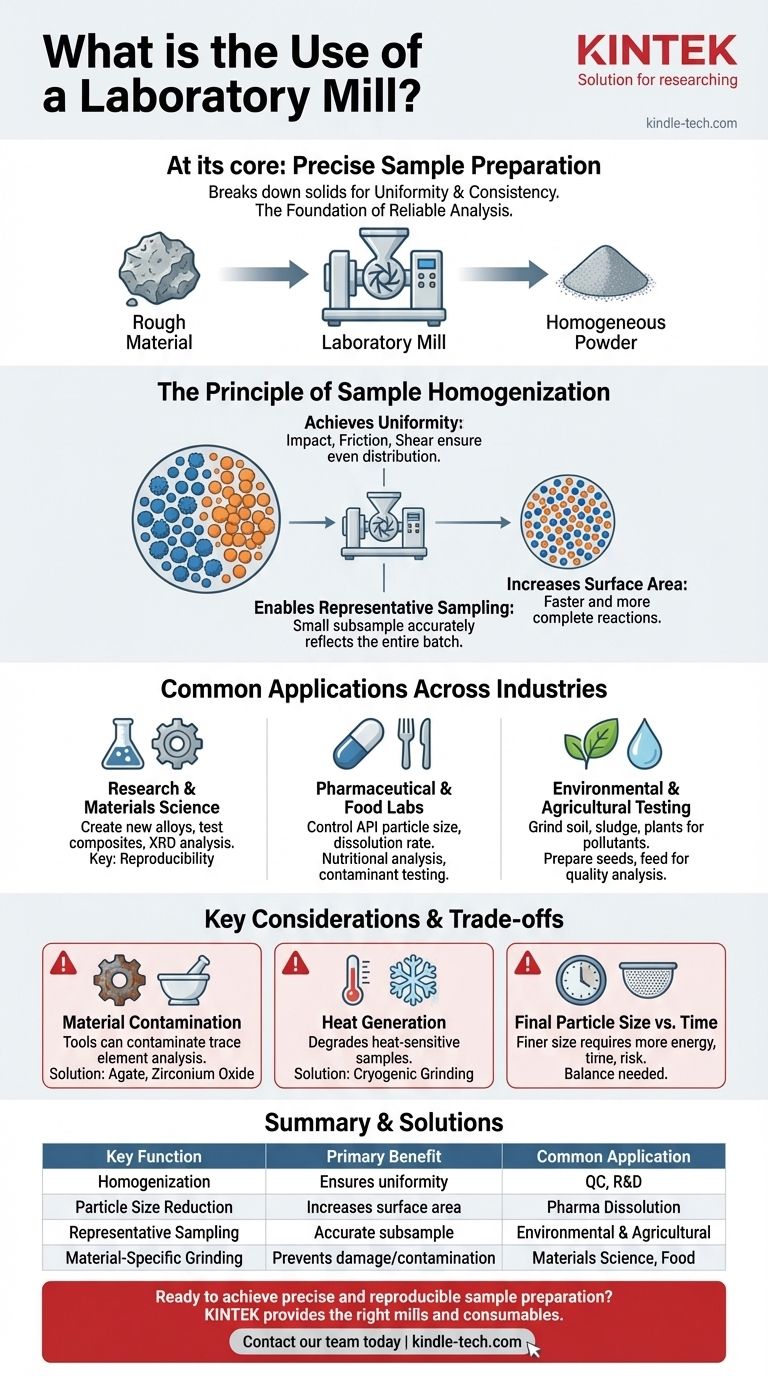
At its core, a laboratory mill is a device designed to break down solid materials into smaller, more uniform particles. It is a fundamental tool for sample preparation, used for grinding, pulverizing, or homogenizing a vast range of substances—from hard minerals and brittle ceramics to soft plant tissues and elastic polymers.
The primary purpose of a laboratory mill is not simply to make things smaller. It is to create a homogenous and representative sample, which is the non-negotiable first step for obtaining accurate and reproducible analytical results.

The Principle of Sample Homogenization
Nearly all analytical techniques, from chemical assays to physical property tests, rely on examining a very small portion of a much larger batch. The accuracy of the final result is entirely dependent on how well that tiny sample represents the whole.
Achieving Uniformity
A laboratory mill achieves homogenization by subjecting a material to mechanical forces—such as impact, friction, or shear. This process thoroughly mixes and grinds the sample, ensuring that its constituent components are evenly distributed.
Without this step, a sample might be heterogeneous. For example, one part of a soil sample may have a higher concentration of a mineral than another, leading to wildly inaccurate measurements.
Enabling Representative Sampling
By reducing a coarse, non-uniform material into a fine, consistent powder, a mill makes it possible to take a small subsample that accurately reflects the composition of the original bulk material. This principle of representative sampling is the foundation of all reliable quality control and scientific research.
Increasing Surface Area
Grinding a material dramatically increases its total surface area. This is critical for processes where reaction speed is important, such as dissolving a sample in acid for chemical analysis or testing the efficacy of a pharmaceutical tablet. A larger surface area allows for faster and more complete reactions.
Common Applications Across Industries
The need for precise sample preparation is universal, making laboratory mills essential in a wide variety of fields. The specific goal dictates the type of mill and the grinding process used.
Research and Materials Science
In materials science, mills are used to create new alloys, test the properties of novel composites, and grind materials for analysis by methods like X-ray diffraction (XRD). Reproducibility is key to comparing results between experiments.
Pharmaceutical and Food Labs
Mills are used to control the particle size of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), which directly affects their dissolution rate and bioavailability. In the food industry, they homogenize samples for nutritional analysis, moisture content determination, and contaminant testing.
Environmental and Agricultural Testing
Environmental labs grind soil, sludge, and dried plant matter to test for pollutants like heavy metals or pesticides. Agricultural labs use mills to prepare seeds, grains, and feed for quality analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While essential, using a laboratory mill is not a one-size-fits-all process. The choice of mill and grinding parameters involves critical trade-offs that can impact your results.
Material Contamination
The grinding tools themselves (e.g., bowls, balls) can be a source of contamination. Grinding a rock sample in a steel container can introduce trace amounts of iron and chromium, which would interfere with trace element analysis. Choosing grinding media made of inert materials like agate or zirconium oxide is often necessary.
Heat Generation
The mechanical energy of grinding generates heat. This can be a significant problem for heat-sensitive samples, such as biological tissues or volatile organic compounds, which could degrade or change their chemical structure. Cryogenic grinding, which uses liquid nitrogen to chill the sample, is a common solution.
Final Particle Size vs. Time
Achieving a very fine particle size requires more energy and longer grinding times. This increases the risk of both contamination and heat generation. You must balance the need for a specific fineness with these potential negative effects.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct approach depends entirely on your material and your ultimate analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is quality control: Prioritize a mill and process that delivers extremely high reproducibility to ensure consistent results over time.
- If your primary focus is trace metal analysis: Choose grinding media that are certified to be free of the elements you are measuring to avoid sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is analyzing heat-sensitive organic compounds: Utilize cryogenic grinding methods to preserve the integrity of your sample.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose research: Select a versatile mill that can accommodate different material types and grinding jar sizes to adapt to various experimental needs.
Ultimately, proper use of a laboratory mill transforms an unreliable, heterogeneous substance into a scientifically valid sample.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Primary Benefit | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Homogenization | Ensures sample uniformity for accurate analysis | Quality Control, Research & Development |
| Particle Size Reduction | Increases surface area for faster reactions | Pharmaceutical Dissolution Testing |
| Representative Sampling | Allows a small subsample to reflect the whole batch | Environmental & Agricultural Testing |
| Material-Specific Grinding | Prevents contamination and heat damage | Materials Science, Food Analysis |
Ready to achieve precise and reproducible sample preparation?
KINTEK specializes in providing the right laboratory mills and consumables for your specific needs—whether you're in pharmaceuticals, materials science, or environmental testing. Our experts can help you select the ideal equipment to ensure sample homogeneity, prevent contamination, and obtain reliable analytical results.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and find the perfect mill for your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Laboratory Disc Cup Vibratory Mill for Sample Grinding
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- Laboratory Micro Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
People Also Ask
- What is the particle size for XRD analysis? Optimize Your Results with the Right Preparation
- What is the primary purpose of using grinding tools like agate mortars? Optimize LTO Electrode Performance
- What is the function of an Agate Mortar and Pestle in sodium battery preparation? Ensure Contaminant-Free Mixing
- What is the function of a mortar and pestle in ZnS nanoparticle prep? Optimize Your Sample Refinement
- What is a mortar and pestle used for in a lab? A Guide to Precision Grinding and Mixing



















