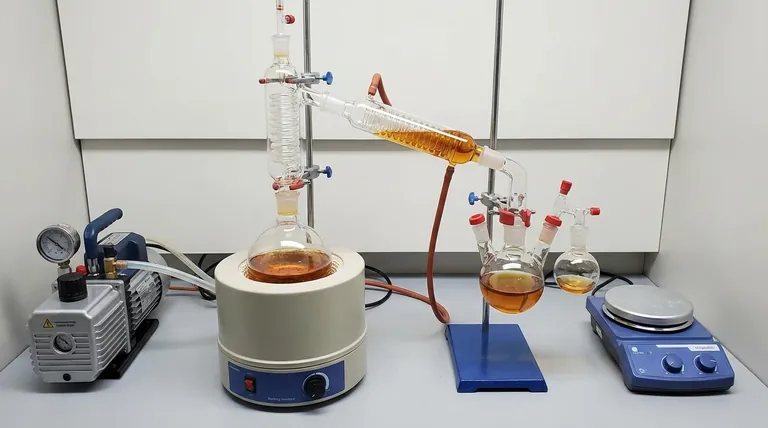
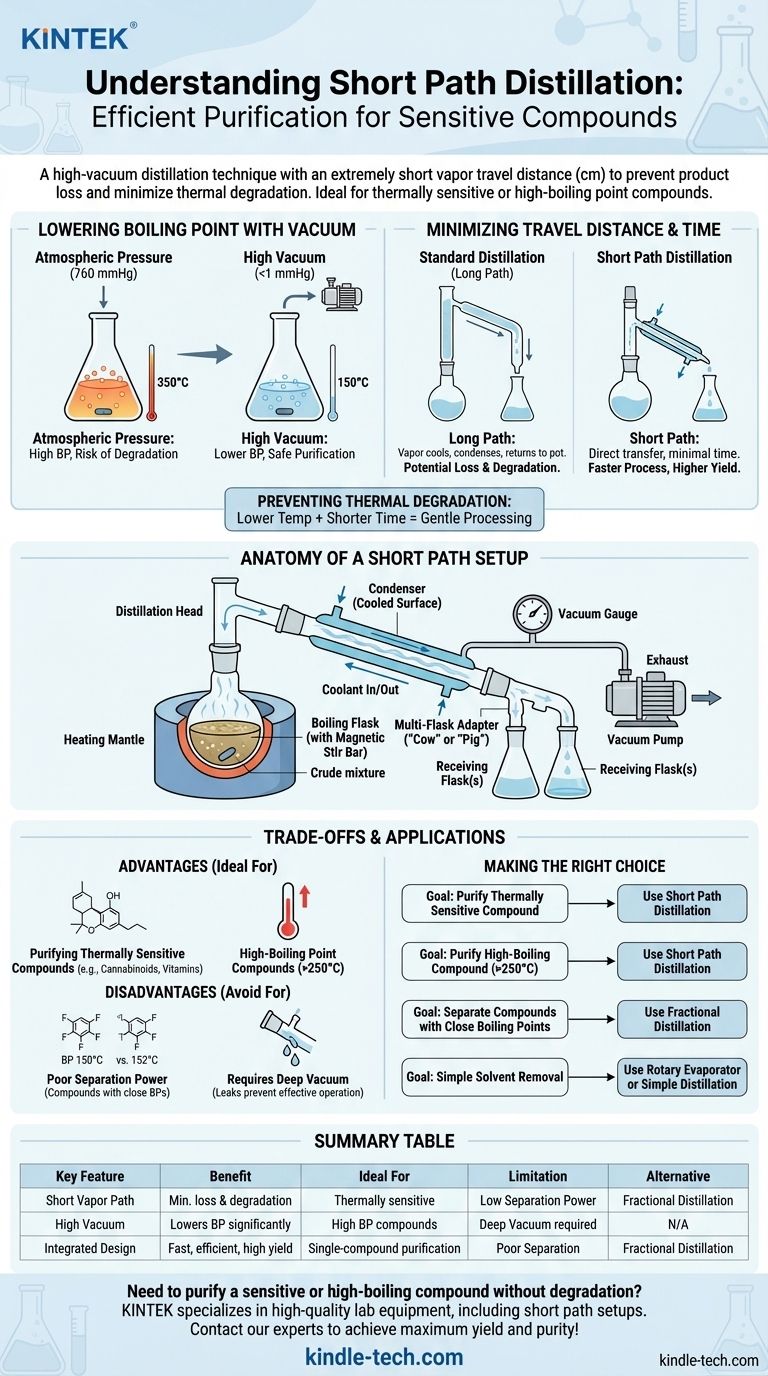
In essence, a short path setup is a laboratory distillation technique used to purify compounds under vacuum. Its defining feature is the extremely short distance—often just a few centimeters—that the vapor travels from the boiling flask to the condenser, which prevents product loss and minimizes the time the compound spends at high temperatures.
The core purpose of short path distillation is to safely purify compounds that are either thermally sensitive (prone to decomposition with heat) or have very high boiling points. The combination of high vacuum and a short travel distance makes this possible where other distillation methods would fail.

The Core Principle: Why "Short Path" Matters
To understand the value of a short path setup, you must first grasp the two physical principles it exploits: the relationship between pressure and boiling point, and the problem of material loss in traditional distillation.
Lowering the Boiling Point with Vacuum
Every liquid has a boiling point, the temperature at which its vapor pressure equals the pressure of the gas above it. By attaching a vacuum pump, we drastically reduce the pressure inside the apparatus.
This lower pressure means the compound can boil at a much lower temperature. For a molecule that would decompose or "crack" at its atmospheric boiling point of, say, 350°C, a high vacuum might lower its boiling point to a much safer 150°C.
Minimizing Travel Distance and Time
In a standard distillation setup, vapor must travel up a long neck or column to reach the condenser. For high-boiling compounds, this long, hot path is a problem.
The vapor can cool and condense on the glass walls before reaching the condenser, falling back into the pot and never being collected. A short path setup minimizes this by integrating the condenser directly across from the boiling liquid, ensuring the vapor has almost no distance to travel. This leads to a faster, more efficient process with higher yield.
Preventing Thermal Degradation
Combining these two factors—a lower boiling temperature and a shorter time spent at that temperature—is the key to preventing thermal degradation. The molecule is gently coaxed into the vapor phase and immediately re-condensed, giving it very little opportunity to break down.
Anatomy of a Short Path Setup
The genius of the short path apparatus lies in its compact, integrated glassware design. While setups vary, they all share these critical components.
The Boiling Flask
This is a round-bottom flask containing the crude mixture you intend to purify. It should always contain a magnetic stir bar to ensure smooth, even boiling and prevent "bumping."
The Distillation Head
This is the heart of the setup. It's a single piece of glassware that combines the vapor path, condenser, and distillate path. The vapor rises from the boiling flask, is immediately exposed to the condenser, and the resulting liquid distillate drips down a small path into a collection flask.
The Condenser
This is typically a glass coil or jacket built into the distillation head. A coolant, usually water or a specialized fluid, is continuously pumped through it to provide a cold surface for the vapor to condense upon.
The Receiving Flask(s)
The purified liquid (distillate) drips into one or more receiving flasks. Advanced setups use a "cow" or "pig" adapter that allows you to rotate and switch between several receiving flasks without breaking the vacuum, enabling the collection of different fractions.
The Vacuum Source & Gauge
A high-quality vacuum pump is non-negotiable. Equally important is a vacuum gauge (e.g., a Pirani or McLeod gauge) to measure the level of vacuum accurately. Controlling the pressure is essential for controlling the boiling point.
The Heat Source
A heating mantle is used to cradle the boiling flask and provide uniform, controllable heat. Direct heating with a flame is never used due to the risk of cracking the glass and creating dangerous hot spots.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A short path setup is a specialized tool, not a universal solution. Its design creates distinct advantages but also significant limitations.
Advantage: Purifying High-Boiling or Sensitive Compounds
This is the primary application. It is the gold standard for purifying cannabinoids, vitamins, fatty acids, and other large organic molecules that cannot withstand the conditions of traditional distillation.
Disadvantage: Poor Separation Power
The short path's primary strength—its lack of a long column—is also its greatest weakness. It has very low "theoretical plates," meaning it is ineffective at separating compounds with close boiling points.
If your goal is to separate two liquids that boil 20°C apart, a fractional distillation column is the correct tool. A short path setup would likely result in a distillate containing a mixture of both.
Pitfall: The Importance of a Deep Vacuum
The entire method hinges on achieving and maintaining a deep vacuum. Leaks at glass joints (which must be properly sealed with vacuum grease), from old tubing, or from an underpowered pump will prevent the boiling point from being sufficiently lowered, defeating the purpose of the setup and risking thermal degradation of your product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right purification method requires you to match the tool to the chemical properties of your compound and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is purifying a thermally sensitive compound: Short path distillation is the ideal choice to prevent decomposition.
- If your primary focus is purifying a compound with a very high boiling point (e.g., >250°C): Short path minimizes product loss and ensures an efficient distillation that might otherwise be impossible.
- If your primary focus is separating two liquids with close boiling points: Do not use a short path; a fractional distillation setup is the correct tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is simple solvent removal from a non-sensitive product: A rotary evaporator or a standard simple distillation is faster, cheaper, and more appropriate.
Ultimately, mastering the short path setup is about understanding when its unique advantages are required to overcome a specific chemical challenge.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Short Vapor Path | Minimizes product loss & thermal degradation | Thermally sensitive compounds (e.g., cannabinoids, vitamins) |
| High Vacuum | Lowers boiling points significantly | Compounds with very high boiling points (>250°C) |
| Integrated Design | Fast, efficient purification process | Single-compound purification where high yield is critical |
| Limitation | Impact | Alternative Method |
| Low Separation Power | Ineffective for compounds with close boiling points | Fractional Distillation |
Need to purify a sensitive or high-boiling compound without degradation?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including reliable short path distillation setups, vacuum pumps, and heating mantles designed for demanding laboratory purification. Our experts can help you select the right system to achieve maximum yield and purity for your specific application.
Contact our lab equipment specialists today to discuss your purification challenges and find the optimal solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the units for vacuum pressure? Torr, mbar, and Pascal Explained
- How is vacuum pressure measured? A Guide to Accurate Gauges and Techniques
- Which material should not be used inside vacuum chamber? Avoid Outgassing and Contamination
- What instrument is used to measure vacuum? Selecting the Right Gauge for Your Pressure Range
- What can carbon nanotubes be used for? Unlock Superior Performance in Batteries & Materials



















