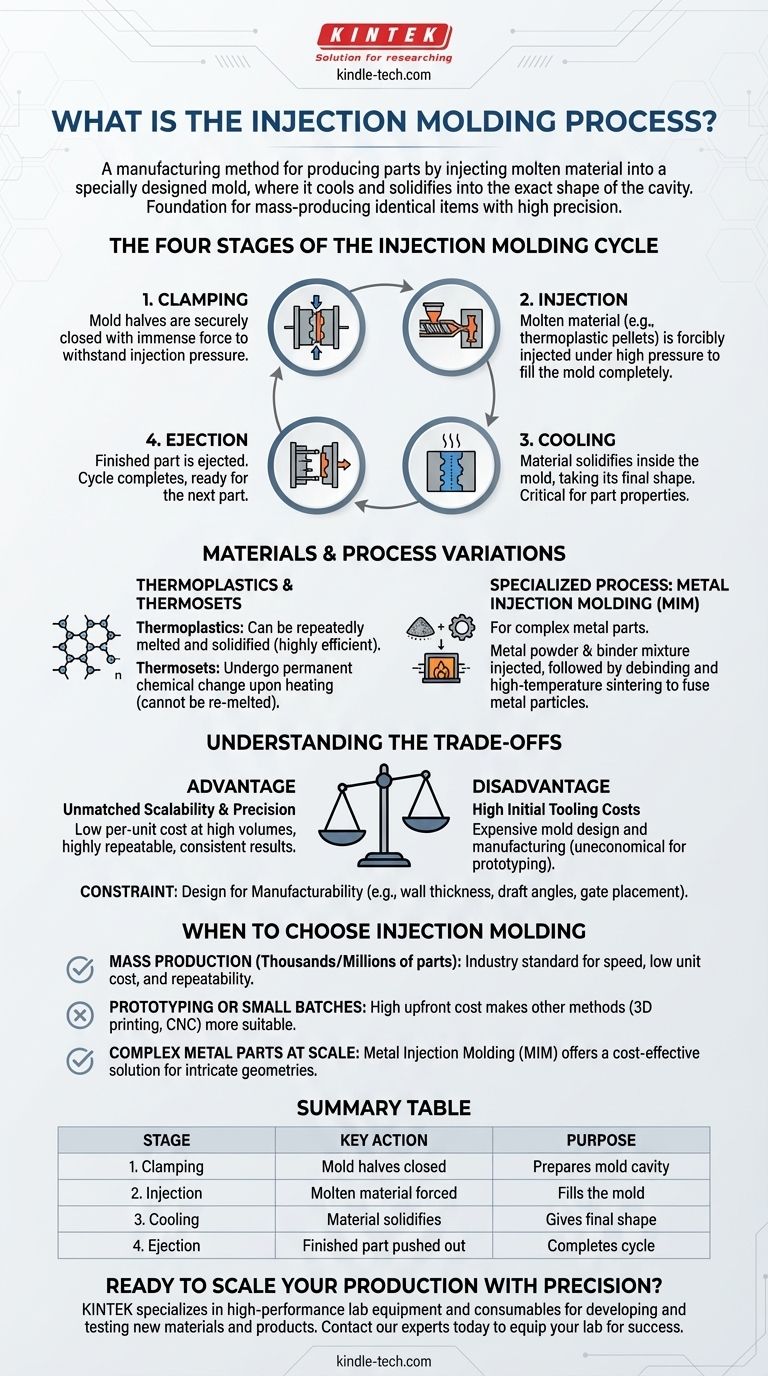
At its core, injection molding is a manufacturing method for producing parts by injecting molten material into a specially designed mold. The material, most commonly a thermoplastic, is then cooled and solidified, taking the exact shape of the mold cavity. This process is the foundation for mass-producing countless identical items with high precision.
Injection molding's primary value lies in its unparalleled ability to produce complex parts at an extremely high volume and low per-unit cost. However, this efficiency is balanced by a significant upfront investment in the creation of the mold itself.

The Four Stages of the Injection Molding Cycle
The process is a highly repeatable and rapid cycle, often taking only seconds to complete. Each cycle consists of four distinct stages.
Stage 1: Clamping
Before any material is injected, the two halves of the mold, or "tool," must be securely closed. A clamping unit applies immense force to hold the mold shut against the pressure of the injection stage.
Stage 2: Injection
Raw plastic material, typically in the form of small pellets, is fed into an injection unit. Here, it is heated and melted, then forcibly injected under high pressure into the closed mold cavity. The pressure ensures the mold is completely filled.
Stage 3: Cooling
Once the molten plastic fills the cavity, it begins to cool. As it cools, it solidifies and takes the shape of the mold. The cooling phase is often the longest part of the cycle and is critical for the final properties of the part.
Stage 4: Ejection
After the part has cooled sufficiently, the mold opens. An ejection mechanism, typically using pins, pushes the solidified part out of the mold. The machine is now ready to begin the next cycle.
Materials and Process Variations
While the core process remains the same, the materials used can vary significantly, leading to specialized applications.
Thermoplastics and Thermosets
The vast majority of injection molding uses thermoplastics. These polymers can be repeatedly melted and solidified without significant degradation, making them highly efficient for the process. Thermosetting plastics can also be used, but they undergo a chemical change when heated and cannot be re-melted.
A Specialized Process: Metal Injection Molding (MIM)
For creating complex metal parts, a variation called Metal Injection Molding (MIM) exists. In this process, fine metal powder is mixed with a polymer binder to create a feedstock.
This mixture is injected into the mold just like plastic. After ejection, the part undergoes a secondary process to remove the polymer binder.
Finally, the part is heated in a furnace to a high temperature, causing the metal particles to fuse together. This step, called sintering, also causes the part to shrink significantly as porosity is eliminated. Molds are therefore designed oversized to account for this shrinkage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Injection molding is a powerful tool, but it is not the right choice for every project. Understanding its core advantages and disadvantages is crucial.
The Advantage: Unmatched Scalability and Precision
The primary benefit is low per-unit cost at high volumes. While the initial investment is large, the cost to produce each subsequent part is incredibly low. The process is also highly repeatable, ensuring that the millionth part is virtually identical to the first.
The Disadvantage: High Initial Tooling Costs
The mold is a complex and highly engineered piece of steel or aluminum. The cost to design and manufacture this tool can range from thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars. This makes injection molding completely uneconomical for prototypes or low-volume production runs.
The Constraint: Design for Manufacturability
Parts must be carefully designed to be successfully molded. Factors like uniform wall thickness, draft angles to aid ejection, and the placement of gates (where plastic enters the mold) are critical for producing a quality part without defects.
When to Choose Injection Molding
Your production goals will determine if injection molding is the appropriate technology for your project.
- If your primary focus is mass production of thousands or millions of parts: Injection molding is the definitive industry standard for its speed, low unit cost, and high repeatability.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or producing a small batch: The high upfront cost of the mold makes other methods, such as 3D printing or CNC machining, far more suitable and economical.
- If your primary focus is creating complex metal parts at scale: Metal Injection Molding (MIM) offers a powerful solution that can be more cost-effective than machining for intricate geometries.
Understanding this fundamental balance between high initial investment and exceptional per-part efficiency is the key to leveraging injection molding effectively.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Clamping | Mold halves are securely closed. | Prepares the mold cavity for injection. |
| 2. Injection | Molten material is forced into the mold. | Fills the mold cavity completely. |
| 3. Cooling | The material solidifies inside the mold. | Gives the part its final shape and properties. |
| 4. Ejection | The finished part is pushed out of the mold. | Completes the cycle, readying the mold for the next part. |
Ready to scale your production with precision? The injection molding process requires reliable equipment for consistent results. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories that develop and test new materials and products. Whether you need precise temperature control for material testing or durable tools for prototyping, we have the solutions to support your innovation. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can equip your lab for success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between injection molding and pressure molding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Process
- What is molding technique? A Guide to High-Volume, Complex Part Manufacturing
- What is the manufacturing process of rubber molding? Injection, Compression, or Transfer Molding?
- What is a positive of injection moulding? Achieve High-Volume Production with Unmatched Efficiency
- What are the parameters to be considered for selecting the thin wall molding machine? Key Specs for High-Speed Production



















