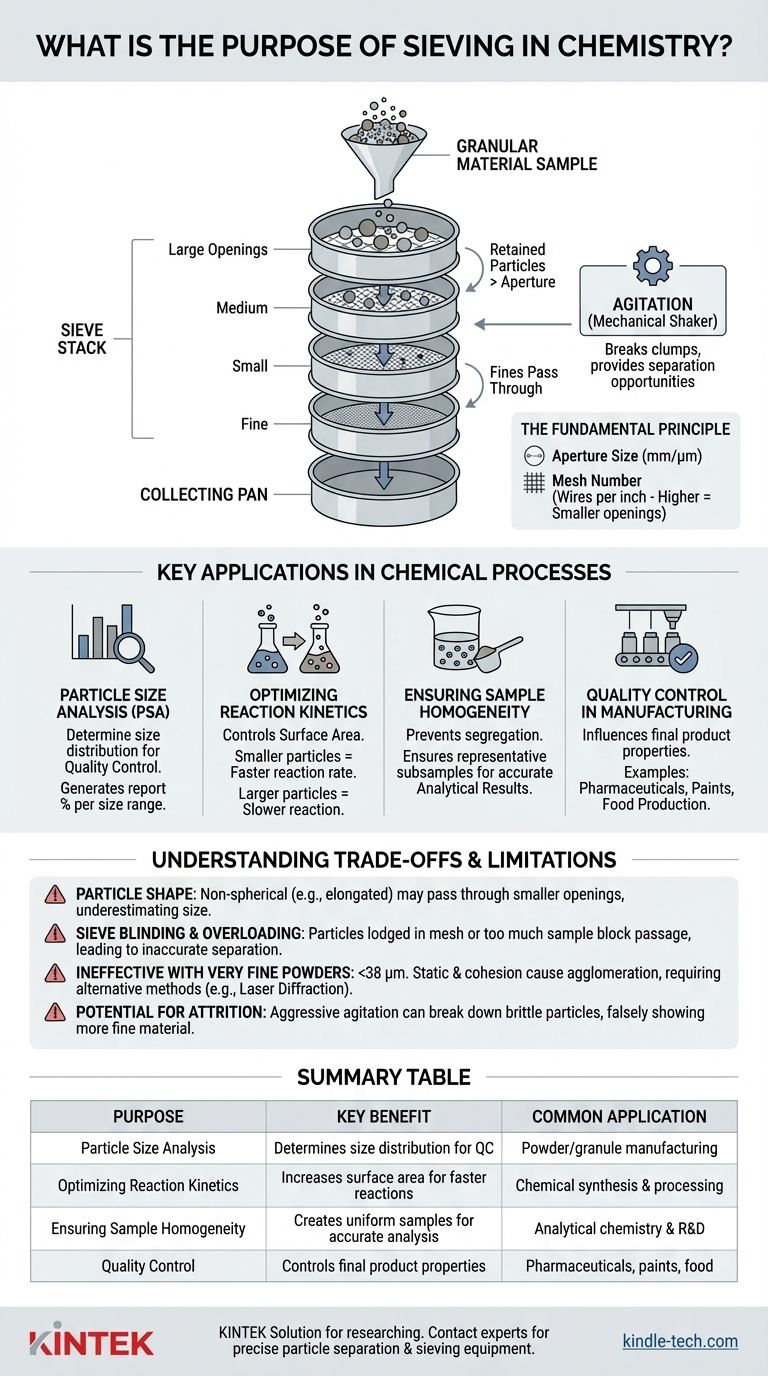
In short, the purpose of sieving in chemistry is to separate a granular material into fractions based on particle size. This is achieved by passing the material through a screen, or mesh, with specific-sized openings. Particles smaller than the openings pass through, while larger particles are retained.
Sieving is more than just a simple separation technique; it is a fundamental method for controlling and analyzing one of the most critical physical properties of a solid material: its particle size distribution. This distribution directly impacts a substance's chemical reactivity, solubility, flowability, and final product quality.

The Fundamental Principle: How Sieving Works
Sieving, also known as a sieve analysis, is a mechanical process. Its effectiveness relies on a simple physical principle combined with controlled execution.
The Mechanics of a Sieve Stack
A laboratory sieve is a precision instrument, typically a circular metal frame with a wire mesh screen stretched across the bottom.
These sieves are designed to be stacked, with the sieve having the largest openings at the top and each subsequent sieve below having progressively smaller openings. A solid pan is placed at the very bottom to collect the finest particles.
The Role of Agitation
A sample is placed in the top sieve, and the entire stack is agitated. This is usually done with a mechanical shaker that vibrates or taps the stack.
This agitation serves two purposes: it breaks up clumps of material and gives each particle multiple opportunities to find an opening and pass through to the next level.
Understanding Sieve Terminology
The size of the openings in the mesh is called the aperture size, typically measured in millimeters (mm) or micrometers (μm).
You will also encounter a mesh number, which refers to the number of wires per inch. A higher mesh number indicates more wires and therefore smaller openings. For example, a 40-mesh sieve has much larger openings than a 200-mesh sieve.
Key Applications in Chemical Processes
Controlling particle size is critical across research, development, and industrial manufacturing. Sieving is the primary tool for this control.
Particle Size Analysis (PSA)
The most common application is to determine the particle size distribution of a sample.
By weighing the material retained on each sieve, you can generate a report and graph showing what percentage of the sample falls within each size range. This is a cornerstone of quality control for powders and granules.
Optimizing Reaction Kinetics
A chemical reaction involving a solid only occurs on its surface. Smaller particles have a much higher surface-area-to-volume ratio than larger particles.
By using sieving to isolate a fraction of fine particles, chemists can dramatically increase reaction rates. Conversely, they can use larger particles to slow a reaction down.
Ensuring Sample Homogeneity
In analytical chemistry, it is crucial that the small portion of material being analyzed is representative of the entire batch.
Sieving a sample to a uniform particle size range prevents segregation of larger and smaller particles, ensuring that any subsample taken is homogeneous and yields repeatable analytical results.
Quality Control in Manufacturing
Particle size directly influences the properties of a final product.
- Pharmaceuticals: The particle size of an active ingredient affects its dissolution rate in the body, impacting bioavailability.
- Paints & Coatings: Pigment particle size determines color opacity, gloss, and finish.
- Food Production: The particle size of flour, sugar, or spices affects texture, mouthfeel, and how they mix.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, sieving is not a perfect method. An expert understands its limitations and when to choose an alternative technique.
The Problem of Particle Shape
Sieve analysis inherently assumes that all particles are perfect spheres. In reality, particles can be elongated (acicular) or flat (flaky).
These non-spherical particles may pass through a mesh opening end-on or diagonally, leading to an underestimation of their true size.
Sieve Blinding and Overloading
Sieve blinding occurs when particles become lodged in the mesh openings, preventing other particles from passing through. This is common with particles that are very close to the aperture size.
Overloading a sieve with too much sample creates a thick bed of material. Particles deep in the bed may not get a chance to reach the mesh, leading to inaccurate and inefficient separation.
Ineffectiveness with Very Fine Powders
For very fine particles (typically below about 38 micrometers, or a 400-mesh sieve), sieving becomes impractical.
Forces like static electricity and cohesion cause the fine particles to clump together (agglomerate), preventing them from passing through the mesh. For these materials, techniques like laser diffraction or dynamic light scattering are used instead.
The Potential for Attrition
The mechanical agitation of a sieve shaker can be aggressive. For soft, brittle, or friable materials, the sieving process itself can break down the particles.
This attrition changes the particle size distribution during the measurement, leading to inaccurate results that show more fine material than was originally present.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply sieving effectively, you must first clarify your objective.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: Use a standardized set of sieves and a documented procedure for agitation time and sample weight to ensure your results are repeatable and comparable over time.
- If your primary focus is optimizing a chemical reaction: Use sieving as a preparative tool to isolate the particle size fraction that gives you the ideal balance between surface area and material handling.
- If your primary focus is preparing a sample for analysis: Sieve your material to a uniform and narrow size range to guarantee that any small amount you test is truly representative of the bulk material.
- If your primary focus is characterizing nanoparticles or cohesive powders: Recognize the physical limits of mechanical sieving and select a more appropriate method, such as laser diffraction, to avoid inaccurate data.
Mastering sieving is about understanding that it gives you direct control over a fundamental physical property that dictates how materials behave.
Summary Table:
| Sieving Purpose | Key Benefit | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size Analysis | Determines size distribution for quality control | Powder and granule manufacturing |
| Optimizing Reaction Kinetics | Increases surface area to speed up reactions | Chemical synthesis and processing |
| Ensuring Sample Homogeneity | Creates uniform samples for accurate analysis | Analytical chemistry and R&D |
| Quality Control | Controls final product properties like dissolution and texture | Pharmaceuticals, paints, and food production |
Ready to achieve precise particle separation and improve your lab's results?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory sieves and precision sieving equipment designed for accurate particle size analysis and material separation. Whether you are working in pharmaceuticals, materials science, or chemical manufacturing, our equipment helps you control particle size distribution—a critical factor for reaction kinetics, product quality, and analytical accuracy.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving solution for your specific laboratory needs and ensure your materials meet the highest standards.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- Why is a standardized sieving system necessary for elephant grass research? Ensure Reliable Sample Consistency
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment



















