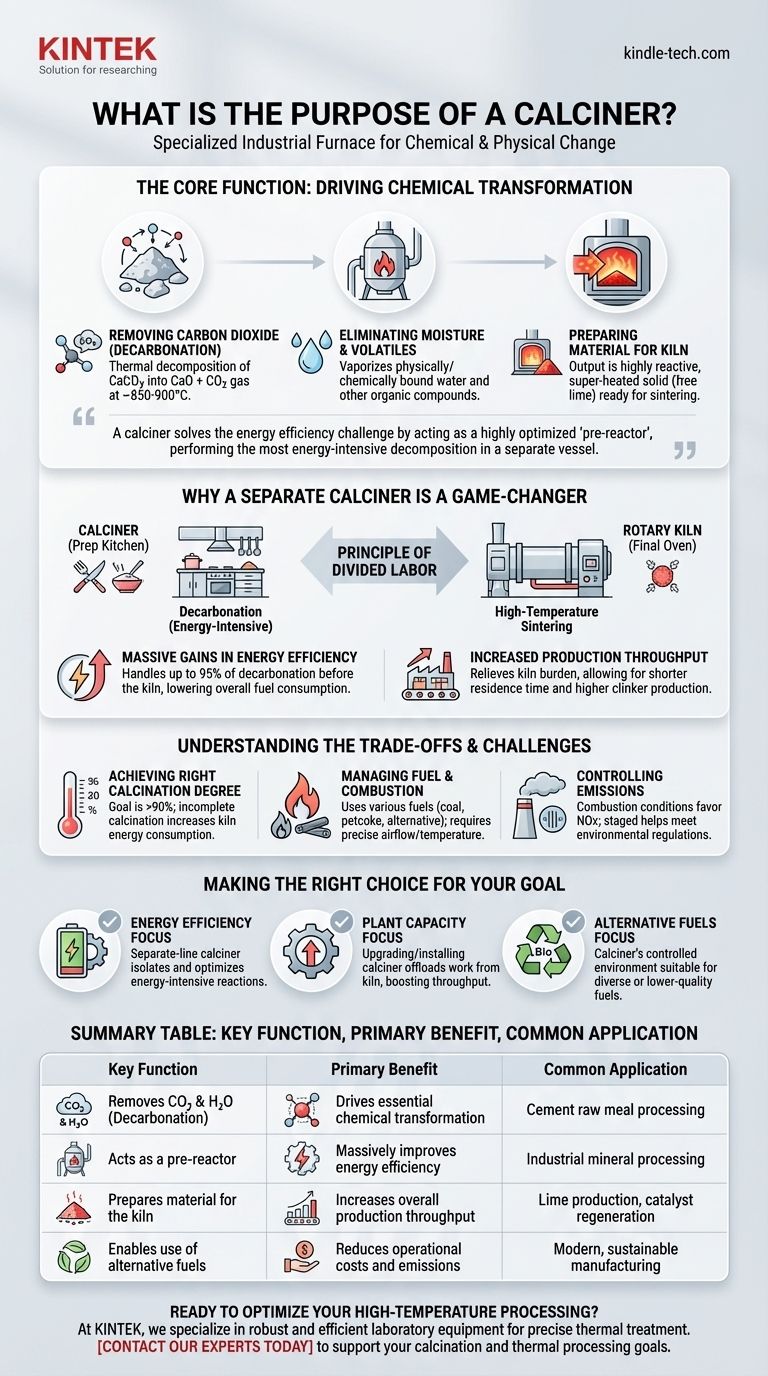
At its core, a calciner is a specialized industrial furnace designed to heat a material to a high temperature to cause a chemical and physical change. Its primary purpose is to remove volatile components—most commonly carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O)—from a raw substance. In the context of cement manufacturing, it executes the critical first step in making clinker by pre-processing the raw meal before it enters the main rotary kiln.
The central challenge in high-temperature processing is energy efficiency. A calciner solves this by acting as a highly optimized "pre-reactor," performing the most energy-intensive decomposition reaction (calcination) in a separate vessel, thereby dramatically reducing the fuel consumption and workload of the main kiln.

The Core Function: Driving Chemical Transformation
A calciner’s job is not simply to heat a material, but to fundamentally alter its chemistry. This preparation is essential for the next stages of processing.
Removing Carbon Dioxide (Decarbonation)
The most important reaction in a cement calciner is the thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃), the main component of limestone.
When heated to approximately 850-900°C (1560-1650°F), it breaks down into calcium oxide (CaO), or free lime, and carbon dioxide gas. This process, decarbonation, is the essence of calcination.
Eliminating Moisture and Other Volatiles
Before decarbonation can occur efficiently, any physically or chemically bound water in the raw meal must be driven off.
The calciner's hot gas stream vaporizes this moisture, ensuring the energy is then used for the intended chemical reaction. It also removes other volatile organic compounds that may be present.
Preparing Material for the Kiln
The output of the calciner is not the final product. It is a highly reactive, super-heated solid (now mostly calcium oxide) that is chemically ready for the final transformation.
This "calcined" material is fed directly into the rotary kiln, where it will be heated to even higher temperatures (around 1450°C) to sinter and form the final clinker nodules.
Why a Separate Calciner is a Game-Changer
In modern cement plants, the calciner is not part of the kiln; it is a distinct unit that precedes it. This separation is the key to modern process efficiency.
The Principle of Divided Labor
Think of the calciner as a prep kitchen and the rotary kiln as the final oven. The calciner does the energy-intensive "chopping and pre-cooking" (decarbonation) so the kiln can focus exclusively on its critical, high-temperature task (sintering).
This division of labor allows each piece of equipment to be designed for maximum efficiency at its specific task.
Massive Gains in Energy Efficiency
Calcination is an endothermic reaction, meaning it requires a significant input of energy. Modern calciners are designed to perform this task with extreme efficiency.
By handling up to 95% of the material's decarbonation before the kiln, the system drastically lowers overall fuel consumption. The calciner itself can be designed to use various fuels, often becoming the primary combustion chamber for the entire plant.
Increased Production Throughput
Because the kiln is relieved of the calcination burden, its residence time can be shorter and its focus can be entirely on sintering.
This effectively debottlenecks the process, allowing the entire plant to produce significantly more clinker than an older system without a separate calciner.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While highly effective, a calciner is a complex system that requires careful management to balance competing priorities.
Achieving the Right Degree of Calcination
The goal is to achieve a high degree of calcination (typically >90%) in the calciner. If calcination is incomplete, the remaining reaction must take place in the kiln, which consumes more energy and can destabilize its operation.
Managing Fuel and Combustion
Calciners are often designed to burn a wide range of fuels, including lower-grade coal, petcoke, and alternative fuels like tires or biomass.
However, each fuel has different combustion characteristics and ash content, which requires precise control over airflow and temperature to ensure complete combustion and prevent operational issues.
Controlling Emissions
The combustion temperatures and conditions within a calciner are favorable for the formation of nitrogen oxides (NOx), a key pollutant.
Modern calciners use sophisticated designs, such as staged combustion, to create reduction zones that break down NOx before it can exit the system, helping plants meet strict environmental regulations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The strategic value of a calciner is best understood by its impact on specific operational goals.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: A modern, separate-line calciner is non-negotiable, as it isolates and optimizes the most energy-intensive reaction in the process.
- If your primary focus is increasing plant capacity: Upgrading or installing a calciner is one of the most effective ways to offload work from the kiln, boosting the throughput of the entire system.
- If your primary focus is using alternative fuels: The calciner's controlled environment is often better suited for burning diverse or lower-quality fuels compared to the main kiln burner, providing significant cost and sustainability advantages.
Ultimately, the calciner transforms the industrial process from a single, inefficient stage into a highly optimized, multi-stage system built for performance.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Primary Benefit | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Removes CO₂ & H₂O (Decarbonation) | Drives essential chemical transformation | Cement raw meal processing |
| Acts as a pre-reactor | Massively improves energy efficiency | Industrial mineral processing |
| Prepares material for the kiln | Increases overall production throughput | Lime production, catalyst regeneration |
| Enables use of alternative fuels | Reduces operational costs and emissions | Modern, sustainable manufacturing |
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust and efficient laboratory equipment and consumables for industries that rely on precise thermal treatment. Whether you are developing new materials or scaling up a production process, our expertise can help you achieve greater energy efficiency and throughput.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can support your calcination and thermal processing goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product



















