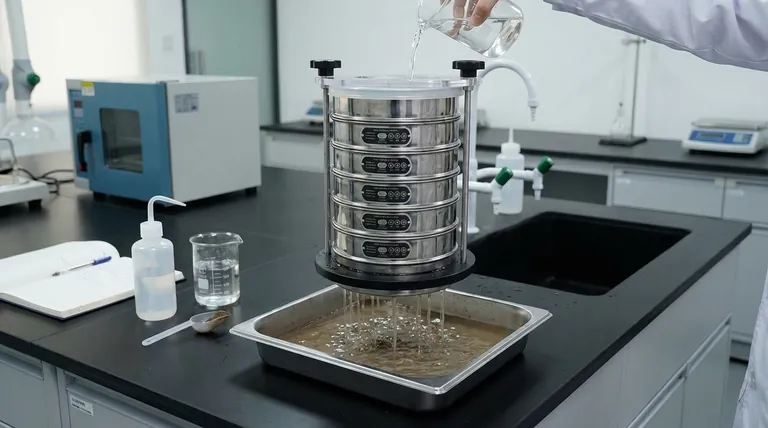
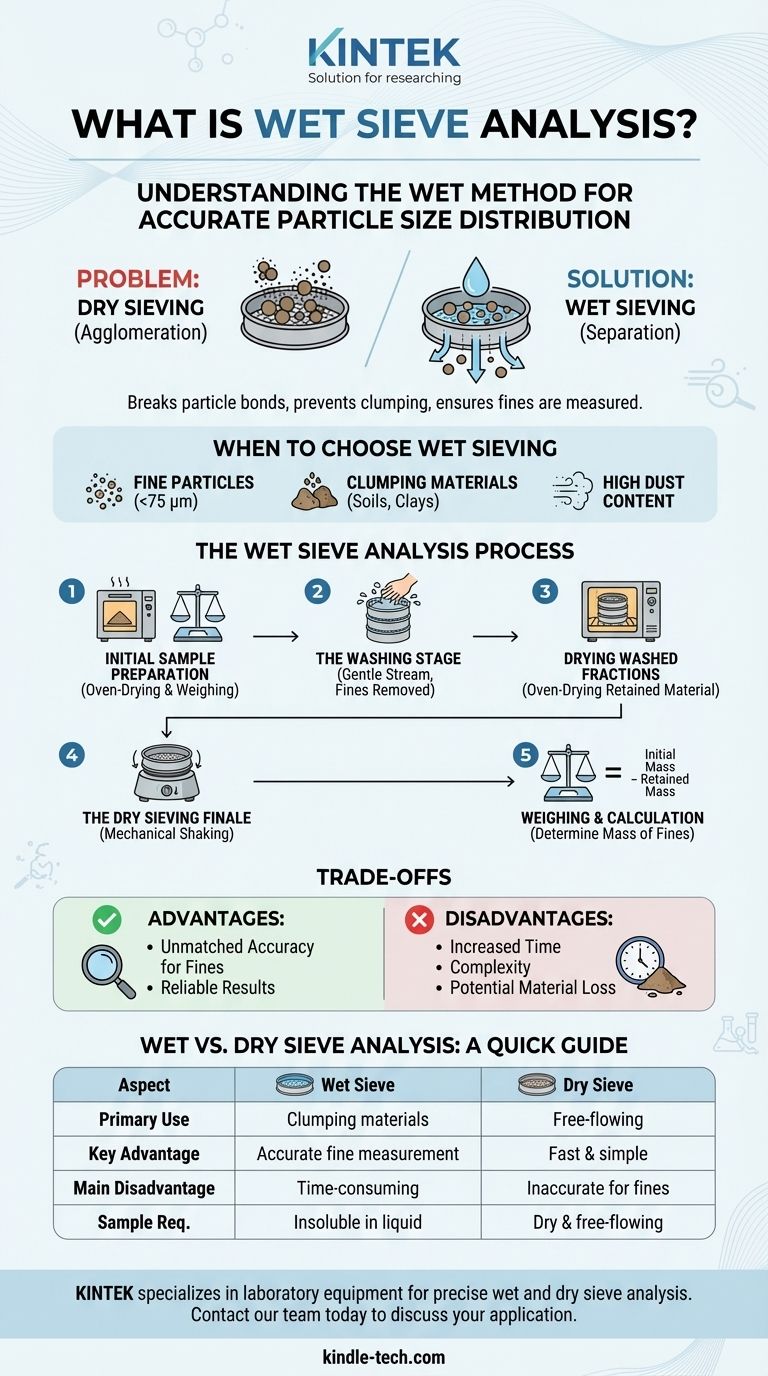
In short, wet sieve analysis is a laboratory technique used to determine the particle size distribution of materials that contain very fine particles or tend to clump together when dry. It involves washing a sample with a liquid (typically water) through a stack of sieves to ensure fine particles are properly separated from coarser ones, preventing inaccuracies caused by agglomeration.
Wet sieving is not a replacement for dry sieving, but a necessary modification. It solves the critical problem of fine particles sticking to larger ones, a common issue that makes standard dry sieving unreliable for materials like soils, clays, and certain fine powders.

When to Choose Wet Sieving Over Dry Sieving
Standard dry sieve analysis is fast and effective, but it relies on one key assumption: that all particles are individual and free-flowing. When this assumption is false, the results are incorrect.
The Problem with Fines and Agglomerates
Very fine particles (often defined as those smaller than 75 or 45 microns) have a high surface area-to-mass ratio. This makes them highly susceptible to electrostatic forces and surface moisture, causing them to stick to each other and to larger particles.
When shaken in a dry sieve, these clumps behave like a single, larger particle, completely skewing the analysis and under-reporting the amount of fine material in the sample.
Materials That Demand the Wet Method
You must consider wet sieving if your material exhibits clumping or contains a significant amount of fine silt or clay.
Common examples include soils, mineral aggregates with high dust content, clays, and certain manufactured powders that are not perfectly free-flowing.
The Goal: Isolate Every Particle
The fundamental purpose of wet sieving is to use a liquid to break the bonds between particles. The water washes away the fines and allows each coarse particle to be measured on its own merit, ensuring a true and accurate particle size distribution.
The Wet Sieve Analysis Process
While sharing principles with dry sieving, the wet method introduces a critical washing stage. The exact procedure can vary based on industry standards like ASTM C117, but generally follows these steps.
Step 1: Initial Sample Preparation
The process begins by oven-drying the material to a constant weight and then recording this initial total dry mass. This provides the baseline for all subsequent calculations.
Step 2: The Washing Stage
The weighed sample is placed on the top sieve of a stack, which typically includes a fine-mesh sieve (e.g., 75 µm or No. 200) at the bottom.
A gentle stream of water is used to wash the sample. The water and the fine particles that pass through the bottom sieve are collected in a pan or drained away. This continues until the water running through the sieve is clear, indicating all separable fines have been removed. For some materials, a dispersing agent may be added to the water to help break up clumps.
Step 3: Drying the Washed Fractions
The material remaining on each sieve after washing is carefully collected and placed into an oven. It must be dried to a constant weight, ensuring all the water used in the washing process has been removed.
Step 4: The Dry Sieving Finale
Once the washed, coarser material is completely dry, it is often sieved again using a standard mechanical shaker. This final step accurately separates the remaining coarse fractions that were not fully segregated during the gentle washing process.
Step 5: Weighing and Calculation
Each fraction retained on the sieves is weighed. The mass of the fine particles that were washed away is calculated by subtracting the total mass of the dried, retained fractions from the initial total dry mass of the sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wet method introduces both benefits and complexities that you must weigh.
Advantage: Unmatched Accuracy for Fines
For materials with agglomerated fines, wet sieving is not just an option—it is the only way to obtain reliable and repeatable results. It directly solves the core problem that makes dry sieving fail.
Disadvantage: Increased Time and Complexity
The wet method is significantly more labor-intensive and time-consuming than dry sieving. The additional steps of washing, decanting, and especially drying can add hours or even a full day to the procedure.
Disadvantage: Potential for Material Loss
Great care must be taken during the washing stage to avoid losing any coarse material. Any splashing or mishandling can lead to a loss of sample and introduce errors into the final calculation.
Constraint: Material Must Be Insoluble
The technique is only viable if the sample material is insoluble in the washing liquid. Using water to test a water-soluble material, for example, would dissolve the sample rather than separate it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Your choice of method depends entirely on the physical characteristics of your material and the data you need to collect.
- If your material is dry, free-flowing, and contains minimal fines (e.g., sand or plastic pellets): Use the standard dry sieving method for its speed and simplicity.
- If your material contains significant fine particles (<75 µm), clumps when dry, or consists of clays and soils: The wet method is essential for achieving an accurate particle size distribution.
- If you must meet a specific industry standard (e.g., for construction aggregates or pharmaceuticals): Follow the prescribed wet or dry sieving procedure outlined in that standard without deviation.
Ultimately, selecting the correct analytical method is the first step toward generating data you can trust.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Wet Sieve Analysis | Dry Sieve Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Materials with fines that clump (e.g., soils, clays) | Dry, free-flowing materials (e.g., sand) |
| Key Advantage | Prevents agglomeration for accurate fine particle measurement | Fast, simple, and less labor-intensive |
| Main Disadvantage | Time-consuming; requires washing and drying steps | Inaccurate for materials with clumping fines |
| Sample Requirement | Material must be insoluble in the washing liquid (e.g., water) | Material must be dry and free-flowing |
Struggling to get accurate particle size data from your fine or clumping materials?
KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, providing reliable sieve shakers, test sieves, and ovens designed for precise wet and dry sieve analysis. Our experts can help you select the right equipment and methodology to ensure your results are trustworthy and repeatable.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your lab's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment



















