In short, the mesh used for sieving is a screening medium designed with openings of a perfectly uniform size and shape. This medium is what performs the actual separation of particles. It can be made from various materials—such as woven wire, punched metal plate, or electrodeposited film—depending on the specific application and the material being analyzed.
The critical concept is not a single type of mesh, but the principle of uniform openings. The entire purpose of sieving for analysis relies on the mesh acting as a precise barrier, allowing only particles smaller than its openings to pass through.

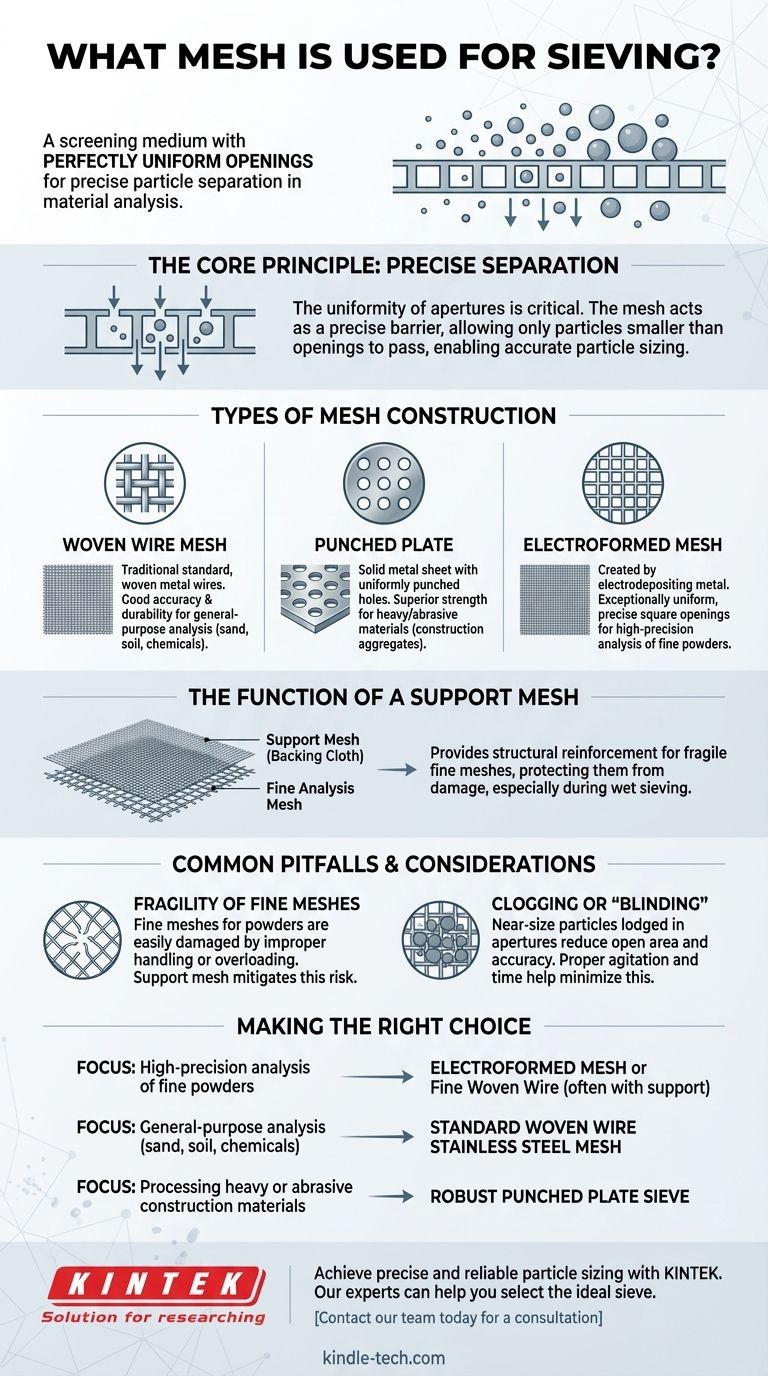
The Role of Mesh in Material Analysis
Sieving is a fundamental technique for determining the particle size distribution of a granular material. The mesh is the heart of this process, acting as the measurement tool. Its construction directly impacts the accuracy and reliability of your results.
The Core Principle: Precise Separation
The defining characteristic of a sieve mesh is the uniformity of its apertures, or openings. Every opening is manufactured to be the same size.
When a sample is agitated on the sieve, particles smaller than the mesh openings fall through, while larger particles are retained on its surface. This simple mechanical action is what allows for precise particle sizing.
Types of Mesh Construction
While woven wire is the most common, different materials and methods are used to create the screening medium.
- Woven Wire Mesh: This is the traditional standard, created by weaving metal wires together. It offers a good balance of accuracy and durability for a wide range of materials, from fine powders to coarse sands.
- Punched Plate: For larger particles or heavy-duty applications (like construction aggregates), a solid sheet of metal with uniformly punched holes is used. This provides superior strength.
- Electroformed Mesh: For extremely fine particles requiring the highest precision, this mesh is created by electrodepositing metal onto a template. It results in exceptionally uniform and precise square openings.
The Function of a Support Mesh
In certain applications, especially with very fine powders, the primary analysis mesh can be extremely fragile.
A support mesh, also called a backing cloth, is a coarser and stronger sieve cloth placed underneath the fine mesh. Its sole purpose is to provide structural reinforcement, protecting the delicate analysis mesh from damage, particularly during wet sieving operations.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While the concept is straightforward, the physical reality of sieving presents challenges that are directly related to the mesh. Understanding these helps ensure you get accurate and repeatable results.
Fragility of Fine Meshes
The smaller the particle you need to measure, the finer and more delicate the mesh wire must be. Meshes for fine powders can be easily damaged by improper handling, cleaning, or overloading with sample material.
Using a support mesh is the primary way to mitigate this risk, especially when liquids are involved in the sieving process.
Clogging or "Blinding"
Blinding occurs when particles that are very close to the size of the mesh openings become lodged in the apertures. This effectively reduces the open area of the sieve and prevents other particles from passing through, leading to inaccurate results.
Proper sieve agitation and selecting the right sieving time can help minimize this issue, but it remains a key operational challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate sieving medium is entirely dependent on the material you are analyzing and the precision you require.
- If your primary focus is high-precision analysis of fine powders: An electroformed mesh or a fine woven wire mesh, often paired with a support mesh, is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose analysis of sand, soil, or chemicals: A standard woven wire stainless steel mesh provides the necessary accuracy and durability.
- If your primary focus is processing heavy or abrasive construction materials: A robust punched plate sieve is required to withstand the demanding load without damage.
Ultimately, understanding the function and material of your sieve mesh is the first step toward reliable and repeatable material analysis.
Summary Table:
| Mesh Type | Best For | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Woven Wire | General-purpose analysis (sand, soil, chemicals) | Good accuracy and durability; standard for most labs |
| Punched Plate | Heavy/abrasive materials (construction aggregates) | Superior strength for large particles |
| Electroformed Mesh | High-precision analysis of fine powders | Exceptionally uniform and precise square openings |
| Support Mesh | Protecting fine, fragile meshes | Coarse backing cloth for structural reinforcement |
Achieve precise and reliable particle sizing with the right sieve mesh from KINTEK.
Whether you are analyzing fine powders, chemicals, or heavy aggregates, selecting the correct sieve medium is critical for accurate results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieves and consumables, offering a full range of mesh types to meet your specific material analysis needs.
Our experts can help you select the ideal sieve to enhance your lab's efficiency and data accuracy.
Contact our team today for a consultation and ensure your sieving process is built on a solid foundation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to process dried SiC mixed powders through sieving equipment? Ensure Uniform Powder Quality
- Why is the use of a standard sieve necessary before the press-molding of NaSICON powders? Ensure Superior Sintered Density
- What is the purpose of sieving in chemistry? Master Particle Size Control for Better Reactions & Quality
- What size are test sieves? A Guide to Frame Diameters and Mesh Sizes
- What are the steps in a sieving test? Master the Systematic Procedure for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What are laboratory sieves used for? Measure Particle Size for Quality Control & R&D
- What is the preferred size in sieving method? Optimize Your Particle Analysis Accuracy
- What is sieve analysis of raw materials? Control Quality with Particle Size Data



















