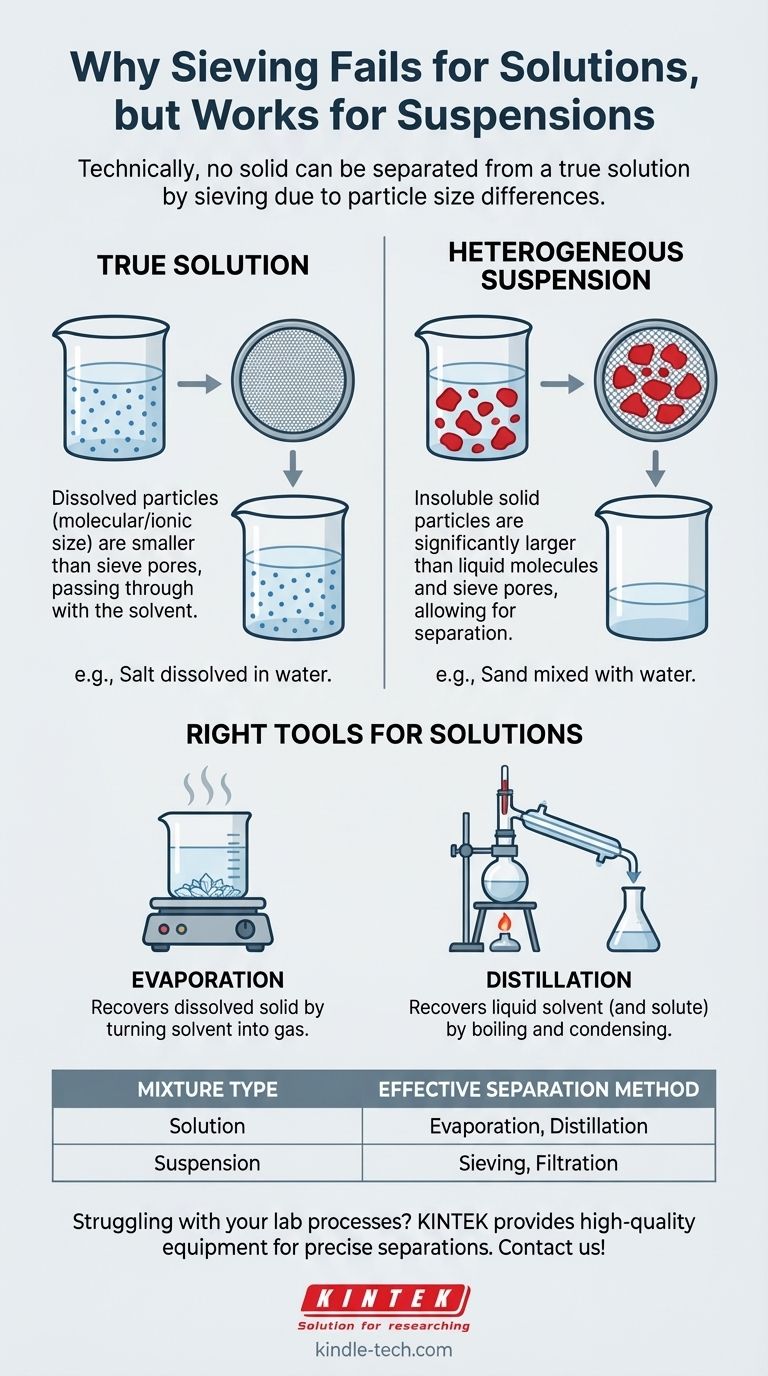
Technically, no solid can be separated from a true solution by sieving. This is because, in a solution, the solid has dissolved into individual molecules or ions, which are far too small to be caught by the pores of any sieve. They pass through along with the liquid solvent.
The user's question highlights a common point of confusion between a solution and a mixture. Sieving is a technique based on particle size, making it effective for separating large, undissolved solids from a liquid, but fundamentally incompatible with true solutions where the solid particles are molecular-sized.

Understanding the Nature of a Solution
Dissolved vs. Undissolved Particles
A true solution is a homogeneous mixture, meaning the components are uniformly mixed down to the molecular level. When a solid like salt dissolves in water, its crystal structure breaks apart.
The individual sodium and chloride ions become surrounded by water molecules. These dissolved particles are infinitesimally small.
Why Sieving Fails for Solutions
A sieve works by having pores of a specific size that allow smaller particles to pass through while blocking larger ones.
Since the dissolved ions or molecules in a solution are often no larger than the solvent molecules themselves, they flow through the sieve's mesh without any separation. It would be like trying to catch water with a fishing net.
When Sieving with Liquids is Effective
Sieving becomes a viable method when you are dealing not with a solution, but with a heterogeneous mixture called a suspension.
The Principle: Significant Size Difference
In a suspension, the solid particles are insoluble and are merely dispersed or suspended within the liquid. The key is that these solid particles are significantly larger than the liquid molecules.
This size difference is what allows a sieve, or a filter, to work. The mesh holes are small enough to block the solid particles but large enough to let the liquid pass through.
Practical Examples of Sieving
This principle is used in many everyday situations:
- Separating gravel or sand from water.
- Straining cooked pasta from water.
- Removing tea leaves from brewed tea with a strainer.
- Separating fruit pulp from juice.
In all these cases, the solid is not dissolved in the liquid; it is simply mixed with it.
The Right Tools for Separating Solutions
Because sieving is ineffective for solutions, other methods that rely on different physical properties must be used.
Evaporation
This is the most common method to recover a dissolved solid from a liquid solvent.
By heating the solution, the liquid solvent turns into a gas and evaporates, leaving the solid solute behind. This is how sea salt is harvested from ocean water.
Distillation
If you need to recover the liquid solvent (or both the solvent and the solute), distillation is the correct technique.
The solution is heated to boil the solvent, the resulting vapor is captured and cooled in a condenser, and it turns back into a pure liquid that is collected separately. The solid solute remains in the original container.
Choosing the Right Separation Method
Your choice of technique depends entirely on the nature of your mixture.
- If your goal is to separate an insoluble solid from a liquid (a suspension): Sieving (for large particles) or filtration (for finer particles) is the correct approach.
- If your goal is to recover a dissolved solid from a liquid (a solution): Use evaporation.
- If your goal is to recover the liquid solvent from a solution: Use distillation.
Understanding whether your solid is truly dissolved or simply suspended is the key to selecting the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Mixture Type | Solid State | Effective Separation Method |
|---|---|---|
| Solution | Dissolved (molecular/ionic) | Evaporation, Distillation |
| Suspension | Undissolved (large particles) | Sieving, Filtration |
Struggling to choose the right lab equipment for your separation processes? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including filtration systems and distillation apparatus, to help you achieve precise and efficient separations. Our experts can help you select the perfect tools for your laboratory's specific needs. Contact us today to optimize your workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- Why must standard test sieves be used to screen silicon nitride ceramic powder? Ensure Uniformity and Strength
- What is the best material for a sieve? Match the Material to Your Application for Accurate Results
- What is the purpose of sieve analysis of sand? Ensure Material Quality for Construction & Filtration
- What are the limitations of sieve size analysis? Avoid Costly Errors in Particle Characterization
- Why use a 500-mesh sieve for wool biochar? Ensure uniform dispersion and flawless coatings.
- What are the factors affecting sieving method? Achieve Precise Particle Analysis
- Why do we need to sieve the powder? Achieve Precise Particle Control for Superior Products
- Why is it important to sieve? Ensure Material Quality and Process Control



















