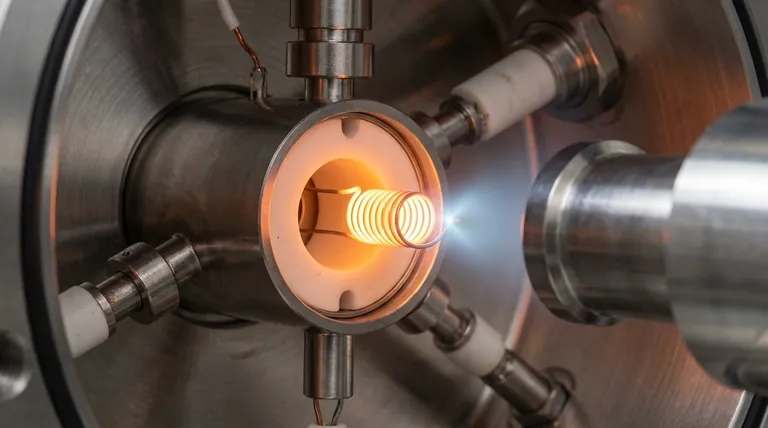
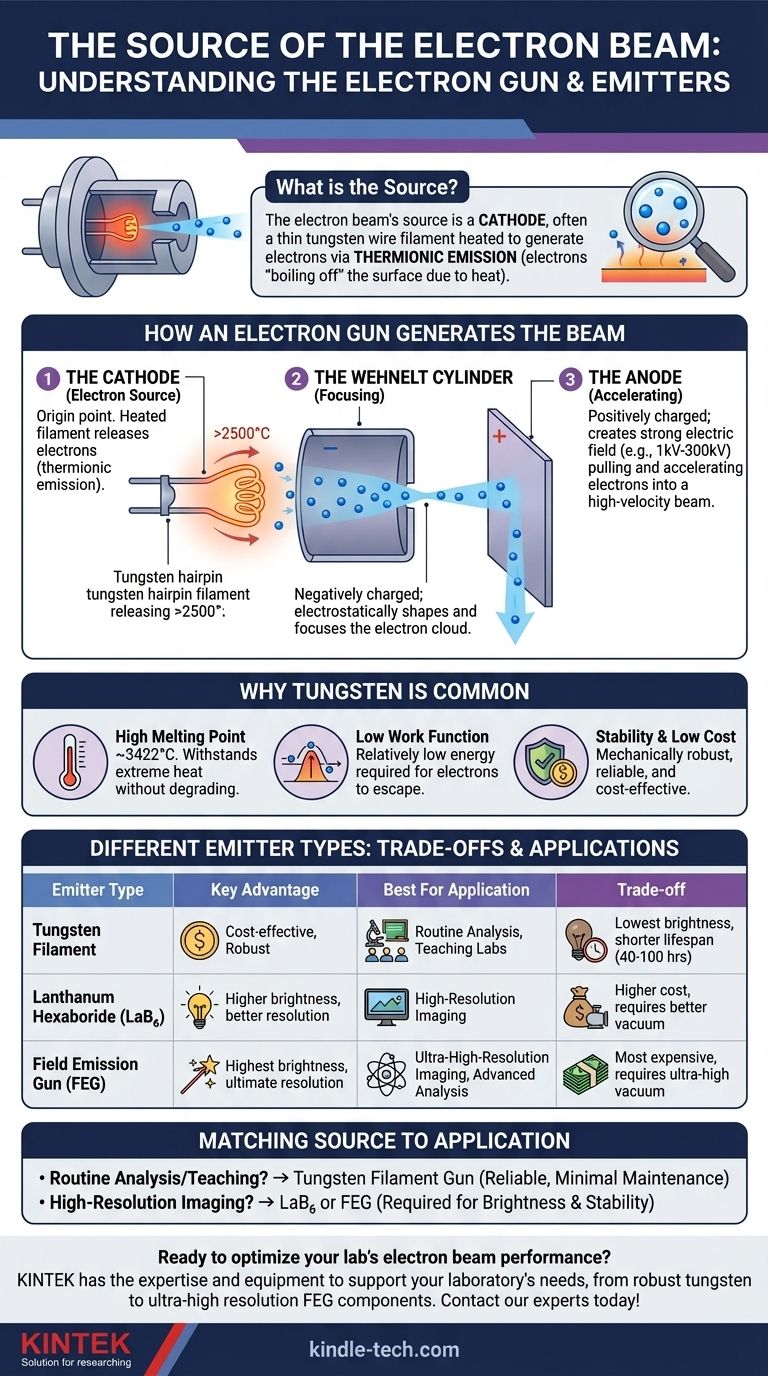
The source of an electron beam is a component known as a cathode, which is most often a thin wire filament. This filament, typically a loop of tungsten metal, is the heart of a larger assembly called an electron gun, which generates, accelerates, and shapes the beam.
The core principle is thermionic emission: a material is heated to such a high temperature that its electrons gain enough energy to "boil off" the surface, creating a cloud of free electrons that can then be formed into a precise beam.
How an Electron Gun Generates the Beam
An electron gun is a sophisticated system designed to produce a stable, controllable stream of high-energy electrons. It consists of three primary components working in concert.
The Cathode: The Electron Source
The cathode is the origin point of the electrons. In the most common design, this is a tungsten hairpin filament. When a current passes through this filament, it heats up to over 2500°C.
At these extreme temperatures, electrons on the surface of the tungsten gain enough thermal energy to overcome the forces holding them to the material. They escape into the surrounding vacuum, a process called thermionic emission.
The Anode: Accelerating the Electrons
Once freed from the cathode, the electrons are rapidly pulled away by the anode, which is held at a very high positive potential (e.g., 1,000 to 300,000 volts) relative to the cathode.
This powerful voltage difference creates a strong electric field that accelerates the negatively charged electrons, forming them into a high-velocity beam directed down the instrument's column.
The Wehnelt Cylinder: Focusing the Beam
Surrounding the filament is a negatively charged electrode called the Wehnelt cylinder or grid cap. Its purpose is to electrostatically shape the electron cloud and provide initial focus.
This component concentrates the emitted electrons into a fine point, known as the beam crossover, which serves as the virtual source of the electron beam for the rest of the system.
Why Tungsten is a Common Material
Tungsten is the workhorse material for standard electron emitters for several key reasons that make it uniquely suited for the harsh conditions inside an electron gun.
High Melting Point
Tungsten has one of the highest melting points of any metal (~3422°C). This allows it to withstand the extreme temperatures required for efficient thermionic emission without degrading or melting.
Low Work Function
While not the lowest available, tungsten has a relatively low "work function"—the minimum energy required for an electron to escape from its surface. This makes it an efficient emitter at achievable temperatures.
Stability and Low Cost
Tungsten is a mechanically stable, robust, and relatively inexpensive material. This makes tungsten filaments cost-effective and reliable for a wide range of general-purpose applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Different Emitter Types
While tungsten is common, it is not the only option. The choice of emitter involves significant trade-offs between performance, cost, and operational requirements.
Tungsten Hairpin Guns
These are the most basic and economical sources. They are robust and tolerant of less-than-perfect vacuum conditions. However, they offer the lowest beam brightness (fewer electrons in a given spot size) and have a shorter lifespan, typically 40-100 hours.
Lanthanum Hexaboride (LaB₆) Emitters
LaB₆ crystals have a lower work function than tungsten, allowing them to produce a much brighter beam at lower temperatures. This results in better signal-to-noise and higher-resolution capabilities. The trade-off is a higher cost and a strict requirement for a much better vacuum to prevent contamination.
Field Emission Guns (FEG)
Field emitters do not rely primarily on heat. Instead, they use an extremely strong electric field to pull electrons directly from a very sharp tip. This produces the brightest, most coherent beam, essential for ultra-high-resolution imaging. They are the most expensive and demand an ultra-high vacuum environment to operate.
Matching the Source to the Application
Your choice of electron source fundamentally determines the capability and cost of the entire system.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis, teaching, or cost-effectiveness: A tungsten filament gun is the standard and most practical choice, offering reliable performance with minimal maintenance.
- If your primary focus is high-resolution imaging or advanced analytical work: A LaB₆ or, ideally, a Field Emission Gun (FEG) is necessary to achieve the required beam brightness and stability.
Ultimately, understanding the electron source is the first step to mastering the performance and limitations of your instrument.
Summary Table:
| Emitter Type | Key Advantage | Best For Application |
|---|---|---|
| Tungsten Filament | Cost-effective, robust | Routine analysis, teaching labs |
| Lanthanum Hexaboride (LaB₆) | Higher brightness, better resolution | High-resolution imaging |
| Field Emission Gun (FEG) | Highest brightness, ultimate resolution | Ultra-high-resolution imaging, advanced analysis |
Ready to optimize your lab's electron beam performance?
The right electron source is critical for achieving your imaging and analysis goals. Whether you need the robust reliability of a tungsten filament or the ultra-high resolution of a field emission gun, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your laboratory's needs.
We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including electron gun components, to ensure your instruments operate at peak performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss the best electron source for your specific application and unlock the full potential of your equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Battery Lab Applications
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
- High Performance Laboratory Stirrers for Diverse Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the available specifications for platinum sheet electrodes? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Electrochemical Needs
- What are the functions of platinum sheet and Ag/AgCl electrodes in corrosion testing? Master Electrochemical Precision
- What are the standard specifications for platinum wire and rod electrodes? Select the Right Form Factor for Your Experiment
- What is the most critical guideline for immersing a platinum sheet electrode in an electrolyte? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What is a common use for a platinum sheet electrode? As a Reliable Counter Electrode in Electrochemical Cells









