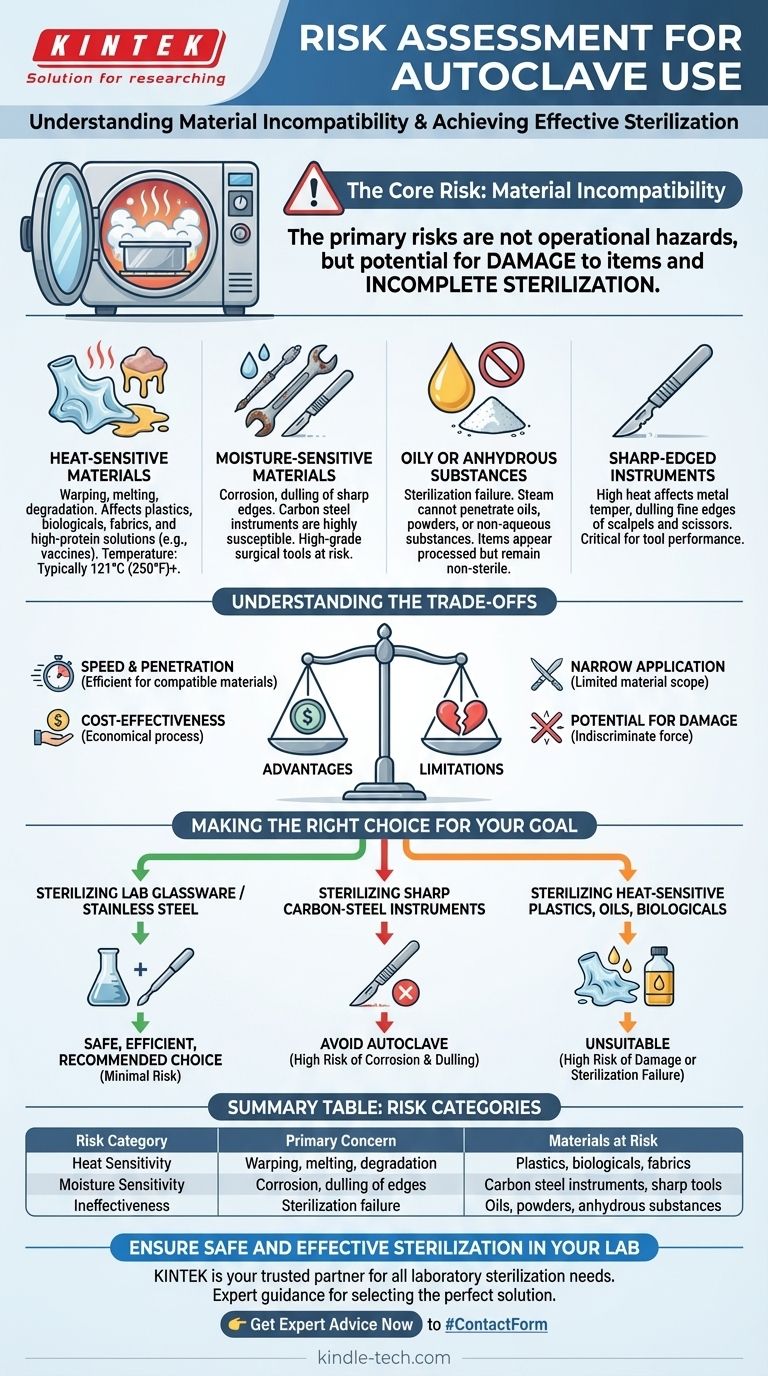
The primary risks of using an autoclave are not operational hazards but rather the potential for damaging the items being sterilized and achieving incomplete sterilization. The intense environment of high-pressure steam is highly effective but can destroy heat-sensitive materials, corrode certain metals, dull sharp instruments, and render complex chemical compounds useless.
An autoclave is a highly effective sterilizer, but its power is also its greatest risk. The core danger lies not in its operation, but in using it on materials that cannot withstand its intense heat and moisture, leading to equipment damage and sterilization failure.

The Fundamental Risk: Material Incompatibility
An autoclave works by using high-pressure steam to transfer heat and kill microorganisms. This mechanism is the source of nearly all its limitations and risks. If a material cannot survive direct contact with steam at high temperatures, it will be damaged or destroyed.
Heat-Sensitive Materials
Many common materials are incompatible with the high temperatures inside an autoclave, typically 121°C (250°F) or higher.
Heat-sensitive plastics can warp or melt, destroying the integrity of containers or equipment.
Delicate items like fabrics or linens can be damaged, while complex biologicals, such as certain vaccines, serums, and high-protein solutions, will degrade and lose their efficacy.
Moisture-Sensitive Materials
The process relies entirely on moisture in the form of steam, which poses a significant risk to certain metals.
While stainless steel is generally safe, carbon steel instruments are highly susceptible to corrosion and damage from the moisture. This makes autoclaving unsuitable for many high-grade surgical tools.
Oily or Anhydrous Substances
An autoclave is completely ineffective for sterilizing oils, powders, or any substance that does not mix with water.
Steam cannot penetrate these materials, meaning the heat transfer required for sterilization never occurs. Attempting to do so creates a risk of sterilization failure, where the items appear processed but remain non-sterile.
Sharp-Edged Instruments
The high heat of an autoclave can affect the temper of metal, dulling the fine edges of sharp instruments.
This is a critical risk for tools like high-grade carbon steel scalpels or scissors, where maintaining a sharp edge is essential for performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A proper risk assessment requires balancing the autoclave's significant advantages against its very specific limitations. It is an exceptional tool, but only for the right job.
Advantage: Speed and Penetration
For compatible materials, an autoclave offers excellent steam penetration on all surfaces and a relatively short procedure time, making it highly efficient.
Limitation: Narrow Application
This efficiency is limited to a narrow category of materials: primarily glassware, stainless steel instruments, and heat-resistant plastics. Anything outside this scope is at risk.
Advantage: Cost-Effectiveness
The process is economical, as it relies on water and electricity without requiring additional chemicals or disposables for the core operation.
Limitation: Potential for Damage
The flip side of its chemical-free power is the physical force of heat and pressure. This force, while effective for sterilization, is indiscriminate and will damage any incompatible item placed inside.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To mitigate risk, your decision to use an autoclave must be based entirely on the composition of the items you need to sterilize.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing general lab glassware or stainless steel tools: The autoclave is a safe, efficient, and highly recommended choice with minimal risk.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing sharp carbon-steel instruments: You must avoid the autoclave, as the high heat and moisture will dull the edges and cause corrosion.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive plastics, oils, or biologicals: The autoclave is unsuitable and poses a high risk of destroying the material or failing to sterilize it completely.
Ultimately, a proper risk assessment for an autoclave is a simple matter of matching the tool to the material.
Summary Table:
| Risk Category | Primary Concern | Materials at Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Sensitivity | Warping, melting, degradation | Plastics, biologicals, fabrics |
| Moisture Sensitivity | Corrosion, dulling of edges | Carbon steel instruments, sharp tools |
| Ineffectiveness | Sterilization failure | Oils, powders, anhydrous substances |
Ensure Safe and Effective Sterilization in Your Lab
Choosing the right sterilization method is critical to protecting your valuable equipment and ensuring process integrity. The intense heat and moisture of an autoclave can damage incompatible materials, leading to costly replacements and failed sterility.
KINTEK is your trusted partner for all laboratory sterilization needs. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance to help you select the perfect autoclave or alternative sterilization solution for your specific materials—from durable glassware and stainless steel to sensitive instruments and heat-labile substances.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation to assess your lab's requirements and safeguard your investments. Let our expertise enhance your lab's efficiency and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is validation in the context of a decontamination process? Ensure Proven Compliance and Safety
- What is incubator sterilization? Essential Guide to Contamination Control for Labs
- What are the 3 types of autoclave? Choose the Right Sterilization Method for Your Lab
- Which autoclave is used in microbiology lab? Gravity Displacement vs. Pre-Vacuum Explained
- Why is a high-pressure hydrothermal autoclave core for g-C3N4/CeO2? Achieve Powerful Heterojunction Synthesis
- What is the purpose of using a high-pressure hydrothermal autoclave in the synthesis of MXene/ferrite composites?
- What function does a PTFE-lined autoclave serve for ZnS nanopowder? Achieve Pure, High-Performance Synthesis
- Can you sterilize without autoclave? Yes, and Here's How to Choose the Right Method



















