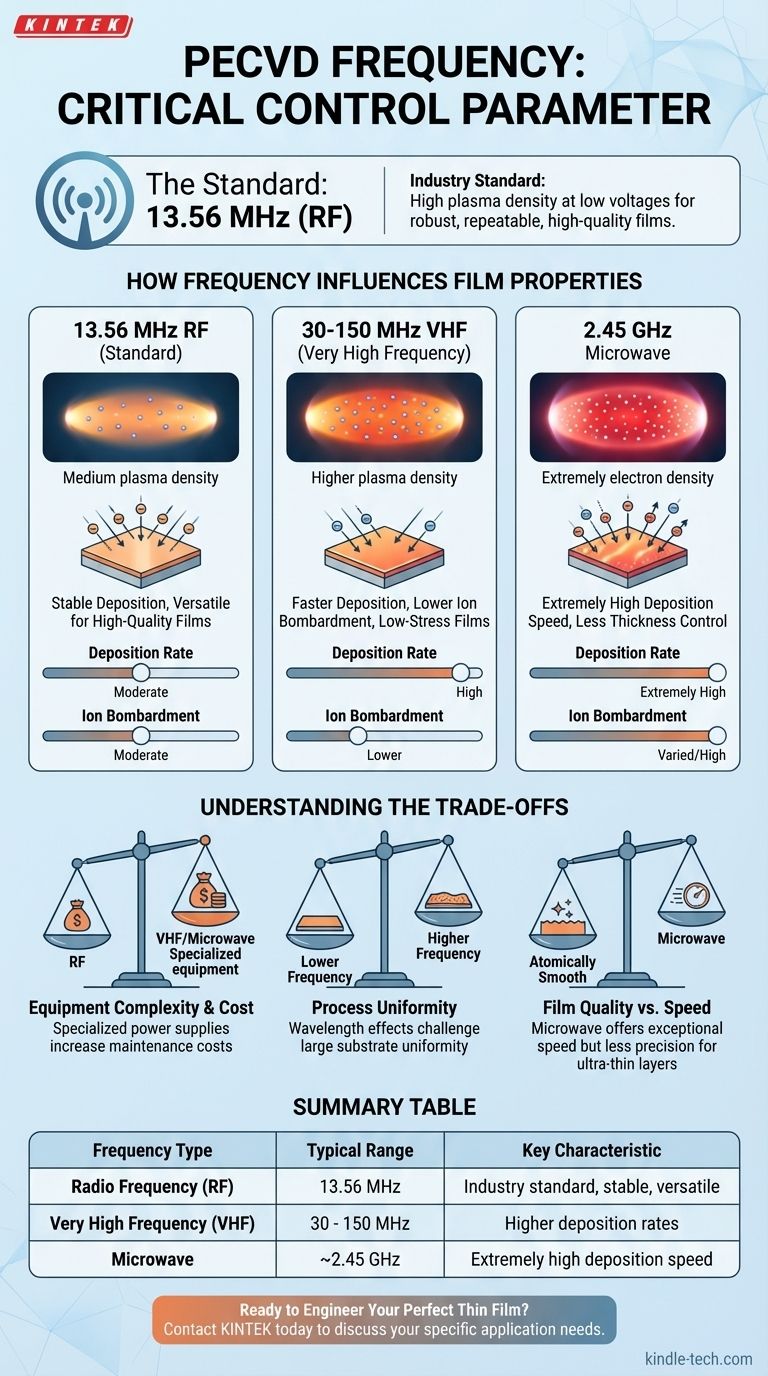
The standard operating frequency for Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is 13.56 MHz, which falls into the Radio Frequency (RF) spectrum. However, the technology also utilizes Very High Frequency (VHF) systems that operate at frequencies up to 150 MHz, as well as microwave-based systems for specialized applications.
The choice of frequency in PECVD is a critical control parameter, not just a technical specification. It directly dictates the plasma density and ion bombardment energy, which in turn determines the deposition rate and the final physical properties of the deposited film.
Why Frequency is a Critical Process Parameter
Understanding the role of frequency is essential to understanding the PECVD process itself. The frequency of the applied electric field fundamentally changes the behavior of the plasma and its interaction with the substrate surface.
The Standard: Radio Frequency (13.56 MHz)
The vast majority of PECVD systems operate at 13.56 MHz. This frequency is an industrial standard because it is highly effective and widely available.
At this frequency, the system can achieve a high plasma density even at relatively low voltages. This efficiency allows for robust and repeatable deposition of high-quality films.
Increasing Deposition Rates with Very High Frequency (VHF)
VHF-PECVD systems operate at higher frequencies, typically in the 30-150 MHz range.
Increasing the frequency generally leads to a higher plasma density. This translates directly to a faster deposition rate, which is highly beneficial for applications requiring high throughput or the deposition of thicker amorphous or microcrystalline films.
The Role of Microwave Frequencies
Microwave PECVD represents another class of the technology, operating at much higher frequencies (e.g., 2.45 GHz).
These systems can achieve extremely high deposition rates, sometimes reaching 100 Å/s. However, this speed often comes at the cost of reduced control over film thickness and higher equipment maintenance costs.
How Frequency Influences Film Properties
The frequency is a primary lever for tuning the outcome of the deposition. By adjusting it, or by using multiple frequencies simultaneously, engineers can precisely control the characteristics of the final material.
Controlling Plasma Density
Higher excitation frequencies are more efficient at trapping and energizing electrons within the plasma chamber.
This enhanced energy transfer results in a higher degree of ionization and dissociation of precursor gases, leading to a denser plasma and making more reactive species available for film growth.
Adjusting Ion Bombardment Energy
Frequency directly influences the energy with which ions strike the substrate surface. This ion bombardment is crucial for controlling film density, adhesion, and internal stress.
Higher frequencies (VHF) tend to reduce the average ion bombardment energy, which is desirable for depositing low-stress films on delicate substrates. Conversely, lower frequencies can increase ion energy, which can be used to create denser films.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a frequency involves balancing competing factors. There is no single "best" frequency; the optimal choice depends entirely on the desired outcome.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
The standard 13.56 MHz RF equipment is mature, reliable, and cost-effective.
Moving to VHF or microwave frequencies requires more specialized and expensive power supplies, matching networks, and chamber designs, which also increases maintenance costs.
Process Uniformity
Achieving a uniform plasma distribution over a large substrate becomes more challenging at higher frequencies.
Wavelength effects can cause standing waves within the chamber, leading to non-uniformity in the film's thickness and properties. This requires more sophisticated engineering to overcome.
Film Quality vs. Deposition Speed
There is often a direct trade-off between the speed of deposition and the precision of the resulting film.
While microwave PECVD offers exceptional speed, it may be less suitable for applications that demand atomically smooth surfaces or highly controlled, ultra-thin layers.
Selecting the Right Frequency for Your Application
Your process goals should guide your choice of PECVD frequency.
- If your primary focus is process stability and versatility: The industry-standard 13.56 MHz is the established workhorse for a vast range of high-quality films.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput for thicker films: VHF-PECVD provides a significant boost in deposition rate over standard RF systems.
- If your primary focus is precise control over stress and density: Utilizing dual-frequency systems allows for independent control of plasma density and ion bombardment, offering the highest degree of process control.
Ultimately, frequency is the primary tool used in PECVD to engineer the plasma environment and, by extension, the final properties of the deposited material.
Summary Table:
| Frequency Type | Typical Range | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Radio Frequency (RF) | 13.56 MHz | Industry standard, stable, versatile |
| Very High Frequency (VHF) | 30 - 150 MHz | Higher deposition rates |
| Microwave | ~2.45 GHz | Extremely high deposition speed |
Ready to Engineer Your Perfect Thin Film?
Selecting the right PECVD frequency is critical for achieving your desired film properties, from stress and density to deposition rate. KINTEK specializes in providing lab equipment and consumables for advanced material deposition, helping laboratories like yours optimize processes for groundbreaking research and development.
Let our experts guide you to the ideal solution. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application



















