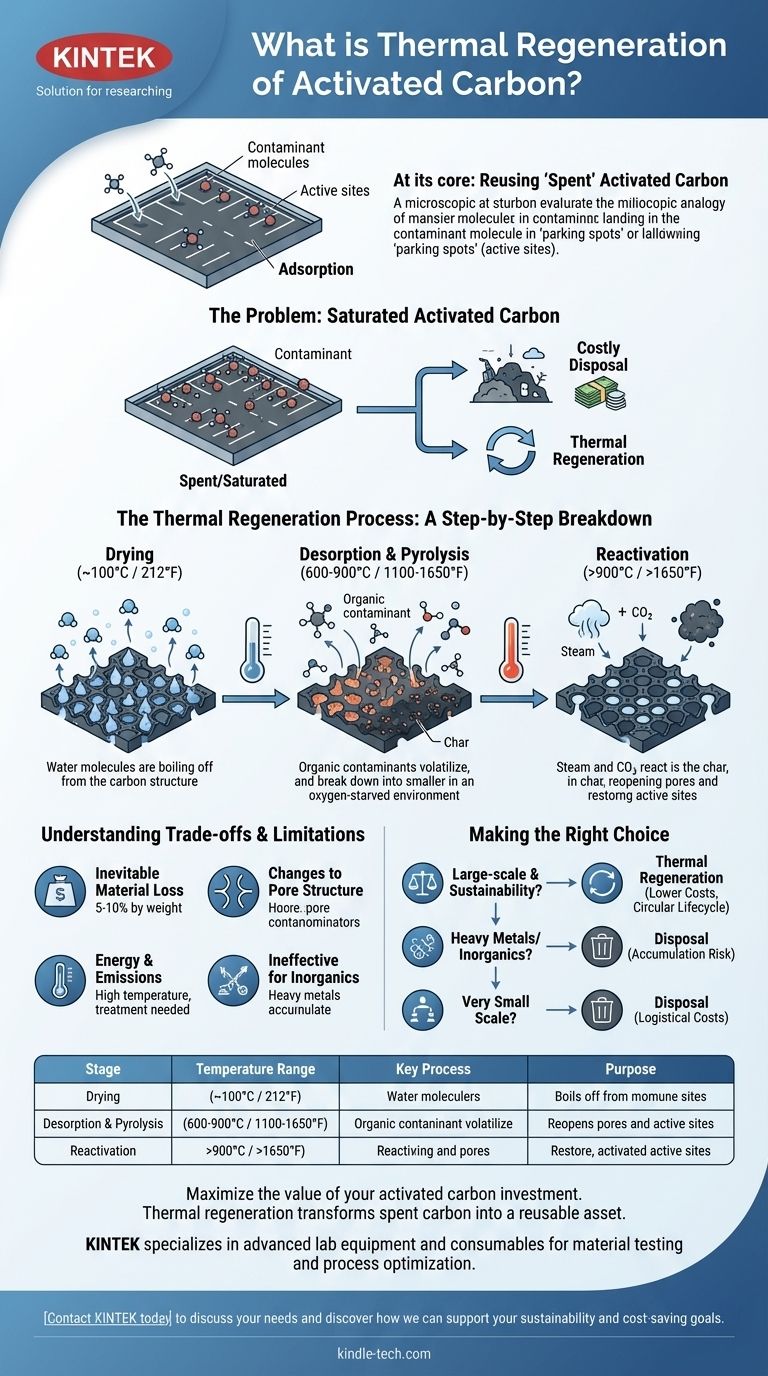
At its core, thermal regeneration is a high-temperature process designed to clean and restore "spent" activated carbon so it can be reused. This controlled heating process destroys the contaminants that the carbon has adsorbed, effectively resetting its capacity to capture more pollutants.
The central takeaway is that thermal regeneration transforms activated carbon from a disposable consumable into a reusable asset. This significantly reduces long-term operational costs and environmental impact by creating a circular life cycle for the material.

The Problem: When Activated Carbon Gets "Full"
To understand regeneration, you first have to understand how activated carbon works. It functions not by absorbing pollutants like a sponge, but by adsorbing them—a process where molecules stick to a surface.
Adsorption: A Surface-Based Attraction
Imagine activated carbon as a vast network of microscopic parking lots. Its enormous internal surface area provides countless "parking spots" (active sites) where contaminant molecules from a liquid or gas can land and stick.
The Point of Saturation
This capacity is finite. Eventually, all the available active sites become occupied, and the carbon is considered "spent" or saturated. At this point, it can no longer effectively remove contaminants from the stream it is treating.
The Cost of Spent Carbon
A facility is then left with two choices: dispose of the spent carbon and purchase new material, or regenerate the existing carbon for reuse. Disposal is often costly and creates a significant waste stream.
The Thermal Regeneration Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
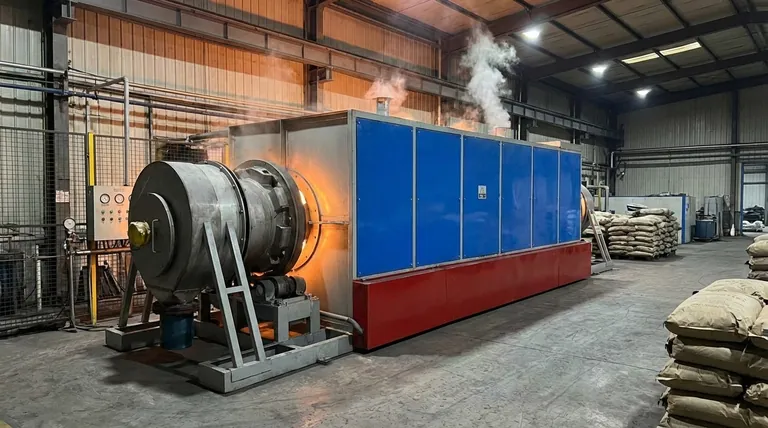
Thermal regeneration, also called reactivation, is a multi-stage process typically performed in a high-temperature rotary kiln or multiple hearth furnace.
Stage 1: Drying (~100°C / 212°F)
The first step involves heating the carbon gently to boil off and remove any residual water. This is a critical preparatory stage that prevents a steam explosion in the higher-temperature zones.
Stage 2: Desorption and Pyrolysis (600-900°C / 1100-1650°F)
In an oxygen-starved environment, the temperature is raised dramatically. This heat causes two things to happen:
- Desorption: The adsorbed organic compounds are volatilized, turning them from a solid/liquid on the carbon's surface into a gas.
- Pyrolysis: The intense heat breaks down these larger, volatilized organic molecules into smaller molecules and a carbonaceous char.
Stage 3: Reactivation (>900°C / >1650°F)
Finally, a controlled oxidizing agent like steam or carbon dioxide is introduced. This gas selectively reacts with the char created in the previous stage, clearing it from the carbon's pores and exposing the original active sites. This step reopens the "parking spots," restoring the carbon's adsorptive capacity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, thermal regeneration is not a perfect process. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Inevitable Material Loss
Each regeneration cycle results in a small amount of carbon loss, typically between 5% and 10% by weight. This is due to mechanical handling and the gasification of some of the base carbon itself during reactivation. This lost volume must be topped up with fresh carbon.
Changes to Pore Structure
Repeated regeneration can subtly alter the pore structure of the activated carbon. Over many cycles, this can slightly change its performance characteristics for adsorbing specific molecules.
Energy and Emissions
The process is energy-intensive due to the very high temperatures required. Furthermore, the off-gases from the kiln contain the destroyed contaminants and byproducts of combustion, which must be treated in a thermal oxidizer or scrubber system to prevent air pollution.
Ineffective for Certain Contaminants
Thermal regeneration is primarily effective for organic compounds. It does not effectively remove inorganic contaminants like heavy metals. These materials can accumulate on the carbon over time, eventually rendering it unsuitable for regeneration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding between regeneration and disposal depends on your scale, contaminant type, and operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is large-scale cost reduction and sustainability: Thermal regeneration is the superior choice, as the cost of reactivation is significantly lower than the cost of new carbon.
- If you are treating streams with heavy metals or other inorganics: You must confirm that these contaminants will not accumulate and poison the carbon, making regeneration unviable.
- If you operate on a very small scale: The logistical costs of transporting a small amount of carbon to a regeneration facility may outweigh the financial benefits.
By restoring its adsorptive power, thermal regeneration allows you to unlock the full economic and environmental value of your activated carbon.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Temperature Range | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drying | ~100°C (212°F) | Boiling off water | Prevents steam explosions |
| Desorption & Pyrolysis | 600-900°C (1100-1650°F) | Volatilizing and breaking down contaminants | Removes organic pollutants |
| Reactivation | >900°C (>1650°F) | Gasification of char with steam/CO₂ | Reopens pores, restores capacity |
Maximize the value of your activated carbon investment.
Thermal regeneration transforms your spent carbon from a recurring expense into a reusable asset, significantly lowering long-term operational costs and minimizing environmental impact. This process is ideal for facilities looking to implement a sustainable, circular lifecycle for their filtration media.
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for efficient material testing and process optimization. If your laboratory or industrial process relies on activated carbon, let our expertise help you evaluate if regeneration is the right strategy for your specific contaminants and scale.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your needs and discover how we can support your sustainability and cost-saving goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- How to regenerate activated carbon? Master the 3-Stage Thermal Process for Cost Savings
- Can you restore activated carbon? Understanding the Industrial Reactivation Process
- How do you carbonize charcoal? Master the 3-Step Pyrolysis Process for High-Purity Carbon
- What are the principles of a rotary kiln? Master the Mechanics of High-Temperature Processing



















