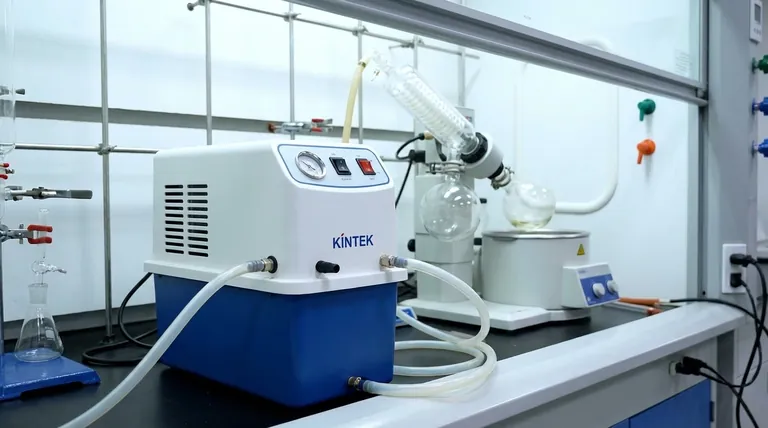
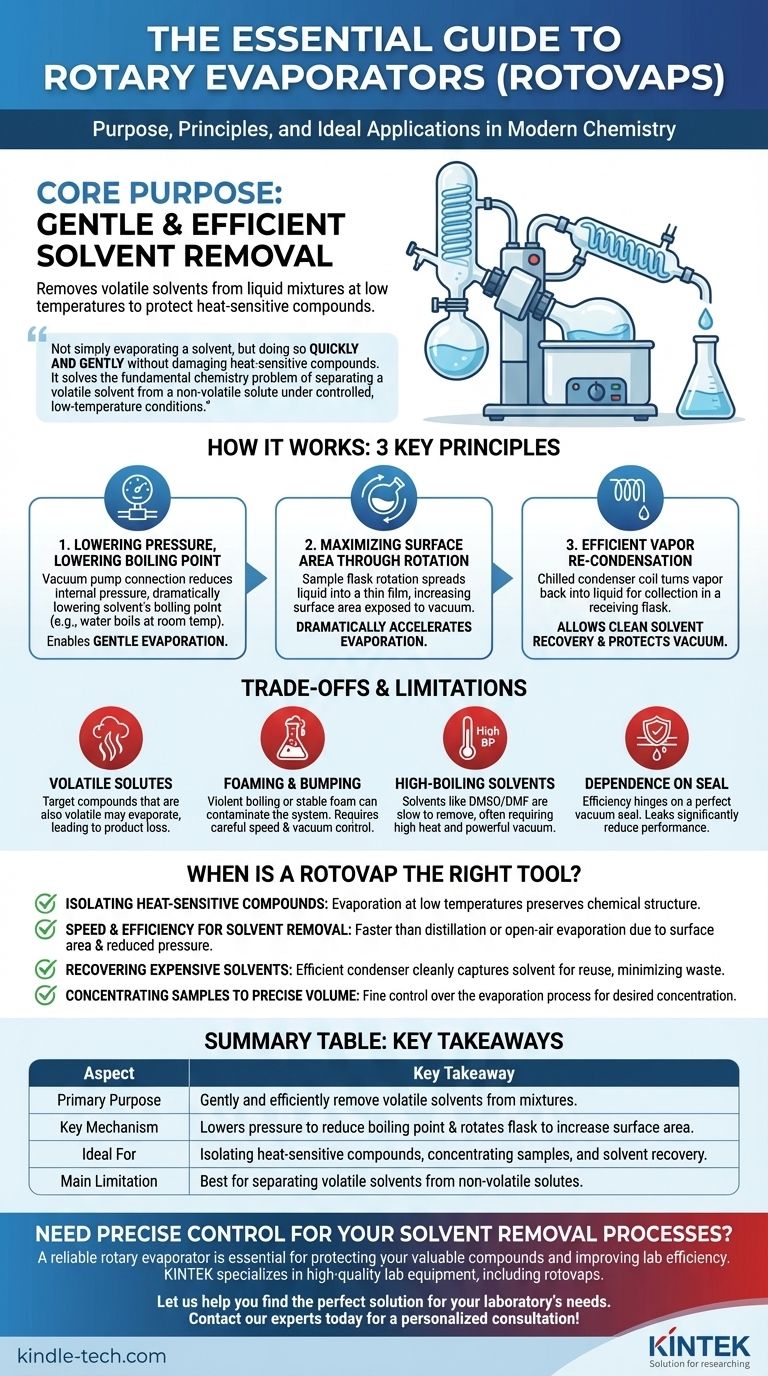
In essence, a rotary evaporator, or "rotovap," is a laboratory instrument designed to gently and efficiently remove a volatile solvent from a liquid mixture. It works by reducing the pressure inside the apparatus, which lowers the solvent's boiling point, while simultaneously rotating the sample to increase the surface area for evaporation. This allows for rapid solvent removal at low temperatures, protecting the desired compounds in the mixture.
The core purpose of a rotovap is not simply to evaporate a solvent, but to do so quickly and gently without damaging heat-sensitive compounds. It solves the fundamental chemistry problem of separating a volatile solvent from a non-volatile solute under controlled, low-temperature conditions.

How a Rotovap Solves the Evaporation Challenge
To understand the rotovap's utility, you must first understand the problem it solves. Standard distillation often requires high temperatures that can degrade or destroy the very compounds a chemist is trying to isolate. The rotovap elegantly bypasses this issue.
The First Principle: Lowering Pressure to Lower Boiling Point
The boiling point of a liquid is not a fixed number; it is entirely dependent on the pressure of the surrounding environment.
A rotovap connects to a vacuum pump, which removes air from the system and dramatically lowers the internal pressure. This pressure reduction directly lowers the solvent's boiling point.
For example, water boils at 100°C (212°F) at standard atmospheric pressure, but under a strong vacuum, it can be made to boil at room temperature or even lower. This principle is the key to gentle evaporation.
The Second Principle: Maximizing Surface Area Through Rotation
Evaporation only happens at the surface of a liquid. A static pool of liquid has a very small surface area relative to its volume, making evaporation a slow process.
The rotovap's signature feature is the rotation of the sample flask. As the flask spins, it continuously spreads the liquid into a thin film across the large interior surface of the glass. This massively increases the effective surface area exposed to the vacuum, which dramatically accelerates the rate of evaporation.
The Third Principle: Efficient Vapor Re-Condensation
Once the solvent turns into a vapor, it needs to be removed from the system. The vapor is drawn over a condenser coil, which is chilled with a circulating fluid (typically cold water or a dedicated chiller).
When the warm vapor hits the cold surface of the coil, it immediately condenses back into a liquid. This recaptured liquid drips down and collects in a separate receiving flask. This not only allows for the clean recovery and potential reuse of the solvent but also protects the vacuum pump from corrosive solvent vapors.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the rotovap is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Best for Non-Volatile Solutes
The rotovap's core function relies on the difference in volatility between the solvent (high volatility) and the solute (low volatility). If your target compound is also volatile, it may evaporate along with the solvent, leading to product loss.
Potential for Foaming and Bumping
Under vacuum, some mixtures can boil violently ("bumping") or create a stable foam. This can cause the sample to splash out of the rotating flask and into the condenser, contaminating the system and leading to loss of your valuable product. Careful control of rotation speed and vacuum application is required to manage this.
Inefficiency with High-Boiling Point Solvents
While a vacuum greatly helps, removing solvents with very high boiling points, like DMSO or DMF, can still be a slow process. It may require a combination of higher heat and a very powerful (and expensive) vacuum pump to be effective.
Dependence on a Perfect Seal
The entire system's efficiency hinges on maintaining a good vacuum. Even a small leak in one of the glass joints or seals will allow air to enter, raising the internal pressure and making evaporation much less effective.
When Is a Rotovap the Right Tool?
Choosing the right tool depends entirely on your objective. A rotovap is the superior choice in several common scenarios.
- If your primary focus is isolating a heat-sensitive compound: The rotovap is the ideal tool because it allows for evaporation at low temperatures, preserving your product's chemical structure.
- If your primary focus is speed and efficiency for solvent removal: The combination of increased surface area from rotation and reduced pressure makes the rotovap significantly faster than simple distillation or open-air evaporation.
- If your primary focus is recovering and reusing expensive solvents: The rotovap's highly efficient condenser cleanly captures the evaporated solvent in a separate flask, minimizing waste and cost.
- If your primary focus is concentrating a sample to a precise volume: The rotovap gives you fine control over the evaporation process, allowing you to stop when the desired concentration is reached.
Ultimately, the rotovap provides an unparalleled level of gentle control for separating liquids, making it an indispensable instrument in the modern chemistry laboratory.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Gently and efficiently remove volatile solvents from mixtures. |
| Key Mechanism | Lowers pressure to reduce boiling point and rotates flask to increase surface area. |
| Ideal For | Isolating heat-sensitive compounds, concentrating samples, and solvent recovery. |
| Main Limitation | Best for separating volatile solvents from non-volatile solutes. |
Need precise control for your solvent removal processes?
A reliable rotary evaporator is essential for protecting your valuable compounds and improving lab efficiency. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including rotovaps, designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern chemistry.
Let us help you find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- 30T 40T Split Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- What can I use a vacuum pump for? Powering Industrial Processes from Packaging to Automation
- What is the purpose of the compression chamber in a vacuum pump? The Heart of Vacuum Generation
- How does the impeller rotation affect the gas flow in a water circulating vacuum pump? A Guide to the Liquid Ring Principle
- Why is a water circulating vacuum pump suitable for handling flammable or explosive gases? Inherent Safety Through Isothermal Compression
- What is the importance of a vacuum pump for Schottky hybrid interfaces? Achieve Atomic-Level Purity and Bonding



















