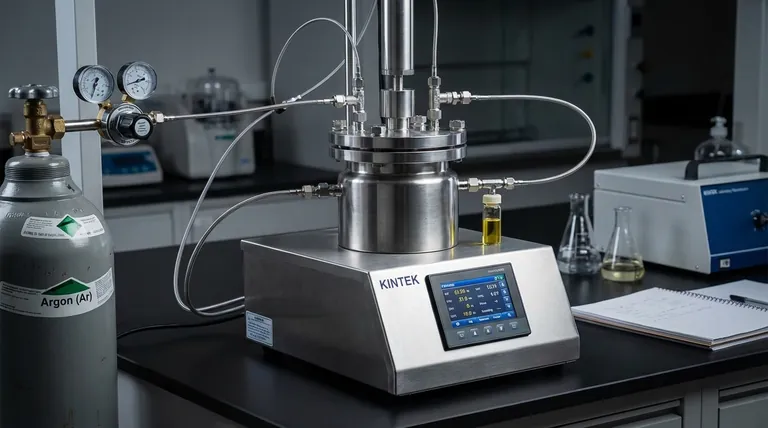
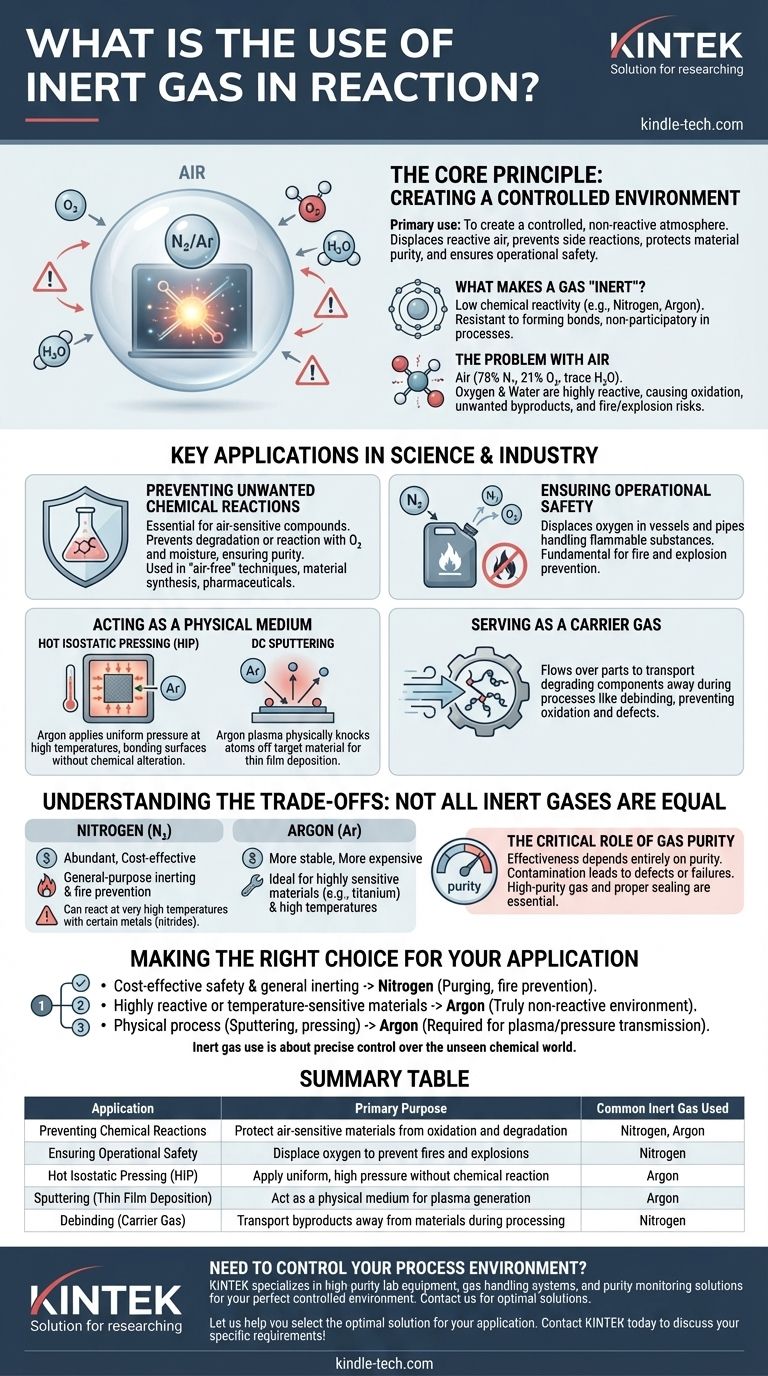
In practice, the primary use of an inert gas is to create a controlled, non-reactive atmosphere. This prevents unwanted and often hazardous side reactions with components in the air, like oxygen or water vapor. By displacing the reactive air, an inert gas ensures that a chemical or physical process proceeds exactly as intended, protecting material purity and ensuring operational safety.
The fundamental role of an inert gas is to act as a neutral background player. It allows a specific process—whether a chemical reaction, heat treatment, or physical deposition—to occur in isolation, free from the unpredictable and often damaging interference of its surrounding environment.

The Core Principle: Creating a Controlled Environment
To understand the value of an inert gas, we first must understand the problem it solves. Many processes are highly sensitive to the reactive gases that make up the air we breathe.
What Makes a Gas "Inert"?
An inert gas, like nitrogen (N₂) or argon (Ar), has very low chemical reactivity. This stability comes from its electron configuration, which makes it resistant to forming chemical bonds with other elements.
This non-reactive nature is its most valuable asset, allowing it to be present during a process without participating in it chemically.
The Problem with Air
Standard air is approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and has trace amounts of other gases, including water vapor. Oxygen and water are highly reactive and can cause undesirable outcomes.
These outcomes include oxidation (like rusting) on metal surfaces, the formation of unwanted chemical byproducts, or even providing the fuel for a fire or explosion in the presence of flammable materials.
Key Applications in Science and Industry
Using an inert gas is about controlling the outcome by removing variables. This principle is applied across a wide range of fields for different reasons.
Preventing Unwanted Chemical Reactions
For chemists working with air-sensitive compounds, an inert atmosphere is non-negotiable. It prevents the target material from degrading or reacting with oxygen or moisture, ensuring the purity of the final product.
This is a cornerstone of "air-free" laboratory techniques, which are critical for synthesizing advanced materials, pharmaceuticals, and catalysts.
Ensuring Operational Safety
In industrial settings, flammable substances are often handled. Pumping a volatile liquid or fine powder can create a combustible atmosphere inside pipes or vessels.
Purging this equipment with an inert gas like nitrogen displaces the oxygen required for combustion. This is a fundamental fire and explosion prevention measure.
Acting as a Physical Medium
Sometimes, the inert gas isn't just preventing a reaction; it's a key part of a physical process.
In Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), argon gas is heated and pressurized to extremely high levels. It applies uniform, isostatic pressure to a material from all directions, collapsing internal voids and bonding surfaces together without chemically altering the part.
In DC Sputtering, argon gas is used to create a plasma. Ions from this plasma bombard a target material, physically knocking atoms off its surface, which then deposit as a thin film onto a substrate. The argon serves as the medium for this physical process, not a chemical reactant.
Serving as a Carrier Gas
During processes like debinding in metal manufacturing, unwanted polymers must be removed. An inert gas flows over the part, acting as a carrier that picks up and transports the degrading components away from the surface.
This prevents the byproducts from causing oxidation or other defects on the metal, ensuring a clean and uniform final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Not All Inert Gases are Equal
While the concept is simple, the choice of gas and its purity have significant implications. The term "inert" is relative to the conditions of the reaction.
Nitrogen vs. Argon: The Cost-Reactivity Balance
Nitrogen is the most common inert gas because it is abundant and relatively inexpensive. For most general-purpose inerting and fire prevention, it is the ideal choice.
However, at very high temperatures, nitrogen can become reactive with certain metals, forming nitrides. For highly sensitive materials like titanium alloys, the more stable and more expensive argon is required because it remains inert even under extreme conditions.
The Critical Role of Gas Purity
The effectiveness of an inerting process depends entirely on the purity of the gas. Even small amounts of oxygen or water contamination can defeat the purpose, leading to product defects or failed experiments.
Therefore, using high-purity gas and ensuring the process chamber is properly sealed and purged of all atmospheric air are critical for success.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct approach depends entirely on your material sensitivity, process conditions, and budget.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective safety and general inerting: Nitrogen is almost always the correct choice for purging vessels and preventing combustion.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive or temperature-sensitive materials: A more noble gas like argon is necessary to guarantee a truly non-reactive environment.
- If your primary focus is a physical process like sputtering or pressing: The choice (typically argon) is dictated by the specific requirements for plasma formation or pressure transmission.
Ultimately, using an inert gas is about exercising precise control over the unseen chemical world.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Purpose | Common Inert Gas Used |
|---|---|---|
| Preventing Chemical Reactions | Protect air-sensitive materials from oxidation and degradation | Nitrogen, Argon |
| Ensuring Operational Safety | Displace oxygen to prevent fires and explosions | Nitrogen |
| Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) | Apply uniform, high pressure without chemical reaction | Argon |
| Sputtering (Thin Film Deposition) | Act as a physical medium for plasma generation | Argon |
| Debinding (Carrier Gas) | Transport byproducts away from materials during processing | Nitrogen |
Need to Control Your Process Environment?
Whether you are working with air-sensitive compounds, require fire prevention measures, or need a stable atmosphere for physical processes like sputtering or pressing, the right inert gas strategy is critical.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including gas handling systems and purity monitoring solutions, to help you create the perfect controlled environment for your laboratory or production needs. Our expertise ensures your processes are safe, efficient, and free from contamination.
Let us help you select the optimal solution for your application. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- Super Sealed Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
People Also Ask
- Which critical experimental conditions does a high-pressure autoclave provide? Optimize Mixed Sulfide Leaching
- What is the function of a high-pressure static autoclave in biomass HTL? Optimize Your Biomass Conversion Research
- What is the significance of the hydrothermal environment in HA preparation? Optimize Mesoporous Structure and Purity
- How does a high-pressure hydrothermal autoclave facilitate the synthesis of BiVO4@PANI nanocomposites? Unlock Precision.
- What is the role of a high-pressure reactor in h-BN magnetic nanocomposite synthesis? Master Precision Deposition

















