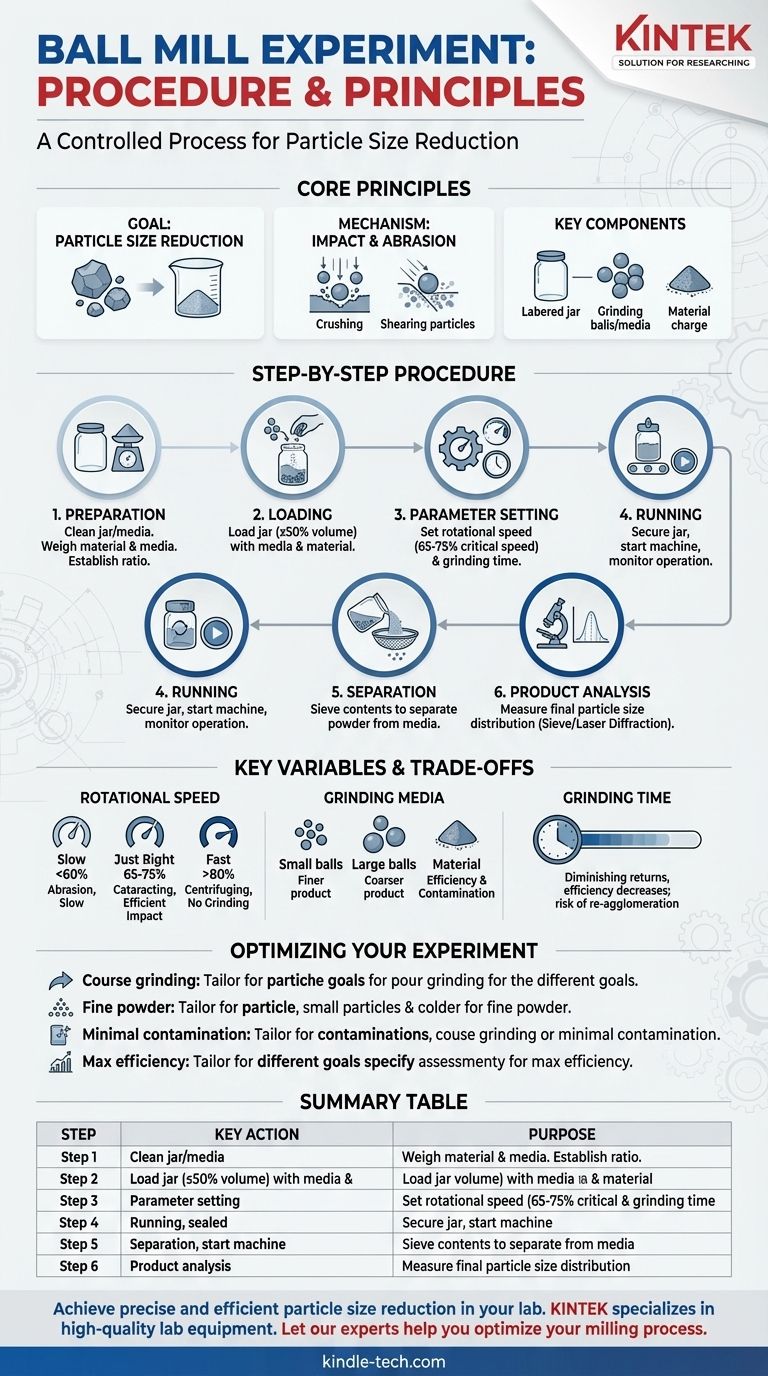
The standard procedure for a ball mill experiment involves preparing and weighing your material and grinding media, loading them into the mill jar, setting the rotational speed and duration, and running the mill. After the cycle, the ground material is carefully separated from the media and collected for analysis to determine the final particle size.
A ball mill experiment is more than a simple grinding task; it is a controlled process of particle size reduction. Success depends on deliberately managing key variables—rotational speed, grinding time, and the ratio of grinding media to material—to achieve a predictable and reproducible outcome.

The Core Principles of Ball Milling
Before detailing the procedure, it's essential to understand the goal and the mechanism. This context is what separates a routine task from a successful scientific experiment.
The Goal: Particle Size Reduction
The primary purpose of a ball mill is to reduce the size of solid materials. This is a critical step in many industries, from mineral processing and ceramics to pharmaceuticals and chemical manufacturing.
The Mechanism: Impact and Abrasion
Grinding occurs through two main forces. Impact happens when the grinding balls fall from the top of the rotating jar, crushing the material caught beneath them. Abrasion (or attrition) occurs as the balls slide and roll against each other, shearing and grinding the particles.
Key Components You Will Control
The experiment involves three physical components: the jar (the container), the media (the grinding balls), and the charge (the material you intend to grind).
The Standard Experimental Procedure: A Step-by-Step Guide
Following a systematic procedure ensures safety, consistency, and the collection of reliable data.
Step 1: Preparation of Materials
First, ensure the milling jar and grinding media (balls) are completely clean and dry to prevent contamination.
Carefully weigh the material you intend to grind. This is your material charge. Then, weigh the grinding media. The ratio between these two weights is a critical experimental parameter.
Step 2: Loading the Jar
Place both the grinding media and the material charge into the mill jar.
As a general rule, the total volume of the media and charge should not exceed 50% of the jar's internal volume. This empty space is crucial for allowing the media to fall and create the necessary grinding impacts.
Step 3: Setting Operational Parameters
Securely fasten the lid on the jar. The two most important parameters to set on the machine are rotational speed and grinding time.
Speed is typically set as a percentage of the mill's "critical speed," with the optimal range being 65-75% for maximum grinding efficiency. Time is set based on the material's hardness and the desired final particle size.
Step 4: Running the Mill
Place the sealed jar onto the mill's rollers or clamps and ensure it is secure. Engage any safety guards or housing.
Start the machine and allow it to run for the predetermined duration. Monitor the machine for any unusual noises or movements, especially at the beginning of the run.
Step 5: Unloading and Separation
Once the cycle is complete, turn off the machine and wait for it to come to a complete stop.
Carefully remove the jar and open the lid. Pour the contents through a coarse sieve to easily separate the ground powder (the product) from the larger grinding media.
Step 6: Product Analysis
The final step is to analyze your product. This is most commonly done using sieve analysis for larger particles or laser diffraction for very fine powders to measure the final particle size distribution.
Understanding the Key Variables and Trade-offs
The quality of your result depends entirely on how you manage the trade-offs between the core experimental variables.
Rotational Speed: The Critical Speed Concept
Critical speed is the theoretical speed at which the grinding media would be held against the jar wall by centrifugal force, ceasing all grinding action.
- Too Slow (<60%): The media will cascade down the side of the jar. This favors abrasion over impact and results in slow, inefficient grinding.
- Too Fast (>80%): The media will centrifuge, sticking to the jar wall. This eliminates impacts entirely, and little to no grinding occurs.
- Just Right (65-75%): The media travels up the wall and then falls in a "cataracting" motion, maximizing impact forces and grinding efficiency.
Grinding Media: Size and Material
The choice of grinding media is critical. The size of the balls dictates the final particle size; smaller balls produce a finer product.
The material of the balls (e.g., hardened steel, alumina, zirconia) affects both grinding efficiency and potential contamination. Using harder media is more efficient but increases the risk of introducing trace amounts of the media material into your sample.
Grinding Time: A Point of Diminishing Returns
Longer grinding times will produce a finer product, but only up to a point. Efficiency dramatically decreases as particles get smaller.
Furthermore, excessive grinding can sometimes lead to re-agglomeration of very fine particles or unwanted changes in the material's properties due to heat buildup.
Optimizing Your Experiment for Your Goal
Use these principles to tailor the procedure to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is coarse grinding or initial breakdown: Use larger grinding media and a relatively shorter grinding time to maximize impact forces.
- If your primary focus is achieving a very fine powder: Use smaller grinding media, a higher media-to-material ratio, and be prepared for longer grinding times.
- If your primary focus is minimizing contamination: Use grinding media made of an inert ceramic like zirconia, or if possible, media made of the same material as your sample.
- If your primary focus is maximizing efficiency: Ensure you operate the mill between 65% and 75% of its calculated critical speed to achieve the ideal cataracting motion.
By systematically controlling these variables, you transform the ball milling process from a simple task into a precise and powerful scientific tool.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Clean jar/media; weigh material & media | Ensure purity and set critical charge ratio |
| 2. Loading | Load media & material into jar (≤50% volume) | Allow space for effective impact grinding |
| 3. Parameter Setting | Set rotational speed (65-75% critical speed) and time | Optimize for impact force and desired fineness |
| 4. Running | Secure jar, start machine, monitor operation | Execute the grinding cycle safely |
| 5. Separation | Sieve contents to separate powder from media | Isolate the final product for analysis |
| 6. Analysis | Perform sieve analysis or laser diffraction | Measure final particle size distribution |
Achieve precise and efficient particle size reduction in your lab. The right ball mill is crucial for reproducible results in fields like pharmaceuticals, ceramics, and chemical manufacturing. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including ball mills and grinding media, to meet your specific research and production needs. Let our experts help you optimize your milling process. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and find the perfect solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the effects of ball milling? A Deep Dive into Mechanical Alloying and Material Transformation
- What is the role of a high-energy planetary ball mill in Al-4Cu preparation? Achieve 30nm Grain Refinement
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in evaluating the processing performance of Miscanthus hydrochar?
- What is the principle of planetary ball mill? Achieve Rapid, High-Energy Grinding for Your Materials
- What is the core role of a high-energy planetary ball mill in MCP? Unlock Nanoscale Carbide Synthesis Efficiency



















