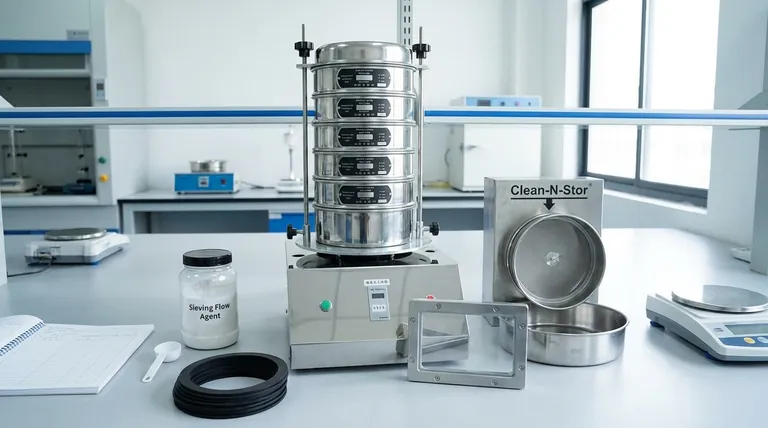
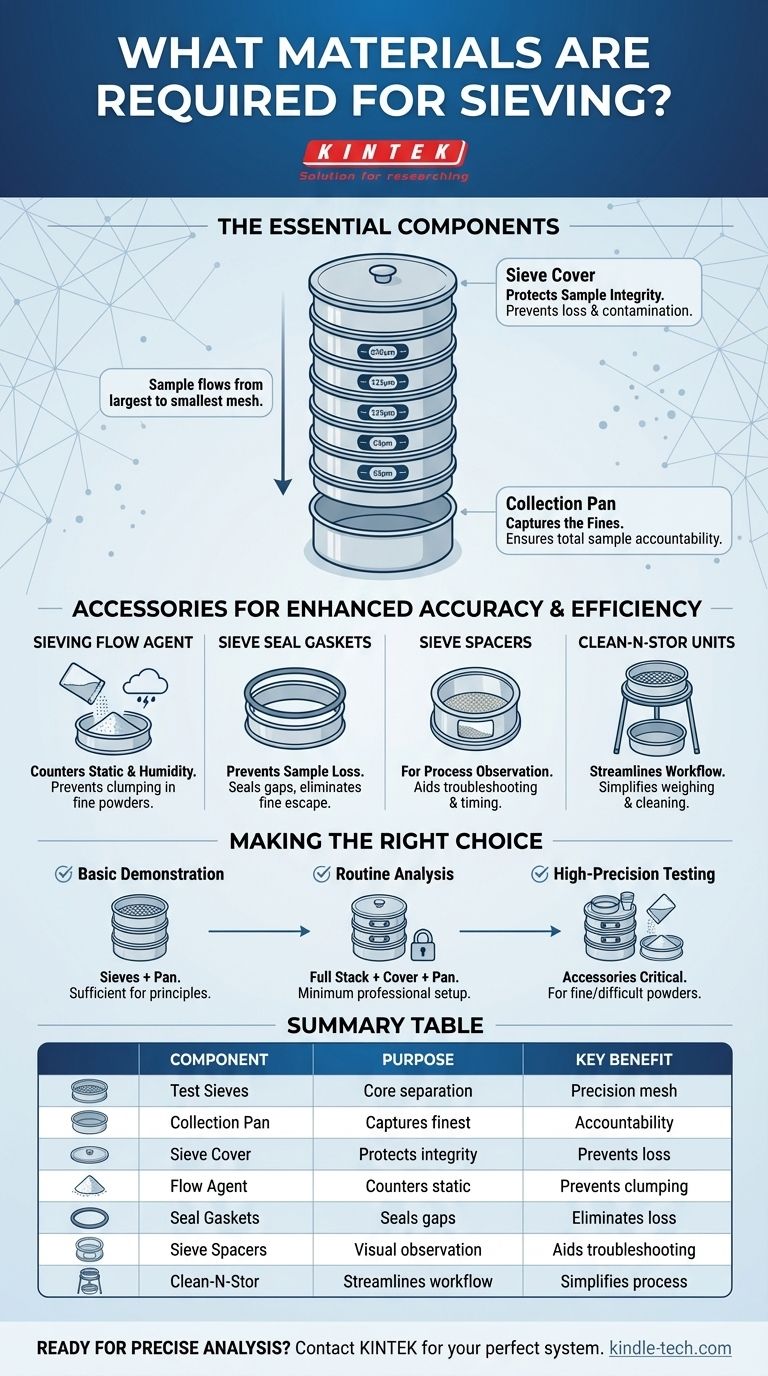
To perform an effective sieve analysis, you require a core set of equipment designed to separate material by particle size. The essentials are a stack of test sieves with graduated mesh sizes, a collection pan for the finest particles at the bottom, and a cover to place on top. These components form the basic apparatus for any particle separation task.
While a stack of test sieves and a collection pan are the bare minimum, achieving accurate and repeatable results depends on a system of accessories designed to prevent sample loss, counter environmental effects, and streamline the entire analytical workflow.

The Essential Components for Sieving
A successful sieve analysis relies on a few non-negotiable components that work together as a system. Understanding the role of each is the first step to ensuring accurate results.
Test Sieves: The Core of the Analysis
Test sieves are the heart of the process. They are precision instruments with a wire mesh or perforated plate of a specific, certified opening size.
Sieves are typically used in a stacked formation, with the largest mesh opening at the top and progressively smaller openings in the sieves below. This allows the sample material to be sorted by size as it moves down the stack.
The Collection Pan: Capturing the Fines
A solid pan, often called a sieve pan, is placed at the very bottom of the sieve stack. Its sole purpose is to collect the finest particles that pass through all the sieves.
Without a collection pan, this portion of the sample—known as the "fines"—would be lost, making it impossible to account for the total sample weight and invalidating the test results.
The Sieve Cover: Protecting Sample Integrity
A cover is placed on the top sieve in the stack. Its function is to prevent two major sources of error.
First, it stops any material from escaping the stack during agitation. Second, it protects the sample from airborne contaminants or changes in ambient moisture, which is critical when working with sensitive materials.
Accessories for Enhanced Accuracy and Efficiency
For professional applications, several accessories are used to address common problems and improve the reliability and efficiency of the sieving process.
For Countering Static and Humidity: Sieving Flow Agent
Certain materials, especially fine powders, can clump together due to static electricity or ambient humidity. This prevents individual particles from passing through the mesh, skewing the results.
A sieving flow agent is a fine, anti-static powder that is added to the sample. It coats the particles, neutralizing static charges and allowing them to flow freely for more accurate separation.
For Preventing Sample Loss: Sieve Seal Gaskets
Even with a tight fit, microscopic gaps can exist between stacked sieves. During agitation, the finest particles can escape through these gaps, leading to sample loss.
Sieve seal gaskets are flexible rings placed between each sieve. They create a perfect seal, ensuring that all fine material is contained within the stack and properly measured.
For Process Observation: Sieve Spacers
Sieve spacers are specialized rings with a plexiglass window that can be inserted into the stack.
Their primary benefit is allowing you to visually observe the sieving action. This helps in troubleshooting issues like sieve blinding (clogging) or determining the optimal agitation time.
For Streamlining Workflow: Clean-N-Stor Units
A Clean-N-Stor unit is a simple but effective device. It acts as a stand that can hold an inverted sieve over a collection pan or a scale.
This accessory significantly simplifies the process of collecting, weighing, and cleaning each individual sieve fraction, reducing handling errors and saving time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing your equipment involves balancing cost against the required level of precision. Not every application requires every accessory.
Bare Minimum vs. Best Practice
For non-critical applications or simple demonstrations, a basic stack of sieves with a pan and cover is often sufficient. The results will give a general overview of particle distribution.
However, for quality control, research, or any application where results must be accurate and repeatable, using accessories is considered best practice. The small investment in gaskets or a flow agent can prevent costly errors and re-testing.
When Accessories Become Necessities
Accessories are not merely "nice-to-haves" in certain conditions. If you are working with very fine powders (< 75 microns), in a humid environment, or with materials prone to static, flow agents and gaskets become necessary for reliable data.
Likewise, in a high-throughput lab, workflow tools like the Clean-N-Stor transition from a convenience to a critical component for maintaining efficiency and accuracy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your equipment based on the precision your application demands.
- If your primary focus is a basic educational demonstration: A set of sieves and a collection pan are sufficient to illustrate the principle of particle separation.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis of standard materials (like sands or aggregates): A full stack with a tight-fitting pan and cover is the minimum professional setup.
- If your primary focus is high-precision testing of fine or difficult powders: Accessories like a sieving flow agent and sieve seal gaskets are critical for achieving reliable and repeatable results.
Equipping your process correctly is the foundational step toward achieving dependable and insightful particle size analysis.
Summary Table:
| Component | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Test Sieves | Core separation by particle size | Precision mesh for accurate sorting |
| Collection Pan | Captures finest particles | Ensures total sample accountability |
| Sieve Cover | Protects sample integrity | Prevents loss and contamination |
| Sieving Flow Agent | Counters static & humidity | Prevents clumping for fine powders |
| Sieve Seal Gaskets | Seals gaps between sieves | Eliminates sample loss |
| Sieve Spacers | Allows visual observation | Aids in troubleshooting and timing |
| Clean-N-Stor Units | Streamlines workflow | Simplifies weighing and cleaning |
Ready to equip your lab for precise and reliable particle size analysis?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific sieving needs. Whether you require a basic sieve set for educational purposes or a full suite of accessories for high-precision quality control, our experts can help you build the perfect system for accurate and repeatable results.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and ensure your sieve analysis is built on a foundation of quality and precision.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
People Also Ask
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- What are the factors affecting sieving performance and efficiency? Optimize Your Particle Separation Process
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability



















