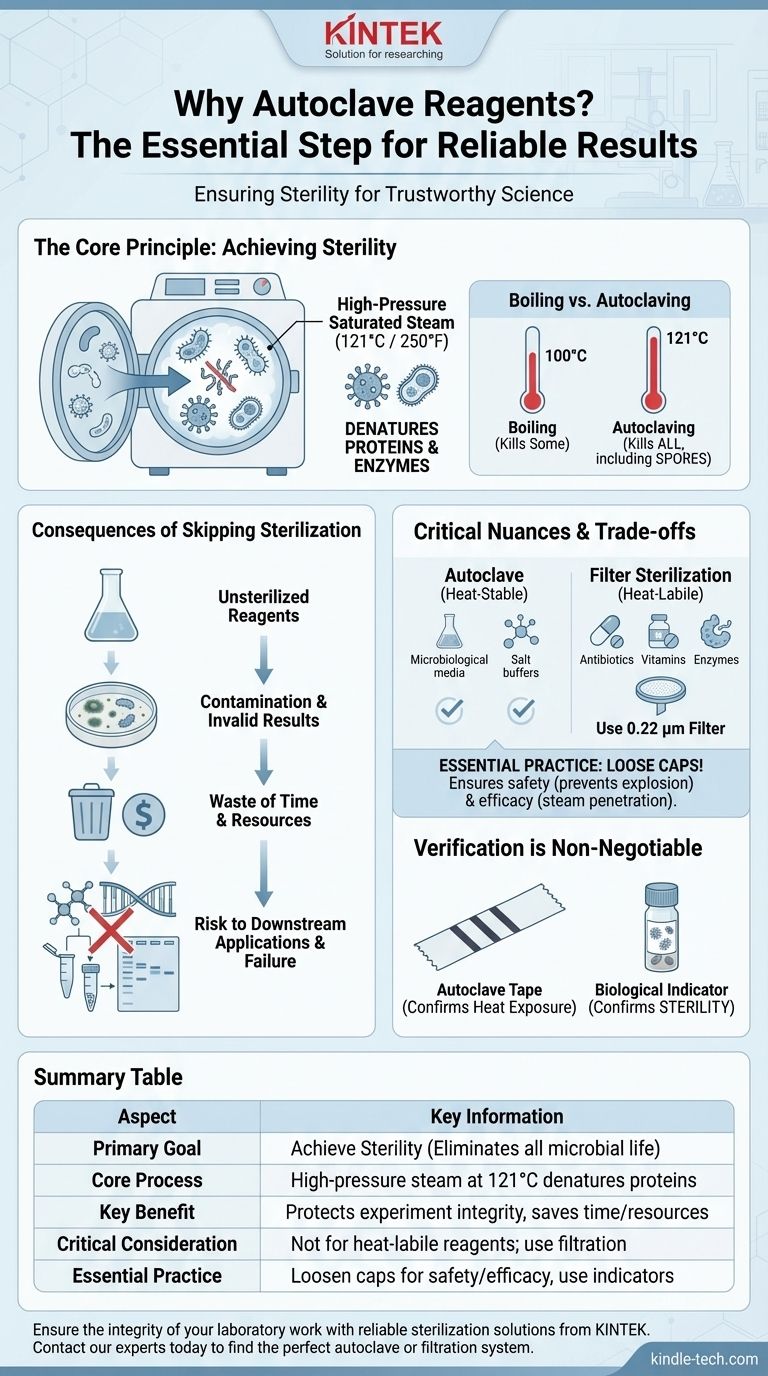
At its core, autoclaving is essential for sterilization. This process uses high-pressure saturated steam to eliminate all forms of microbial life—including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and even highly resistant spores—from reagents and equipment. Failing to do so introduces contaminants that will compromise, and likely invalidate, your experimental results.
The question isn't just about cleaning a reagent; it's about ensuring the integrity of your entire experiment. Autoclaving is the definitive step that removes unwanted microbial variables, making your scientific results reproducible and trustworthy.

The Fundamental Principle: Achieving Sterility
To understand the importance of autoclaving, you must first understand how it achieves a sterile state, a condition that other methods like simple boiling cannot guarantee.
How an Autoclave Works
An autoclave is essentially a highly controlled pressure chamber. It works by creating steam and then increasing the pressure within the chamber. This pressure allows the steam to reach temperatures far beyond the normal boiling point of water (typically 121°C or 250°F).
The combination of intense heat and moisture is exceptionally effective at denaturing essential proteins and enzymes within microorganisms, leading to their death.
Why Simple Boiling Isn't Enough
While boiling water at 100°C can kill many active bacteria, it is ineffective against bacterial endospores. These are tough, dormant structures that some bacteria form to survive harsh conditions.
The high temperatures (121°C) achieved under pressure inside an autoclave are required to reliably destroy these resilient spores, ensuring true sterilization.
The Target: Eliminating All Microbial Variables
The goal is to create a "blank slate." Unsterilized reagents, especially nutrient-rich media, are ideal environments for microbial growth. Autoclaving eliminates:
- Bacteria and Fungi: The most common sources of contamination.
- Viruses: Which can interfere with cell culture work.
- Spores: The dormant forms that can reactivate and ruin an experiment days later.
- Enzymes: Such as DNases and RNases from microbes, which can degrade precious DNA and RNA samples in molecular biology applications.
The Consequences of Skipping Sterilization
Failing to autoclave is not a minor oversight; it has direct and severe consequences for your work.
Contamination and Invalid Results
This is the most immediate outcome. If you are trying to grow a pure culture of E. coli, but your media is contaminated with fungus, you cannot trust any of your observations. The contaminant competes for nutrients and may produce compounds that affect your target organism's growth.
Waste of Time and Resources
Experiments are expensive. Reagents, consumables, and your time are valuable resources. A contaminated experiment is a failed experiment, forcing you to start over from scratch and wasting everything invested in that attempt.
Risk to Downstream Applications
Contamination in a single reagent can have a domino effect. A contaminated buffer used for DNA extraction could introduce DNases that degrade your sample. This makes subsequent steps like PCR or sequencing impossible, and you may not discover the root cause until much later.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Nuances
While essential, autoclaving is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Proper technique and knowing when not to autoclave are just as important.
Not All Reagents Can Be Autoclaved
Many essential reagents are heat-labile, meaning they are degraded or destroyed by high temperatures. Common examples include:
- Antibiotics
- Vitamins and some amino acids
- Certain buffers (e.g., Tris can have its pH altered)
- Proteins and enzymes
For these substances, filter sterilization is the appropriate alternative, where the liquid is passed through a membrane with pores small enough (typically 0.22 µm) to trap microorganisms.
The Importance of Proper Technique (Loose Caps)
As your reference notes, bottle caps must be loosened before autoclaving. This is for two critical reasons:
- Safety: A sealed bottle will build up immense pressure, creating a significant risk of explosion.
- Efficacy: A loose cap allows the pressurized steam to enter the bottle and sterilize the contents. A sealed bottle will not be properly sterilized.
Verification is Non-Negotiable
Using autoclave tape is a standard practice. The stripes on the tape darken when the target temperature is reached. However, this only confirms heat exposure, not successful sterilization.
For true validation, especially for critical applications, biological indicators containing spores of a highly heat-resistant organism (Geobacillus stearothermophilus) are used. If the spores are killed, you can be confident the cycle was successful.
Making the Right Choice for Your Reagents
Applying this knowledge correctly is key to experimental success. Use the nature of your reagent to guide your sterilization method.
- If your primary focus is preparing microbiological media or simple salt buffers: Autoclaving is the gold standard and the most reliable method for ensuring sterility.
- If your primary focus is working with heat-sensitive components like antibiotics or proteins: You must use filter sterilization to avoid destroying your critical reagents.
- If you are unsure about a reagent's stability: Always consult the manufacturer's technical data sheet or established laboratory protocols before proceeding.
Ultimately, proper sterilization is the foundation upon which reliable and reproducible scientific data is built.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Achieve sterility by eliminating all microbial life (bacteria, fungi, viruses, spores). |
| Core Process | Uses high-pressure saturated steam at 121°C (250°F) to denature microbial proteins. |
| Key Benefit | Protects the integrity of experiments, saving time and resources by preventing contamination. |
| Critical Consideration | Not for heat-labile reagents (e.g., antibiotics, enzymes); filter sterilization is required instead. |
| Essential Practice | Always loosen bottle caps for safety and efficacy, and use indicators to verify the cycle. |
Ensure the integrity of your laboratory work with reliable sterilization solutions from KINTEK.
Autoclaving is a foundational step for reproducible science, but the right equipment and technique are paramount. Whether you are preparing microbiological media, buffers, or need solutions for heat-sensitive components, KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables to meet your precise sterilization needs.
Don't let contamination compromise your results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect autoclave or filtration system for your laboratory and achieve the sterility your research demands.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the handling procedures of autoclave? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe Sterilization
- How long does autoclaving take? Mastering Sterilization Times for Your Lab
- What is gravity displacement autoclave? A Guide to Simple, Reliable Sterilization
- What role does a high-pressure hydrothermal autoclave play in 3D-GO synthesis? Optimize Your Graphene Composites
- Why are silver or platinum liners utilized in GaN synthesis? Protecting Purity and Autoclave Integrity
- Why is a High-Pressure Autoclave Needed for Nuclear Fuel Cladding Wear Tests? Ensure Safety in Reactor Simulations
- How is an autoclave utilized in antimicrobial experiments? Ensure Precise Nanoparticle Research Integrity
- When should an autoclave not be used? Avoid Damage and Hazards in Your Lab



















