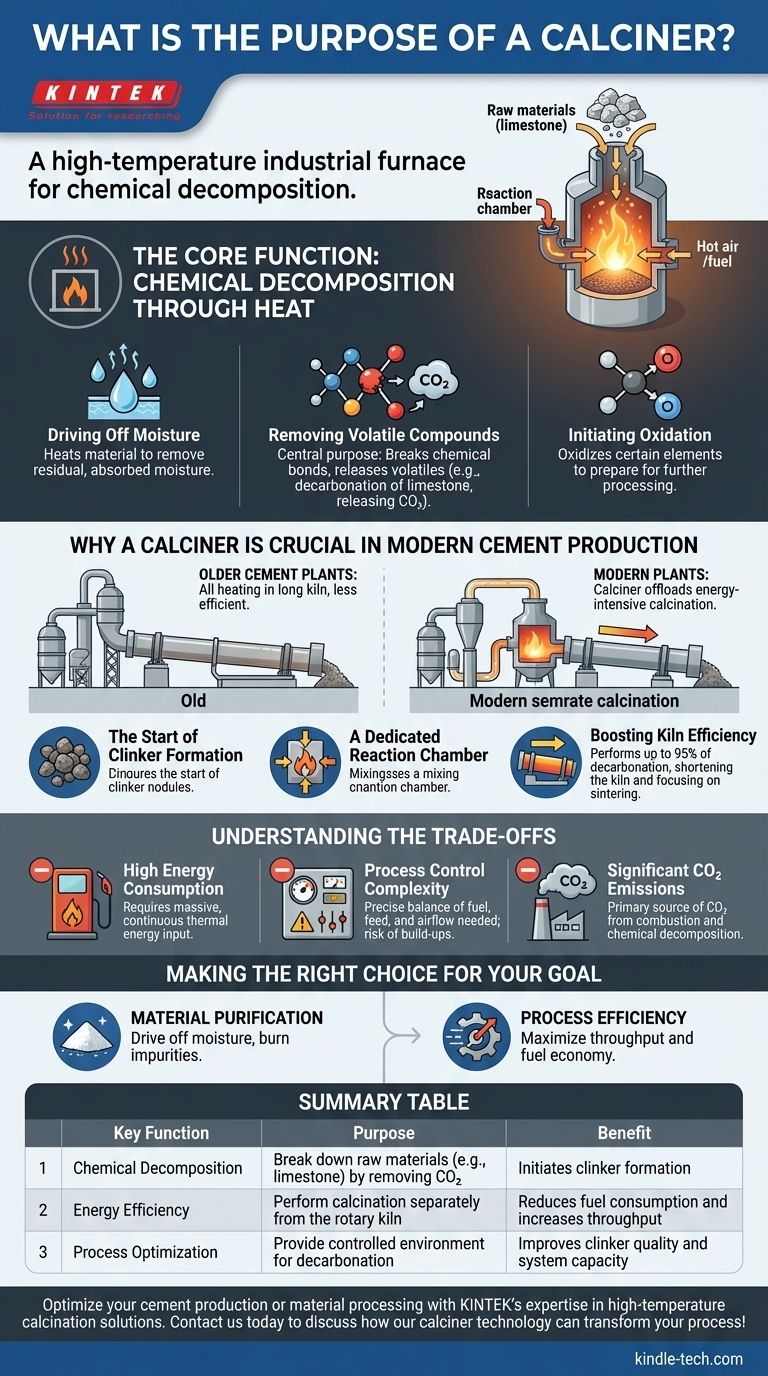
In essence, a calciner is a high-temperature industrial furnace designed to heat a solid material to the point of chemical decomposition. In the context of cement manufacturing, its primary purpose is to mix preheated raw meal with fuel and hot air, initiating the critical calcination reaction that is the first major step in creating clinker.
The core function of a calciner is to perform the energy-intensive task of breaking down raw materials, primarily by removing carbon dioxide, before they enter the main rotary kiln. This separation of tasks dramatically improves the overall fuel efficiency and production capacity of the entire system.

The Core Function: Chemical Decomposition Through Heat
A calciner is not just a simple oven; it's a precisely controlled reactor that subjects materials to extreme heat to achieve specific chemical changes. These changes fall into three main categories.
Driving Off Moisture
The first and simplest objective is to heat the material enough to drive off any residual, physically absorbed moisture that remains after initial preheating stages.
Removing Volatile Compounds
This is the central purpose of calcination. The high heat breaks chemical bonds and releases volatile components as gases. In cement production, this specifically refers to the decarbonation of limestone (calcium carbonate), which releases its carbon dioxide (CO2) to become calcium oxide.
Initiating Oxidation
Depending on the material and the amount of oxygen in the air stream, the calciner can also begin to oxidize certain elements within the substance, further preparing it chemically for the next stage of processing.
Why a Calciner is Crucial in Modern Cement Production
In older cement plants, all heating and chemical reactions happened inside a long rotary kiln. The addition of a separate calciner system revolutionized the efficiency of this process.
The Start of Clinker Formation
The calcination reaction is the true beginning of the transformation from raw meal into clinker, the essential ingredient in cement. The calciner is dedicated entirely to accomplishing this single step effectively.
A Dedicated Reaction Chamber
By design, a calciner provides the ideal environment for its specific reaction. It vigorously mixes the finely ground raw meal with fuel and a stream of hot air, ensuring a rapid and thorough chemical conversion that would be less efficient inside a massive, slow-turning kiln.
Boosting Kiln Efficiency
By performing up to 95% of the decarbonation before the material enters the kiln, the calciner offloads the most energy-intensive part of the process. This allows the rotary kiln to be shorter and focus exclusively on the final, higher-temperature sintering phase where the clinker minerals actually form.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While indispensable for modern, large-scale production, calciner technology comes with significant operational challenges and consequences.
High Energy Consumption
Calciners are a major point of fuel consumption in a cement plant. The process of breaking down calcium carbonate is fundamentally energy-intensive, requiring a massive and continuous input of thermal energy.
Process Control Complexity
The balance of fuel, raw material feed, and airflow must be precisely controlled. An imbalance can lead to incomplete calcination, which harms clinker quality, or system blockages known as "build-ups," which can force a costly plant shutdown.
Significant CO2 Emissions
The calcination process is a primary source of CO2 emissions in the cement industry. CO2 is released from both the combustion of fuel to create heat and, more significantly, from the chemical decomposition of the limestone itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The objective of using a calciner is directly tied to the desired outcome for the material being processed.
- If your primary focus is material purification: The calciner's goal is to drive off moisture and burn away volatile impurities to create a more stable or concentrated final product.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: The calciner's goal is to complete a specific, energy-intensive chemical reaction separately, thereby maximizing the throughput and fuel economy of the entire production line.
Ultimately, the calciner is a specialized furnace engineered to efficiently prepare and chemically alter materials for their final, high-temperature transformation.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Decomposition | Break down raw materials (e.g., limestone) by removing CO₂ | Initiates clinker formation |
| Energy Efficiency | Perform calcination separately from the rotary kiln | Reduces fuel consumption and increases throughput |
| Process Optimization | Provide controlled environment for decarbonation | Improves clinker quality and system capacity |
Optimize your cement production or material processing with KINTEK's expertise in high-temperature calcination solutions. Whether you're focused on enhancing clinker quality, boosting fuel efficiency, or scaling your operations, our specialized lab equipment and consumables are designed to meet rigorous industrial demands. Contact us today to discuss how our calciner technology can transform your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing



















