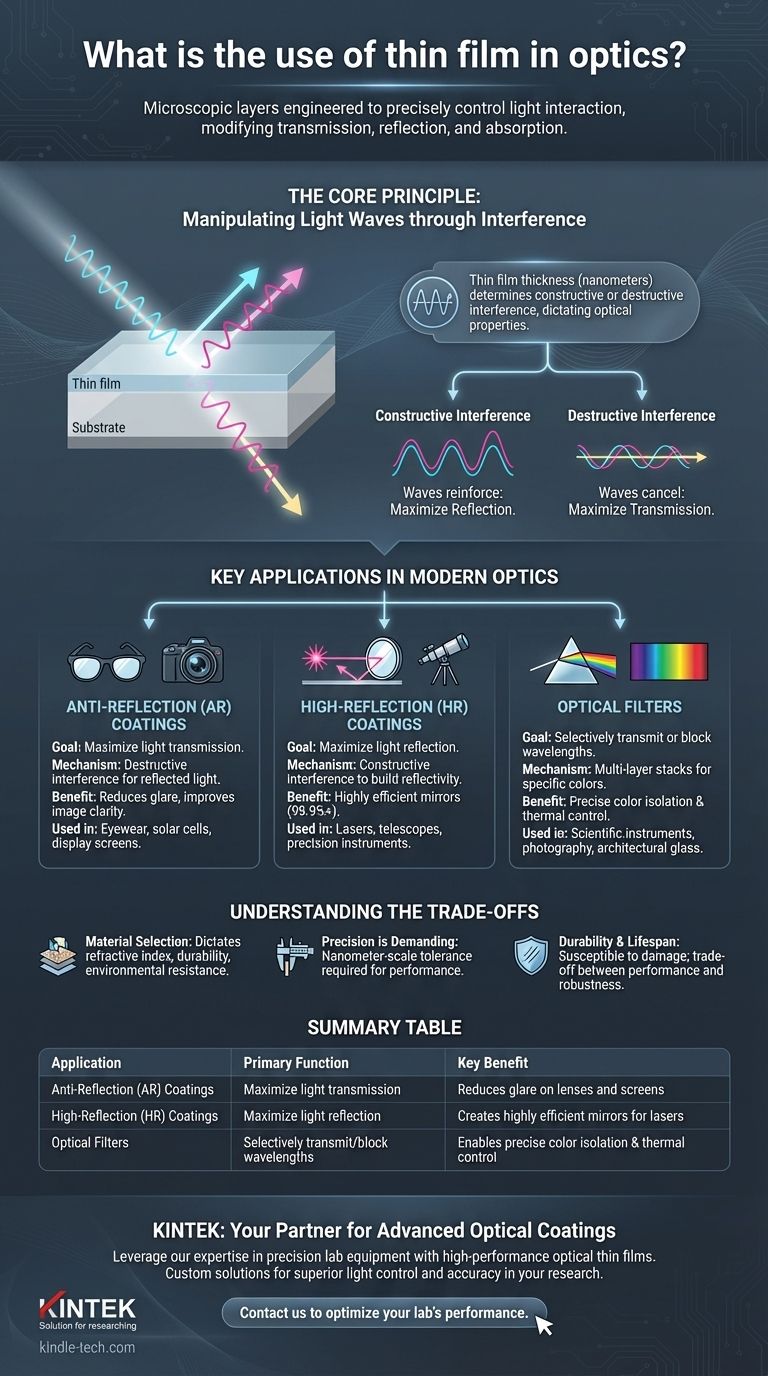
In the field of optics, a thin film is a microscopic layer of material applied to a surface to precisely control how it interacts with light. These films are engineered to modify the transmission, reflection, and absorption qualities of optical components like lenses, mirrors, and filters, enabling everything from anti-glare eyeglasses to advanced scientific instruments.
The true power of an optical thin film lies not just in the material it's made from, but in its precise thickness. By creating layers comparable to the wavelength of light itself, we can manipulate light waves through interference, fundamentally changing a surface's optical properties from what its bulk material would suggest.

The Core Principle: Manipulating Light Waves
To understand the role of thin films, we must move beyond thinking of them as simple protective layers. They are highly engineered structures designed to influence the behavior of light at a fundamental level.
From Bulk Material to Engineered Surface
A block of glass or metal has inherent optical properties. When we reduce a material to a film just a few nanometers thick—often approaching atomic size—its behavior changes. This is because the surface-to-volume ratio skyrockets, and the film's thickness becomes a critical factor in its interaction with light waves.
The Power of Wave Interference
Light behaves as a wave. When a light wave hits a thin film, some of it reflects off the top surface, and some passes through to reflect off the bottom surface. These two reflected waves then interact, or interfere, with each other.
Engineers can design the film's thickness to control whether this interference is constructive (waves reinforcing each other) or destructive (waves canceling each other out). This control is the key to all thin-film optical applications.
Thickness is the Critical Variable
The specific outcome—reflection or transmission—is dictated by the film's thickness relative to the light's wavelength. A coating designed to be anti-reflective for green light will have a different thickness than one designed for blue light. This precision is what makes the technology so powerful and versatile.
Key Applications in Modern Optics
By mastering wave interference, thin films unlock a vast range of applications that are integral to our daily technology and scientific progress.
Anti-Reflection (AR) Coatings
Perhaps the most common application, AR coatings are used on eyeglasses, camera lenses, and solar cells. The film's thickness is chosen to cause destructive interference for reflected light, maximizing the amount of light that passes through. This reduces glare and improves image clarity.
High-Reflection (HR) Coatings
The opposite of AR coatings, these are used to create highly efficient mirrors. By layering materials and choosing thicknesses that cause constructive interference, these films can reflect over 99.9% of light at specific wavelengths. They are critical components in lasers, telescopes, and other precision optical systems.
Optical Filters
Thin films can be layered to create complex filters that selectively transmit or block specific wavelengths, or colors, of light. This is used in everything from camera filters and architectural glass for thermal insulation to advanced scientific instruments that must isolate very narrow bands of the light spectrum.
Advanced and Niche Uses
The versatility of thin-film technology extends to more specialized applications. They are used in head-up displays in cars and aircraft, touch-panel displays, and even self-cleaning glass, where specific coatings provide hydrophobic (water-repelling) properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, thin-film coatings are not a universal solution and come with their own set of engineering challenges.
Material Selection is Crucial
The choice of coating material dictates its refractive index, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. A material ideal for a protected lab environment might be unsuitable for a pair of eyeglasses that must withstand daily wear and cleaning.
Precision is Demanding
Depositing a film with the required uniformity and thickness—often with a tolerance of just a few atoms—is a complex manufacturing process. Any deviation can dramatically alter the optical performance, making high-quality coatings technologically demanding to produce.
Durability and Lifespan
While some coatings are designed for wear protection, all optical coatings are susceptible to damage from scratching, abrasion, or harsh chemicals. The coating's durability is a key design trade-off against its optical performance and cost.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The specific design of a thin film is entirely dependent on the desired outcome for light interaction.
- If your primary focus is maximizing light transmission (e.g., camera lenses, display screens): Your goal is an anti-reflection (AR) coating designed to cause destructive interference for reflected light waves.
- If your primary focus is maximizing light reflection (e.g., laser mirrors, specialized reflectors): You need a dielectric high-reflection (HR) coating that uses constructive interference to build reflectivity.
- If your primary focus is isolating specific colors (e.g., scientific instruments, bandpass filters): You require a multi-layer filter stack engineered to selectively transmit and block very specific wavelengths.
Ultimately, thin-film technology gives us the ability to command light at the most fundamental level, transforming simple surfaces into high-performance optical tools.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Reflection (AR) Coatings | Maximize light transmission | Reduces glare on lenses and screens |
| High-Reflection (HR) Coatings | Maximize light reflection | Creates highly efficient mirrors for lasers |
| Optical Filters | Selectively transmit/block wavelengths | Enables precise color isolation and thermal control |
Ready to integrate high-performance optical thin films into your lab equipment?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing precision lab equipment and consumables that leverage advanced optical coatings to enhance your research and analysis. Whether you need custom filters, coated lenses, or mirrors for specialized instruments, our solutions are designed to deliver superior light control, durability, and accuracy.
Contact us today to discuss how our optical thin film expertise can optimize your laboratory's performance and outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Shortpass Filters for Optical Applications
- Narrow Band Pass Filters for Precision Applications
- Longpass Highpass Filters for Optical Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Sampling Filters
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Head Tweezers with Pointed Elbow Zirconia Ceramic Tip
People Also Ask
- What is the atmospheric pressure CVD process? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is High Temperature Chemical Vapour Deposition (HTCVD) used for? Advanced Silicon Carbide Crystal Growth
- What is CVD in nanotechnology? The Key to Atomic-Level Material Fabrication
- What are the advantages of using a solid precursor sublimation device? Enhance Nucleation in MW-SWP CVD Processes
- How does Vapour deposition work? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Coating Processes
- What are the advantages of thin film resistors? Precision, Stability & Low Noise for Sensitive Circuits
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance
- What temperature is CVD coating? Find the Right CVD Process for Your Material











