In short, ball mills are used in nearly every industry that needs to turn a hard, coarse material into a fine powder. They are essential in mining to process ores, in construction for making cement, in pharmaceuticals to prepare drugs, and in advanced research for creating new materials. The core function of a ball mill is size reduction, but this simple process enables a vast range of critical industrial and scientific outcomes.
The true value of a ball mill isn't just grinding; it's about fundamentally changing a material's properties. By controlling particle size, you control everything from a chemical's reaction rate to the physical strength and finish of a final product.
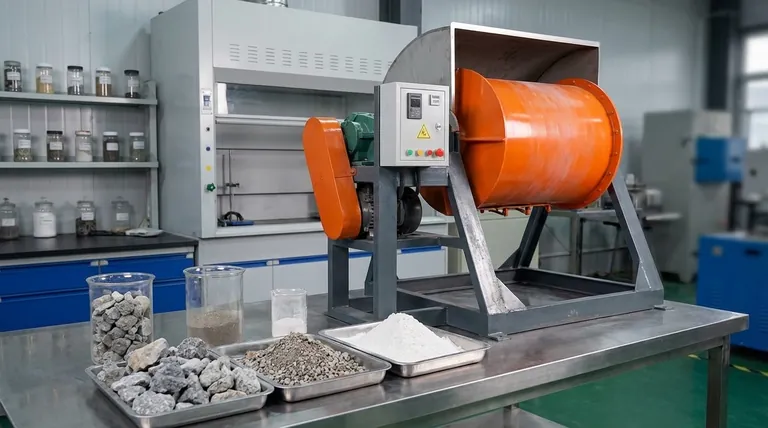

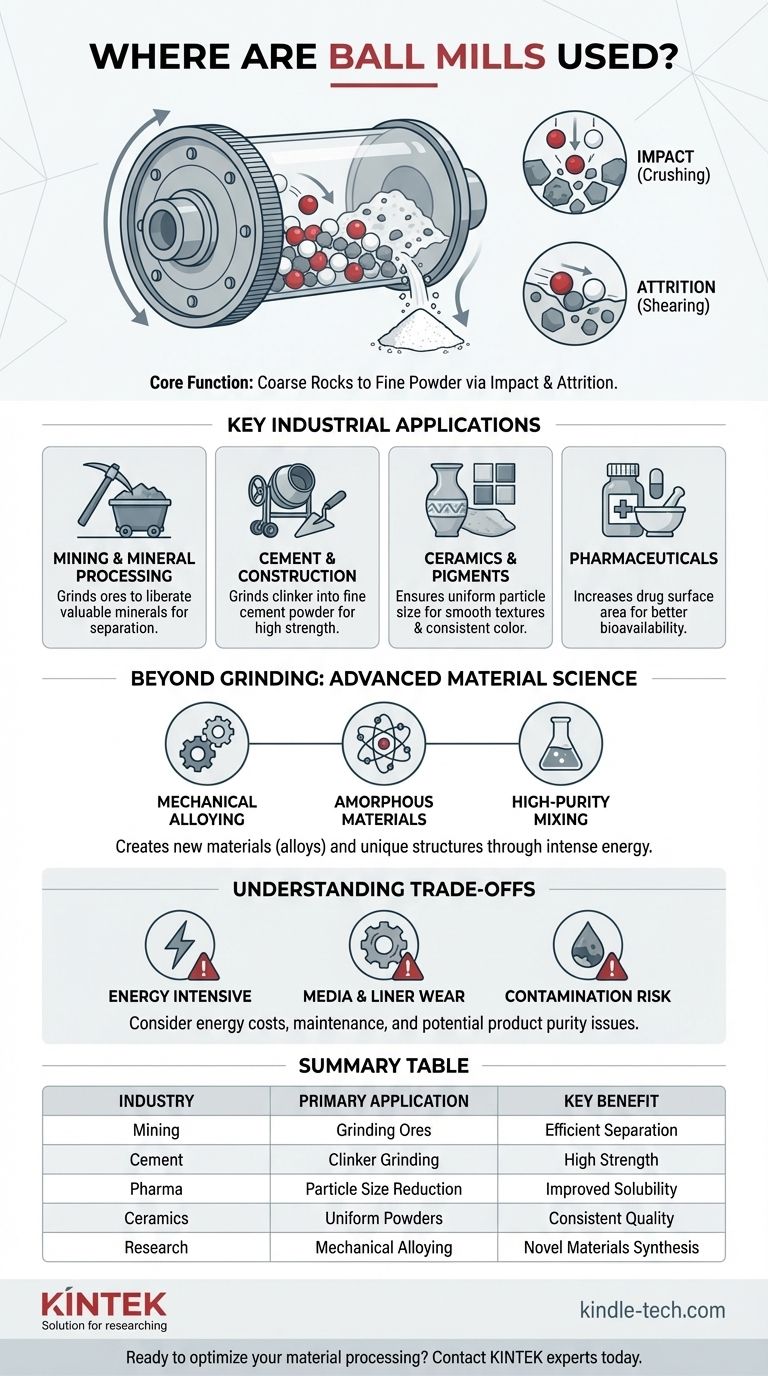
The Core Function: From Coarse Rocks to Fine Powder
A ball mill is a type of grinder used to reduce the particle size of materials. Its versatility comes from its simple, powerful mechanism.
How a Ball Mill Works
A ball mill consists of a hollow cylinder that rotates on its axis. The cylinder is partially filled with the material to be ground, along with a grinding medium—typically hardened steel or ceramic balls.
As the cylinder rotates, the media are lifted up the side and then cascade down. The material is crushed and ground between the balls through this continuous, energetic tumbling motion.
The Power of Impact and Attrition
Two primary forces are at work: impact and attrition.
Impact occurs when the grinding balls drop from the top of the rotating cylinder, crushing the material caught underneath. This is effective for breaking down larger, brittle pieces.
Attrition is the rubbing and shearing action that occurs as the balls slide past each other. This secondary force is responsible for creating very fine, uniform powders.
Key Industrial Applications
The ability to efficiently create fine powders makes the ball mill indispensable across many sectors.
In Mining and Mineral Processing
In mining, valuable minerals are often trapped inside worthless rock (gangue). Ball mills are used to grind the extracted ore into a fine slurry.
This grinding process, known as comminution, liberates the mineral particles, allowing them to be separated and concentrated in subsequent steps.
In Cement and Construction
The production of Portland cement involves grinding a hard, nodular material called "clinker." A ball mill grinds the clinker, along with a small amount of gypsum, into the fine powder we recognize as cement.
This fineness is critical. It creates a massive surface area, allowing the cement to react efficiently with water (hydrate) and gain its strength.
In Ceramics and Pigments
For products like pottery, tiles, and pigments, a uniform and fine particle size is essential for quality. Ball mills grind materials like feldspar and quartz for ceramic bodies and glazes.
This ensures a smooth texture, eliminates defects, and, in the case of pigments, provides consistent color and coverage in paints and coatings.
In Pharmaceuticals
The effectiveness of a drug often depends on its bioavailability—how quickly and completely it is absorbed by the body.
Grinding active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) into fine powders increases their surface area, which can dramatically improve their solubility and absorption rate.
Beyond Grinding: Advanced Material Science
The intense energy inside a ball mill can do more than just reduce particle size; it can create entirely new materials.
Mechanical Alloying
Ball milling can be used to create metal alloys without melting the components. The repeated fracturing and cold-welding of powder particles forced together by the ball impacts can create alloys with a fine, uniform microstructure that is difficult to achieve through conventional melting.
Creating Amorphous Materials
The severe mechanical deformation can also be used to destroy the ordered, crystalline structure of a material. This process, known as amorphization, creates materials with unique magnetic or mechanical properties.
High-Purity Mixing
For applications requiring an extremely homogeneous mixture, such as pyrotechnics or specialized lab reagents, ball mills provide highly effective blending. The tumbling action ensures every particle is thoroughly distributed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, ball mills are not without their operational considerations.
Energy Consumption
Ball mills are energy-intensive machines. Lifting and tumbling tons of steel media and rock requires a significant amount of power, making energy efficiency a key concern in large-scale operations.
Media and Liner Wear
The constant impact and abrasion wear down both the grinding balls and the internal lining of the mill. This not only represents an operational cost but can also introduce contamination into the product.
Contamination Risk
In high-purity applications like pharmaceuticals or advanced ceramics, wear from the grinding media can be a critical issue. Using ceramic media (like zirconia or alumina) instead of steel can mitigate this, but the risk must always be managed.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The decision to use a ball mill is determined by your end goal for the material.
- If your primary focus is raw material processing: A ball mill is the industry standard for liberating valuable components from ore or preparing raw feed for a chemical process.
- If your primary focus is product quality: A ball mill provides essential control over particle size, which directly impacts the strength, finish, and reactivity of products like cement and ceramics.
- If your primary focus is advanced research: A ball mill is a powerful tool for mechanochemistry, enabling the creation of novel alloys and amorphous materials at room temperature.
Ultimately, the ball mill is a foundational tool for transforming the physical nature of solid matter.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Mining & Mineral Processing | Grinding ores to liberate minerals | Enables efficient separation and concentration |
| Cement & Construction | Grinding clinker into fine cement powder | Creates high surface area for strength and reactivity |
| Pharmaceuticals | Reducing particle size of active ingredients | Improves drug solubility and bioavailability |
| Ceramics & Pigments | Creating uniform powders for smooth finishes | Ensures consistent texture, color, and quality |
| Advanced Materials Research | Mechanical alloying and amorphization | Synthesizes novel materials without melting |
Ready to optimize your material processing? Whether you're in mining, pharmaceuticals, or advanced research, KINTEK's precision ball mills deliver the particle size control and reliability you need. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get the right solution for grinding, mixing, or mechanochemistry. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK can enhance your lab's efficiency and outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a planetary ball mill for IZO targets? Achieve Atomic-Level Uniformity in Material Preparation
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in eggshell fertilizer production? Unlock Superior Chemical Reactivity
- What is the function of ball milling equipment in NZSSP electrolyte preparation? Optimize NASICON Solid-State Synthesis
- What is the product size of a ball mill? Achieve Micron-Level Precision for Your Materials
- Why use ball milling for NMC cathode materials? Achieve Precision Particle Sizing for Composite Cathodes



















