In short, a permanent copper/copper sulphate (Cu/CuSO4) reference electrode is a highly stable electrochemical sensor designed for long-term burial in soil. Its specific purpose is to provide a constant, known electrical potential, which serves as a reliable benchmark for measuring the effectiveness of cathodic protection systems on pipelines, storage tanks, and other buried metallic structures.
To measure the voltage of any single object is impossible; you can only measure the voltage difference between two points. The reference electrode acts as a fixed "zero point," allowing you to accurately measure the electrical potential of a structure relative to its environment and confirm it is protected from corrosion.
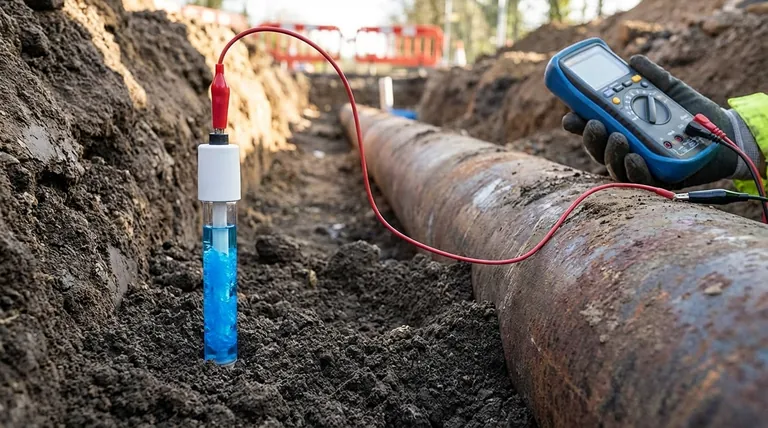

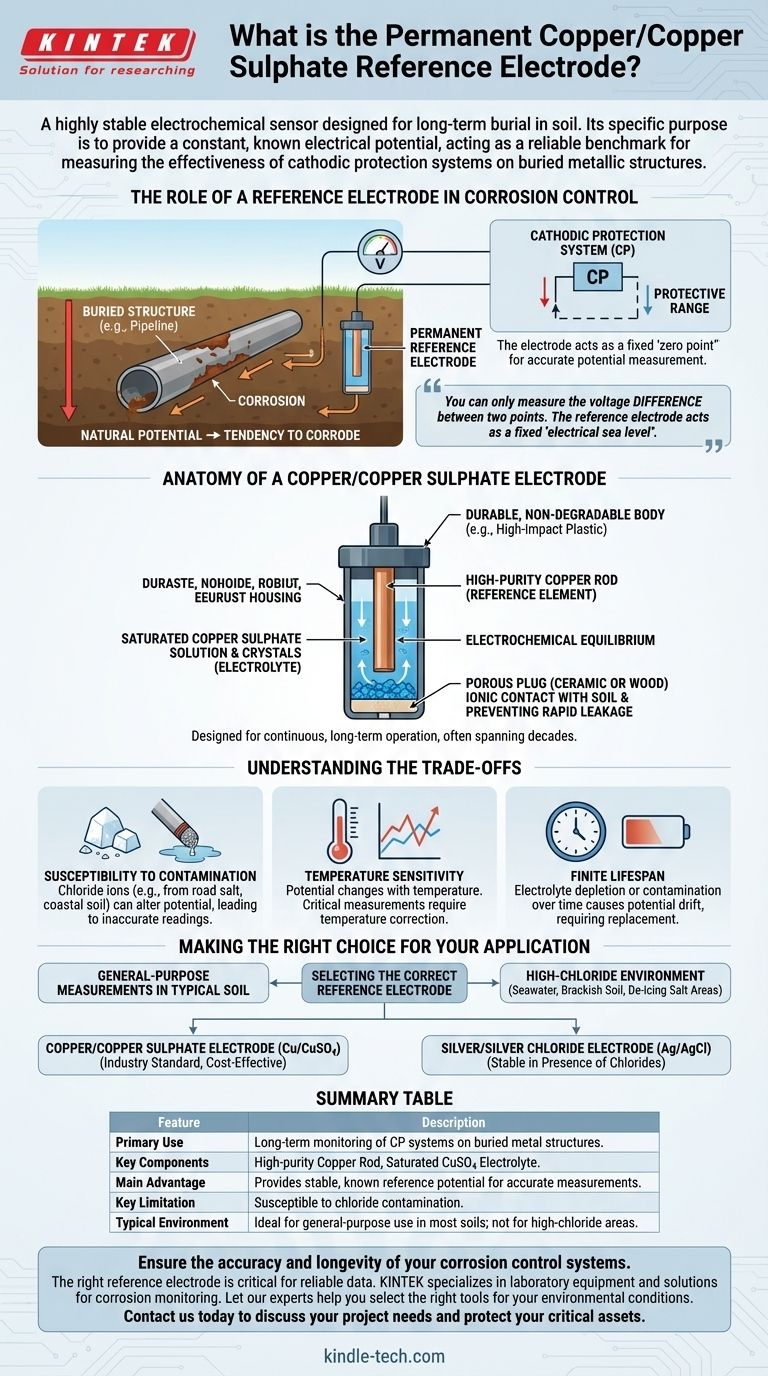
The Role of a Reference Electrode in Corrosion Control
The Problem: Measuring Corrosion Potential
Corrosion is an electrochemical process. A piece of metal buried in soil has a natural electrical potential, and this potential indicates its tendency to corrode.
To prevent this, we use cathodic protection (CP), a system that applies a small electrical current to the structure. This shifts its potential to a level where corrosion effectively stops.
The critical challenge is verifying that the structure's potential is in the correct protective range. This measurement is impossible without a stable reference point.
The Solution: A Stable Benchmark
Think of measuring the height of a mountain. You measure its elevation relative to a universally agreed-upon benchmark: sea level. A reference electrode serves the exact same function for electrical potential.
It provides a constant, predictable potential that does not change with time or environmental fluctuations. By placing the electrode in the soil near your structure, you create a stable "electrical sea level" against which you can measure the structure's potential with a voltmeter.
Anatomy of a Copper/Copper Sulphate Electrode
The Core Components
A Cu/CuSO4 reference electrode is a simple but precise half-cell. It consists of two primary components:
- A high-purity copper rod, which acts as the reference element.
- A saturated solution of copper sulphate crystals in water, which serves as the electrolyte.
The copper rod is immersed in the copper sulphate solution, creating a stable and reproducible electrochemical equilibrium. This equilibrium is what generates the electrode's constant potential.
The Porous Junction
The electrode is housed in a durable body that features a porous plug at one end. This plug, often made of ceramic or wood, allows for electrical contact between the internal copper sulphate solution and the external soil.
This connection allows ions to move, completing the electrical circuit for the measurement, but prevents the internal solution from leaking out rapidly.
Why Is It "Permanent"?
The term "permanent" distinguishes this type of electrode from portable models used for temporary field surveys. A permanent electrode is designed for burial and continuous, long-term operation.
This requires a robust, non-degradable housing and a large reservoir of copper sulphate solution and crystals to ensure a service life that can span decades.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No measurement tool is perfect. While the Cu/CuSO4 electrode is an industry workhorse, it's critical to understand its limitations.
Susceptibility to Contamination
The stability of the electrode's potential is dependent on the purity of its internal electrolyte. The most common issue is chloride contamination.
If the electrode is used in soil with high chloride content (such as coastal areas or road-salt-affected soil), chloride ions can migrate through the porous plug and alter the electrode's potential, leading to inaccurate readings.
Temperature Sensitivity
The potential of a Cu/CuSO4 electrode has a known sensitivity to temperature. While often minor, this variation can be significant in applications requiring high precision or where ambient temperatures fluctuate dramatically.
For critical measurements, a temperature correction factor must be applied to the readings to ensure accuracy.
Finite Lifespan
Though called "permanent," the electrode has a finite life. Over many years, the internal electrolyte will eventually become depleted or contaminated, causing the potential to drift. At this point, the electrode must be replaced to maintain the integrity of the CP monitoring system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct reference electrode is fundamental to obtaining reliable corrosion control data. Your decision should be guided by the specific chemical environment of your structure.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose measurements in typical soil: The copper/copper sulphate electrode is the established industry standard, offering excellent reliability and cost-effectiveness.
- If your project is in a high-chloride environment (e.g., seawater, brackish soil, or de-icing salt areas): You must consider a silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl) electrode, as it is specifically designed to remain stable in the presence of chlorides.
Ultimately, choosing the right reference electrode ensures that your measurements are accurate, giving you true confidence in the integrity of your protected assets.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Long-term monitoring of cathodic protection systems on buried metal structures. |
| Key Components | High-purity copper rod and a saturated copper sulphate electrolyte solution. |
| Main Advantage | Provides a stable, known reference potential for accurate voltage measurements. |
| Key Limitation | Susceptible to chloride contamination, which can alter its potential. |
| Typical Environment | Ideal for general-purpose use in most soils; not recommended for high-chloride areas. |
Ensure the accuracy and longevity of your corrosion control systems. The right reference electrode is critical for reliable data. KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables for material testing and analysis, including solutions for corrosion monitoring. Our experts can help you select the right tools for your specific environmental conditions. Contact us today to discuss your project needs and protect your critical assets.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Gold Disc Electrode
People Also Ask
- Why Use a Three-Electrode RDE System for PEM Catalyst Screening? Master Intrinsic Kinetic Activity Analysis
- When should an electrode holder be replaced? Critical Signs for Safety and Weld Quality
- What are the application areas for the Ruthenium-Iridium-Titanium Chlorine Evolution Electrode? Essential for Efficient Chlorine Production
- What general precaution should be taken regarding the electrolyte? Ensure Your Gold & Platinum Electrodes Stay Inert
- Does graphite have a melting point? Unlocking the Extreme Heat Resistance of Graphite
- How should the electrodes of an electrolytic cell be maintained? Ensure Accuracy and Longevity
- Why is the Gas Diffusion Electrode (GDE) essential for H2O2 yield? Unlock Efficient Oxygen Reduction Performance
- What are the application areas for the Lead Dioxide-Titanium Oxygen Evolution Electrode? A Guide to Advanced Oxidation



















