In essence, a wiped film evaporator is a specialized distillation tool used to gently separate compounds from mixtures that are difficult or impossible to process with traditional methods. This technology excels at purifying heat-sensitive, viscous, or high-boiling-point materials by minimizing the time the product is exposed to high temperatures, thereby preventing thermal degradation.
The core value of wiped film evaporation is its ability to perform separations under high vacuum with an extremely short residence time. This preserves the quality and integrity of valuable, thermally sensitive products that would otherwise be destroyed by prolonged heat exposure.

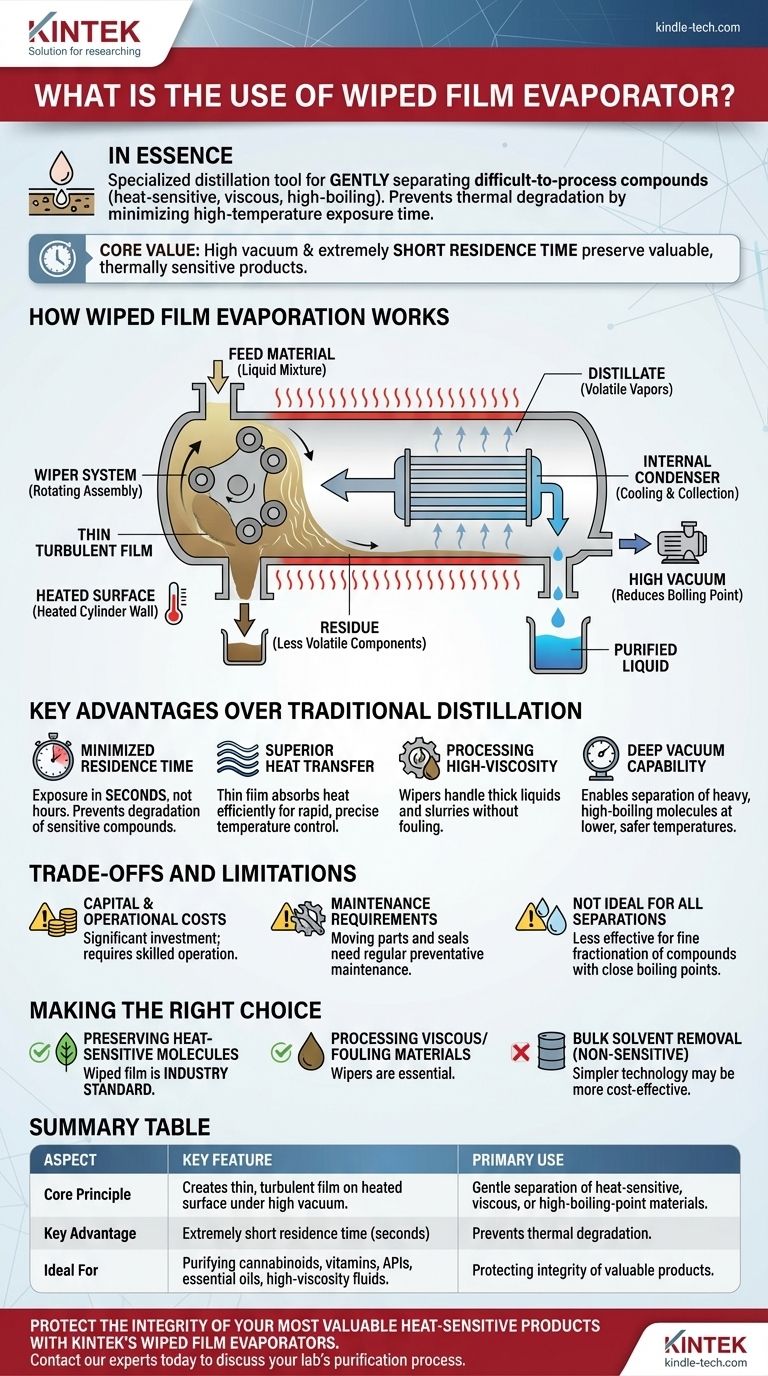
How Wiped film Evaporation Works
A wiped film evaporator, often called a thin film evaporator, operates on a simple but powerful principle: spreading the feed material into an ultra-thin layer across a heated surface. This dramatically improves the efficiency and speed of the evaporation process.
The Core Principle: A Thin Film
The process begins by introducing the liquid mixture into the evaporator. The goal is to create a vast surface area for evaporation, which is achieved by spreading the liquid thinly against the inner wall of a heated cylinder.
The Role of the Wiper System
This is the key mechanical feature. A rotating assembly of wipers or rollers inside the cylinder continuously spreads the feed material into a thin, turbulent film. This action ensures uniform heat distribution and prevents any single portion of the material from overheating.
The Importance of High Vacuum
The entire system operates under a deep vacuum. Lowering the pressure inside the evaporator significantly reduces the boiling point of the components. This allows volatile compounds to vaporize at much lower, safer temperatures.
The Path of Separation
As the thin film moves down the heated wall, the more volatile components (the distillate) evaporate. These vapors travel a very short distance to a centrally located condenser, where they are cooled and collected as a purified liquid. The less volatile components (the residue) do not evaporate and continue down the walls to be collected separately at the bottom.
Key Advantages Over Traditional Distillation
The design of a wiped film system directly addresses the shortcomings of conventional batch distillation, where a large volume of liquid is boiled in a pot for an extended period.
Minimized Residence Time
The most critical advantage is the extremely short residence time. The material is exposed to the heated surface for a matter of seconds, not hours. This is essential for preventing the thermal degradation of sensitive compounds like cannabinoids, vitamins, or complex APIs.
Superior Heat Transfer
A thin, turbulent film is far more efficient at absorbing heat than a large, static pool of liquid. This allows for rapid and precise temperature control, further protecting the product.
Processing High-Viscosity Materials
The mechanical action of the wipers can effectively handle thick, viscous liquids or even slurries. In a traditional still, these materials would foul the heating surface and decompose.
Deep Vacuum Capability
The internal condenser design creates a "short path" for the vapor to travel. This allows the system to operate at very deep vacuum levels, further depressing boiling points and enabling the separation of very heavy, high-boiling-point molecules.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, wiped film evaporation is a specialized tool, and it's important to understand its constraints to determine if it's the right solution.
Capital and Operational Costs
This is sophisticated equipment that represents a significant capital investment compared to simpler distillation setups. It also requires precise control of vacuum, temperature, and feed rate, demanding skilled operation.
Maintenance Requirements
The system contains moving parts, including the wiper assembly and rotating seals. These components are subject to wear and require a regular preventative maintenance schedule to ensure reliable, leak-free operation under deep vacuum.
Not Ideal for All Separations
Wiped film excels at separating components with significantly different boiling points (e.g., removing a light solvent from a heavy oil). It is less effective for fine "fractional" distillations of compounds with very close boiling points.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct technology depends entirely on the nature of your material and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is preserving the integrity of heat-sensitive molecules: Wiped film is the industry standard for protecting valuable compounds from thermal damage.
- If your primary focus is processing highly viscous or fouling materials: The mechanical action of the wipers makes it one of the few viable technologies for effective evaporation.
- If your primary focus is bulk solvent removal from a robust, non-sensitive product: A simpler technology like a falling film or rotary evaporator may be more cost-effective.
Ultimately, adopting wiped film evaporation is a strategic decision to protect product value when heat is the enemy of quality.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Feature |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Gentle separation of heat-sensitive, viscous, or high-boiling-point materials |
| Core Principle | Creates a thin, turbulent film on a heated surface under high vacuum |
| Key Advantage | Extremely short residence time (seconds) prevents thermal degradation |
| Ideal For | Purifying cannabinoids, vitamins, APIs, essential oils, and high-viscosity fluids |
Protect the integrity of your most valuable heat-sensitive products with KINTEK's wiped film evaporators.
Our lab equipment is engineered for maximum efficiency and product preservation, delivering the precise temperature control and deep vacuum capabilities your process demands. Whether you are purifying complex APIs, essential oils, or other sensitive compounds, KINTEK provides the reliable solutions you need.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a wiped film evaporator can enhance your laboratory's purification process and safeguard your product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- How is deposition time calculated? Mastering the Clock for Strategic Legal Advantage
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What is the delta 20 rule of evaporation? Master Safe and Effective Spraying



















