In any industrial or laboratory setting, sieving is the fundamental process for ensuring material quality and consistency. It serves as the primary method for separating particles based on size, which is a critical step for accurately analyzing materials and guaranteeing the integrity of a final product.
The core purpose of sieving extends beyond simple sorting. It is a foundational quality control measure that provides the verifiable data and material consistency necessary to achieve predictable, reliable, and high-quality results in any process dependent on particle size.

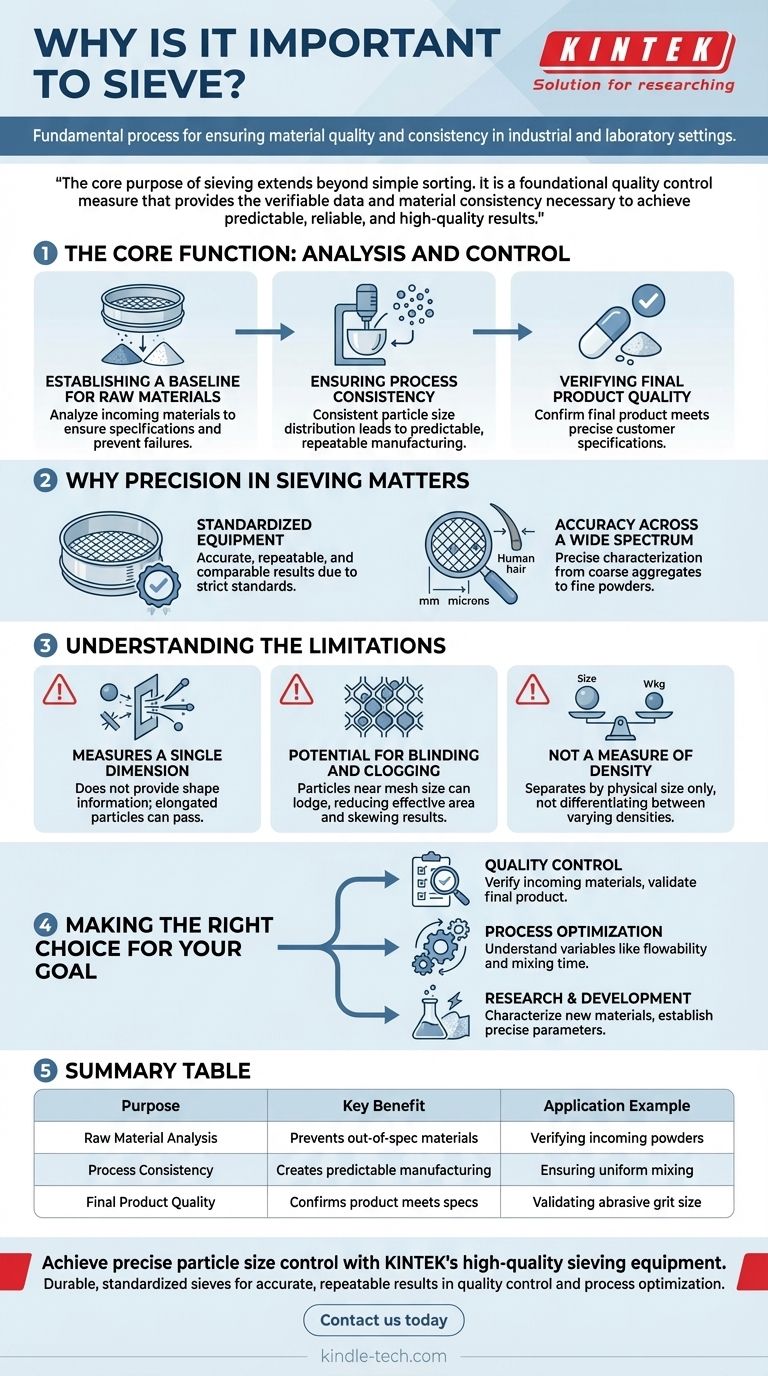
The Core Function: Analysis and Control
Sieving provides the essential function of separating a granular sample into distinct size fractions. This separation is the basis for control over materials and processes.
Establishing a Baseline for Raw Materials
Before any process begins, you must understand your ingredients. Sieving is used to analyze incoming raw materials, additives, and supplies to ensure they meet required specifications.
This initial check prevents out-of-spec materials from entering your production line, which could compromise the entire batch and lead to costly failures.
Ensuring Process Consistency
The size and distribution of particles can dramatically affect how they behave in downstream processes. This includes flow rates, mixing efficiency, reaction speeds, and compaction density.
By using sieves to ensure a consistent particle size distribution for each batch, you create a predictable and repeatable manufacturing process.
Verifying Final Product Quality
Sieving is often the final quality assurance step. It is used to confirm that a finished product—such as a powder, granule, or pellet—meets the precise size specifications required by the customer or application.
This guarantees that the product will perform as expected, whether for pharmaceutical dosages, food textures, or industrial abrasives.
Why Precision in Sieving Matters
Effective sieving relies on calibrated, high-quality equipment. This is not a rough estimation but a precise measurement technique.
The Role of Standardized Equipment
Analytical sieves are manufactured according to strict national and international standards. This ensures that results are accurate, repeatable, and comparable across different labs and production sites.
The use of durable materials like stainless steel guarantees the sieve itself does not contaminate or react with the sample, preserving the integrity of the analysis.
Accuracy Across a Wide Spectrum
Modern sieves offer an extensive range of mesh sizes, from several millimeters down to just a few dozen microns (a human hair is about 70 microns thick).
This versatility allows for precise particle characterization across a vast array of materials, from coarse aggregates to fine chemical powders.
Understanding the Limitations
While indispensable, the sieving method has inherent characteristics that are important to understand for accurate interpretation.
It Measures a Single Dimension
Sieving determines whether a particle can pass through a square or circular aperture. It does not provide information about a particle's shape.
An elongated, needle-like particle may pass through a mesh size that a spherical particle of the same mass or volume could not. This distinction is critical in applications where particle shape influences performance.
Potential for Blinding and Clogging
During the process, particles that are very close to the size of the mesh openings can become lodged in the apertures. This phenomenon, known as blinding, reduces the effective sieving area and can skew results toward a coarser distribution if not managed.
Proper sieving time and motion (tapping or vibration) are essential to minimize this effect and ensure all fine particles have an opportunity to pass through.
Not a Measure of Density
Sieving separates particles by physical size alone. It does not differentiate between particles of varying densities. Two particles of the same size but different materials and weights will be sorted into the same fraction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Sieving should be applied strategically based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is Quality Control: Sieving is your non-negotiable tool to verify incoming raw materials and validate that your final product meets specifications.
- If your primary focus is Process Optimization: Use particle size distribution data from sieving to understand and control variables like flowability, mixing time, and reaction rates.
- If your primary focus is Research & Development: Sieving is essential for characterizing new materials and establishing the precise particle size parameters required for successful formulation and production.
Ultimately, proper sieving transforms the unknown variable of particle size into a known constant, giving you direct control over your process and final outcome.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Benefit | Application Example |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Analysis | Prevents out-of-spec materials from entering production | Verifying incoming powders for pharmaceuticals |
| Process Consistency | Creates predictable and repeatable manufacturing | Ensuring uniform mixing in food production |
| Final Product Quality | Confirms product meets precise size specifications | Validating abrasive grit size for industrial use |
Achieve precise particle size control with KINTEK's high-quality sieving equipment.
As a leading supplier of laboratory equipment and consumables, KINTEK provides durable, standardized sieves that deliver accurate and repeatable results for your quality control and process optimization needs. Whether you're in pharmaceuticals, food production, or materials science, our sieves help you maintain material consistency and ensure final product integrity.
Contact us today to discuss your sieving requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- Why is a standardized sieving system necessary for elephant grass research? Ensure Reliable Sample Consistency
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results



















