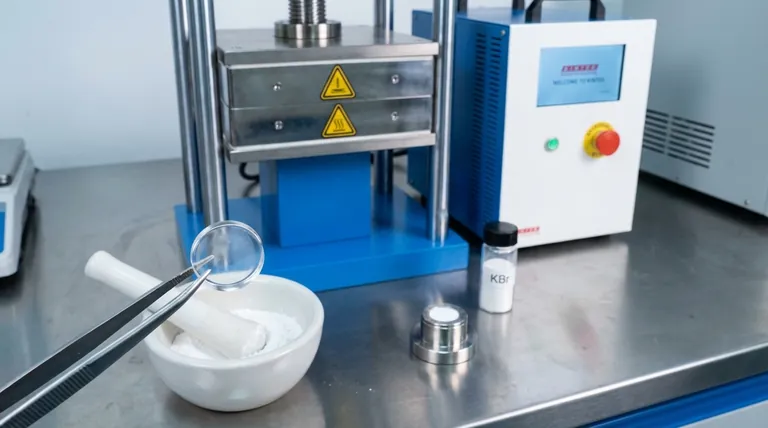
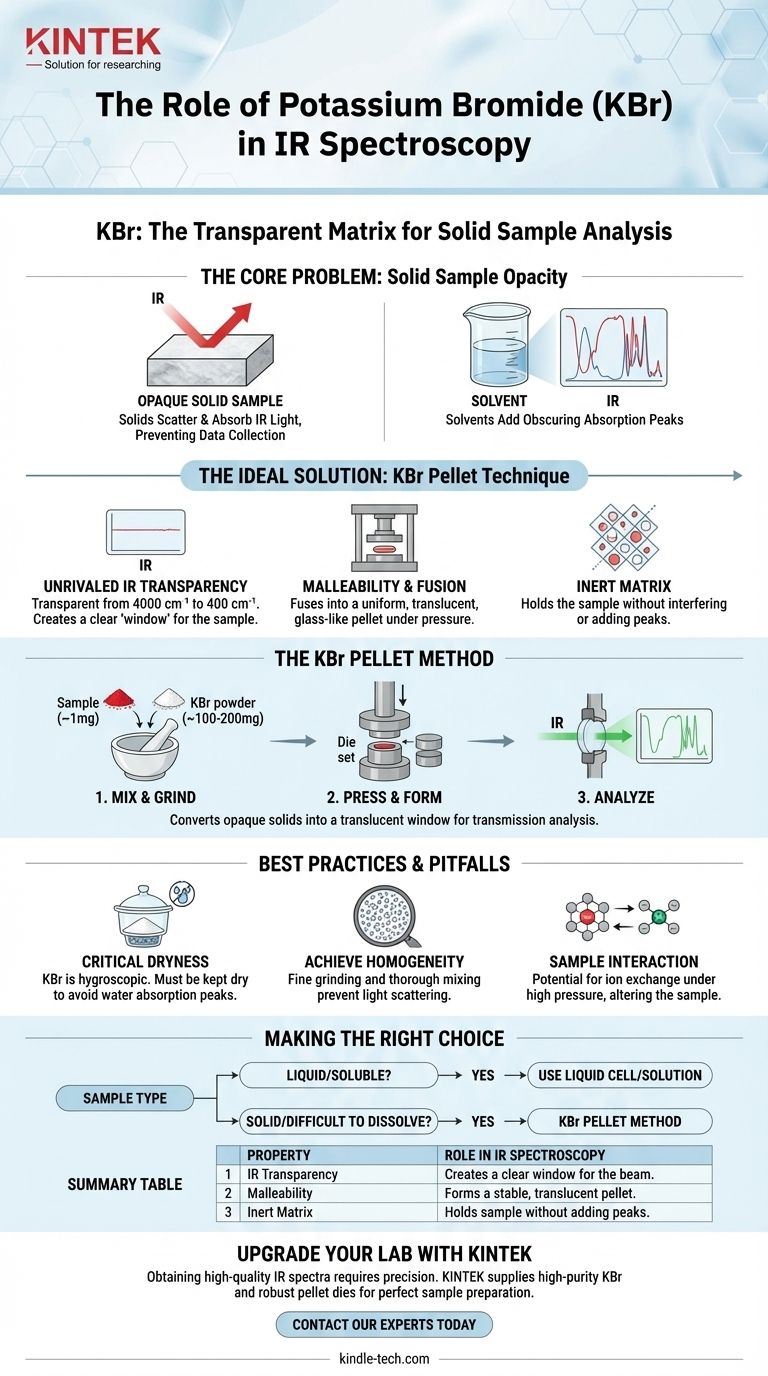
In infrared (IR) spectroscopy, potassium bromide (KBr) is used as an inert matrix to prepare solid samples for analysis. It acts as a transparent medium, allowing the IR beam to pass through a sample without interfering with the measurement. This technique involves finely grinding a solid sample with KBr powder and then compressing the mixture into a thin, translucent pellet.
Potassium bromide's primary value is its optical transparency across the most useful range of infrared frequencies. This property allows it to serve as a perfect "window" or solid-state solvent, making it possible to analyze solid samples that cannot be easily dissolved or melted.

The Core Problem: Analyzing Solid Samples in IR
IR spectroscopy is a powerful technique for identifying chemical compounds, but it requires the infrared beam to pass through the substance being analyzed. This presents a significant challenge when dealing with solids.
The Opaque Nature of Solids
Most solid materials are opaque in their natural state. A block or chunk of a solid sample will scatter or absorb the entire IR beam, preventing any meaningful data from being collected.
The Limitations of Solvents
A common solution is to dissolve the solid in a solvent. However, the solvent itself has a distinct chemical structure that absorbs IR light. These solvent absorption peaks can overlap with and obscure the peaks from your sample, making the resulting spectrum difficult or impossible to interpret.
Why Potassium Bromide is the Ideal Solution
Potassium bromide was adopted as the standard for solid-sample IR analysis because its physical and chemical properties perfectly address these challenges.
Unrivaled IR Transparency
The single most important property of KBr is that it is transparent to infrared radiation across the vast majority of the analytical range (from 4000 cm⁻¹ down to 400 cm⁻¹). It has no vibrational absorptions in this region, meaning it produces a flat, featureless baseline. This ensures that every peak observed in the final spectrum comes from your sample, not the matrix holding it.
Malleability Under Pressure
KBr is a soft, crystalline ionic salt. When it is ground into a fine powder and subjected to very high pressure (typically several tons), the individual crystals deform and fuse together. This process, known as cold-flowing, creates a uniform, glass-like disc or pellet that is mechanically stable and optically clear.
The KBr Pellet Method
This process turns an opaque powder into a translucent window. A tiny amount of the solid sample (typically ~1 mg) is mixed and ground with a much larger amount of pure KBr powder (~100-200 mg). The homogenous mixture is then pressed in a special die to form the pellet, which can be placed directly in the spectrometer's sample holder.
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
While effective, the KBr method requires care and attention to detail to yield high-quality results.
The Critical Role of Dryness
Potassium bromide is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs water from the atmosphere. Water has very strong and broad absorption bands in the IR spectrum that can easily obscure the sample's peaks. Therefore, KBr must be kept scrupulously dry, typically by storing it in a desiccator or a low-temperature oven.
Achieving Homogeneity
The sample must be ground into extremely fine particles and mixed thoroughly with the KBr. If the sample particles are too large, they will scatter the IR light rather than transmit it. This scattering effect results in a sloping baseline and distorted, inaccurate peaks.
Potential for Sample Interaction
While KBr is largely inert, it is an ionic salt. Under the high pressure of pellet formation, it can sometimes interact with certain types of samples, such as other ionic salts. This can lead to ion exchange, altering the sample and producing an unrepresentative spectrum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Sample
The decision to use the KBr pellet technique depends entirely on the physical properties of your sample.
- If your sample is a liquid or can be dissolved in a non-interfering solvent: You likely do not need the KBr method; a liquid cell or solution analysis is often simpler and faster.
- If your sample is a solid that is difficult to melt or dissolve: The KBr pellet method is the industry-standard technique for obtaining a high-quality transmission IR spectrum.
- If you are concerned about sample reactions or moisture sensitivity: You may want to consider alternative solid sampling techniques, such as Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR), which analyzes the surface of a solid directly without extensive preparation.
Ultimately, KBr provides a simple and effective way to render opaque solids transparent to the infrared beam, unlocking their chemical information.
Summary Table:
| Property | Role in IR Spectroscopy |
|---|---|
| IR Transparency | Creates a clear "window" for the IR beam to pass through the sample. |
| Malleability | Fuses under pressure to form a stable, translucent pellet. |
| Inert Matrix | Holds the sample without adding its own absorption peaks to the spectrum. |
Upgrade your lab's analytical capabilities with KINTEK.
Obtaining high-quality IR spectra from solid samples requires precision equipment and reliable consumables. The KBr pellet method is a cornerstone technique, and its success depends on using pure, dry potassium bromide and robust pressing equipment.
KINTEK specializes in supplying high-purity laboratory materials and equipment. We provide the potassium bromide and pellet dies you need to prepare perfect samples for clear, unambiguous IR analysis.
Let KINTEK support your research and quality control.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific lab needs for IR spectroscopy and other analytical techniques. We'll help you select the right products to ensure accurate and efficient results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis



















