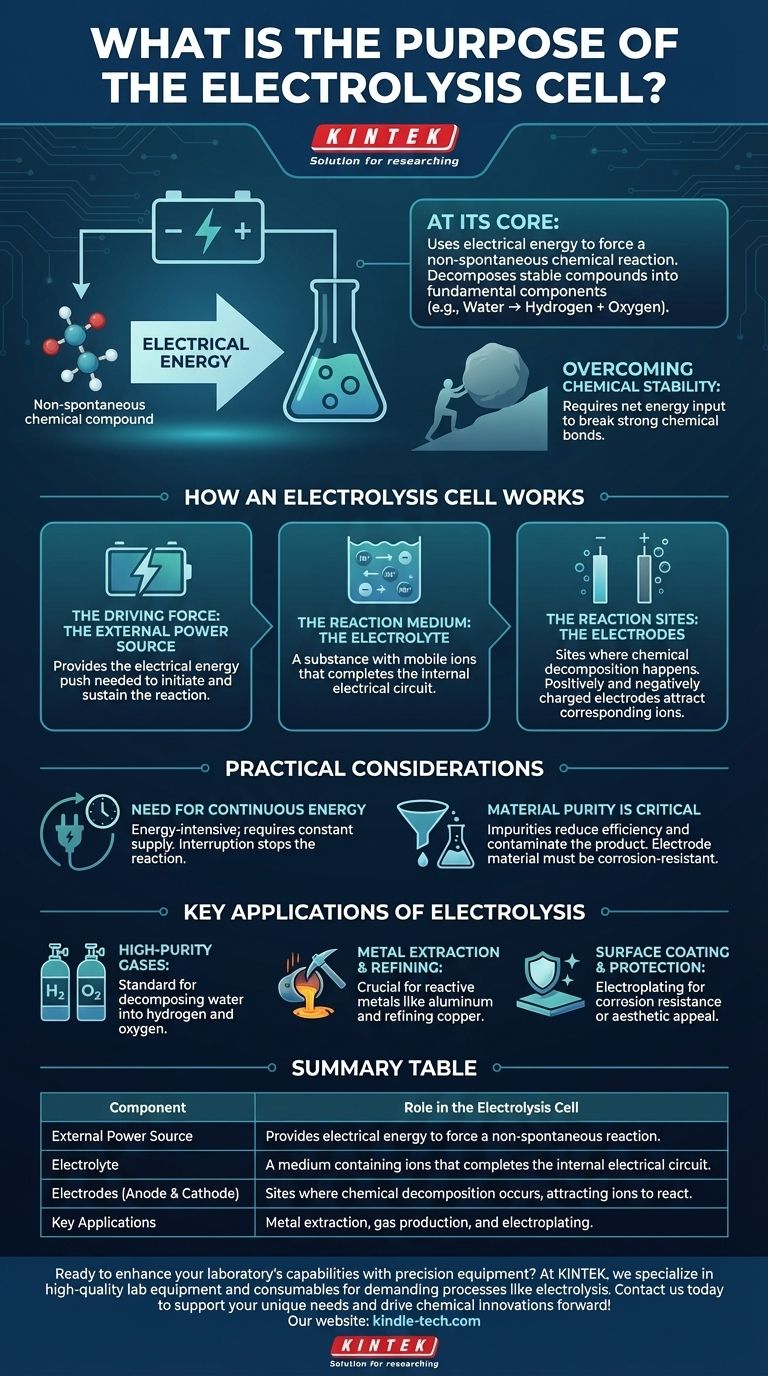
At its core, the purpose of an electrolysis cell is to use electrical energy to force a chemical reaction that would not happen on its own. This process, known as electrolysis, allows us to decompose stable chemical compounds into their more fundamental components, such as breaking down water into hydrogen and oxygen.
While many chemical reactions release energy, some of the most important industrial processes require an energy input to proceed. The electrolysis cell is the fundamental tool designed to provide this energy, using electricity to drive non-spontaneous reactions and create valuable chemical products.
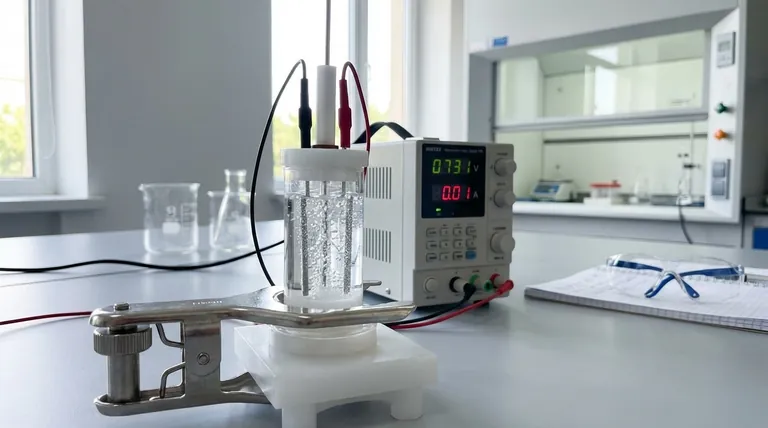

How an Electrolysis Cell Works
An electrolysis cell is a system with three critical components working together to achieve a specific chemical change. Understanding each part clarifies the entire process.
The Driving Force: The External Power Source
An external power source, such as a battery, provides the electrical energy required. This energy acts as the "push" needed to initiate and sustain a chemical reaction that is not energetically favorable. Without this external voltage, the decomposition would not occur.
The Reaction Medium: The Electrolyte
The electrolyte is the medium that enables the flow of charged particles (ions). It is not simply a liquid; it is a substance, typically a solution of dissolved salts in water or a molten salt, that contains mobile ions. This movement of ions between the electrodes is what completes the electrical circuit inside the cell.
The Reaction Sites: The Electrodes
Two electrodes (an anode and a cathode) are immersed in the electrolyte. These are the physical sites where the chemical decomposition actually happens. When the external power source is applied, one electrode becomes positively charged and the other negatively charged, attracting the corresponding ions from the electrolyte and forcing them to react.
The Fundamental Goal: Forcing a Non-Spontaneous Reaction
The entire purpose of the cell is to overcome the natural stability of a compound. This is the key difference between an electrolytic cell and a galvanic cell (like a standard battery), which releases energy from a spontaneous reaction.
Overcoming Chemical Stability
A non-spontaneous reaction is one that requires a net input of energy to proceed. Think of it like pushing a boulder uphill—it will not happen on its own. The electrical energy supplied to the electrolysis cell provides the necessary force to push this "chemical boulder" uphill, breaking strong chemical bonds.
The Meaning of Electrolysis
The name itself explains the function. It comes from "electro," referring to electricity, and the Greek word "lysis," meaning to break up or decompose. The cell uses electricity to break up a compound.
Understanding the Practical Considerations
While powerful, electrolysis is not without its requirements and limitations. Its application is a deliberate engineering choice based on specific trade-offs.
The Need for Continuous Energy
Electrolysis is an energy-intensive process. It requires a constant and often substantial supply of electricity to run. If the power is interrupted, the reaction immediately stops. This energy cost is a primary factor in the economic viability of industrial electrolysis.
Material Purity is Critical
The purity of the electrolyte is crucial. Impurities can lead to unwanted side reactions, reducing the efficiency of the main process and contaminating the final product. The choice of electrode material is also vital, as it must withstand the corrosive environment and not interfere with the desired reaction.
Key Applications of Electrolysis
The right application depends entirely on your end goal. The versatility of electrolysis makes it a cornerstone of modern chemistry and industry.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity gases: Electrolysis is the standard method for decomposing water (H₂O) into exceptionally pure hydrogen and oxygen.
- If your primary focus is metal extraction and refining: The process is indispensable for producing highly reactive metals like aluminum from its ore (bauxite) or refining copper to a high purity.
- If your primary focus is surface coating and protection: A similar electrolytic process, known as electroplating, is used to deposit a thin layer of one metal (like chromium or gold) onto another for corrosion resistance or aesthetic appeal.
Ultimately, the electrolysis cell is a foundational tool for converting electrical energy into valuable chemical change, enabling us to create substances that nature would not produce on its own.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in the Electrolysis Cell |
|---|---|
| External Power Source | Provides electrical energy to force a non-spontaneous reaction. |
| Electrolyte | A medium containing ions that completes the internal electrical circuit. |
| Electrodes (Anode & Cathode) | Sites where chemical decomposition occurs, attracting ions to react. |
| Key Applications | Metal extraction (e.g., aluminum), gas production (e.g., hydrogen), and electroplating. |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with precision equipment? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored for demanding processes like electrolysis. Whether you're refining metals, producing high-purity gases, or conducting electroplating, our reliable tools ensure efficiency and accuracy. Contact us today to discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's unique needs and drive your chemical innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
- Li-Air Battery Case for Battery Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- How should an all-quartz electrolytic cell and its components be maintained for long-term use? A Guide to Maximizing Equipment Lifespan
- What are the standard opening specifications for sealed and unsealed all-quartz electrolytic cells? Optimize Your Electrochemistry Setup
- What materials are used to construct the all-quartz electrolytic cell? A Guide to Purity and Performance
- What are the operational procedures and safety precautions during an experiment using an all-quartz electrolytic cell? Ensure Safety and Accuracy in Your Lab
- Why is a quartz electrolytic cell used for acrylic acid wastewater? Ensure Chemical Stability & Data Integrity



















