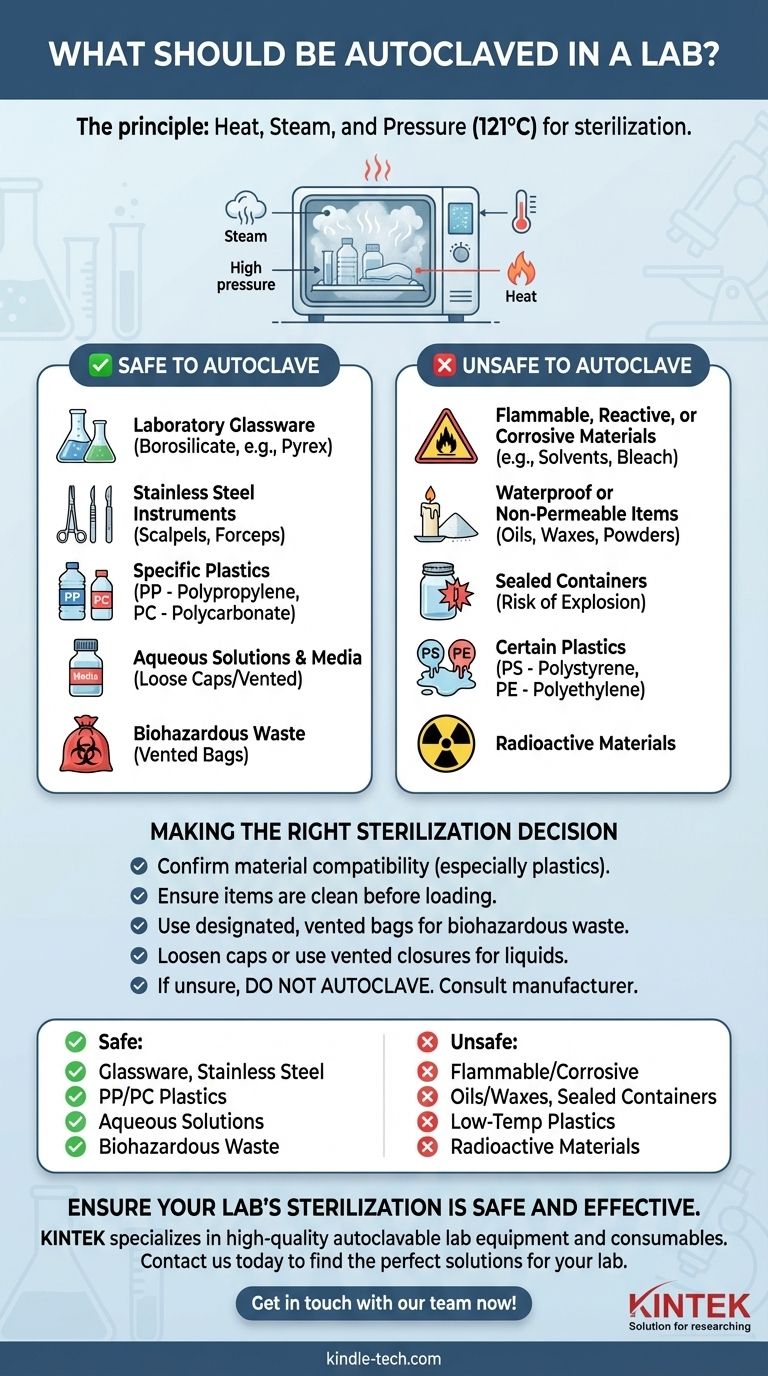
The short answer is that you should only autoclave materials that are compatible with high heat, high pressure, and moisture. This primarily includes laboratory glassware, stainless steel instruments, certain types of plastics like polypropylene, and aqueous solutions or media intended for sterilization. Critically, every item must be processed according to its specific manufacturer instructions to ensure both safety and effective sterilization.
The core principle of autoclaving is steam sterilization. Therefore, the essential question is not just what can be autoclaved, but what cannot be autoclaved, as this is where the significant risks of equipment damage, failed sterilization, and laboratory accidents lie.
The Principle of Autoclaving: Heat, Steam, and Pressure
Autoclaving is a physical method of sterilization that leverages the properties of steam to eliminate transmissible agents like bacteria, viruses, and spores.
How It Works
An autoclave creates an environment where water is heated beyond its boiling point, generating high-pressure steam. This superheated steam, typically at 121°C (250°F) or higher, permeates the items inside the chamber, denaturing proteins and killing microorganisms far more effectively than dry heat alone.
The "Autoclavable" Check
For an item to be considered autoclavable, it must be able to withstand these intense conditions without melting, warping, degrading, or creating a hazard. The material must allow steam to penetrate it or its contents.
What to Autoclave: A Checklist for Success
These items are routinely and safely sterilized using an autoclave, provided proper procedures are followed.
Laboratory Glassware
Most laboratory glassware, particularly borosilicate glass (e.g., Pyrex or Kimax), is designed to handle the thermal shock and pressure of an autoclave cycle.
Surgical and Metal Instruments
Stainless steel instruments, such as scalpels, forceps, and scissors, are ideal for autoclaving. Ensure they are clean of any debris before sterilization to allow for full steam contact.
Specific Plastics
Not all plastics are created equal. Only those that can resist high temperatures are suitable. Look for plastics marked PP (polypropylene) or PC (polycarbonate). In contrast, materials like polystyrene (PS), polyethylene (PE), or high-density polyethylene (HDPE) will melt.
Liquids and Media
Aqueous solutions, such as buffers, reagents, and microbiological culture media, are commonly sterilized by autoclaving. It is essential that their containers are not sealed tightly.
Biohazardous Waste
Autoclaving is a primary method for decontaminating lab waste, such as used petri dishes and disposable culture tubes, before disposal. This must be done in specially designed, vented biohazard autoclave bags.
What NOT to Autoclave: Critical Safety Exclusions
Autoclaving the wrong materials can lead to failed decontamination, release of toxic fumes, damage to the autoclave, or even an explosion. When in doubt, do not autoclave.
Flammable, Reactive, or Corrosive Materials
Never place flammable solvents, radioactive materials, or corrosive chemicals like household bleach (sodium hypochlorite) in an autoclave. Heating these can cause them to vaporize and release toxic or explosive gases.
Waterproof or Non-Permeable Items
Oils, waxes (like paraffin), and powders cannot be autoclaved effectively. Steam cannot penetrate these water-resistant substances, meaning the items will not be sterilized.
Sealed Containers
Autoclaving any tightly sealed container is extremely dangerous. As the liquid inside heats up, pressure builds, creating a significant risk of the container shattering or exploding. Always ensure caps are loose or use a vented closure.
Certain Plastics
As noted, plastics without a high-temperature tolerance will melt into a mass that is difficult to clean and can damage the autoclave. Always verify a plastic's compatibility before processing it.
Making the Right Sterilization Decision
Your approach to autoclaving should be guided by your specific goal and an unwavering commitment to safety.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing reusable labware: Confirm material compatibility (especially for plastics) and ensure items are thoroughly cleaned before being loaded into the autoclave.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating biohazardous waste: Use only designated, vented autoclave bags and adhere strictly to your institution's waste management protocols.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing liquids or media: Use vented caps or cover flasks with aluminum foil to prevent pressure build-up and boil-over.
- If you are ever unsure about an item: Do not autoclave it. The safest action is to consult the manufacturer's documentation or your lab's designated safety officer first.
Ultimately, successful and safe sterilization depends on understanding your materials and meticulously following established protocols.

Summary Table:
| ✅ Safe to Autoclave | ❌ Unsafe to Autoclave |
|---|---|
| Laboratory Glassware (Borosilicate) | Flammable/Corrosive Chemicals |
| Stainless Steel Instruments | Waterproof Items (Oils, Waxes) |
| Specific Plastics (PP, PC) | Sealed Containers |
| Aqueous Solutions & Media | Low-Temperature Plastics (PS, PE) |
| Biohazardous Waste (in Vented Bags) | Radioactive Materials |
Ensure your lab's sterilization is safe and effective.
Choosing the right equipment and consumables is critical for reliable autoclaving. KINTEK specializes in high-quality, durable lab equipment and autoclavable consumables designed to withstand high heat and pressure, ensuring your sterilization protocols are successful every time.
Contact us today to find the perfect autoclave-safe solutions for your laboratory needs. Our experts are ready to help you select the right products to enhance safety and efficiency in your workflow.
Get in touch with our team now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the recommended inspection frequency for laboratory autoclaves? Expert Maintenance Protocols for Safe Operation
- What is the temperature used for autoclaving of microorganisms? Achieve Reliable Sterilization in Your Lab
- What is the temperature that must be reached in an autoclave? Achieve Guaranteed Sterility with the Right Parameters
- What are the advantages of autoclaving in hospitals? Achieve Unmatched Sterilization for Patient Safety
- How often do autoclaves need to be cleaned? A Guide to Protecting Your Lab's Sterilization Integrity
- What are the most common hazards of using an autoclave? Avoid Burns, Explosions, and Sterilization Failures
- What is the primary function of an autoclave system in SiC corrosion research? Simulate BWR conditions accurately.
- What is the autoclaving process in microbiology? Ensure Sterile Results and Lab Safety



















