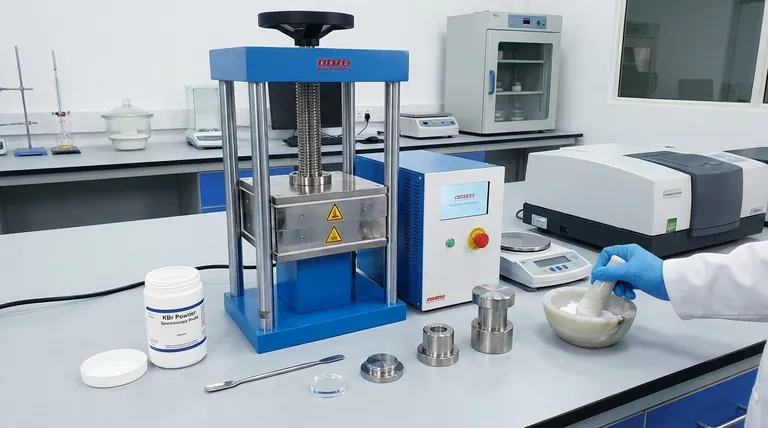
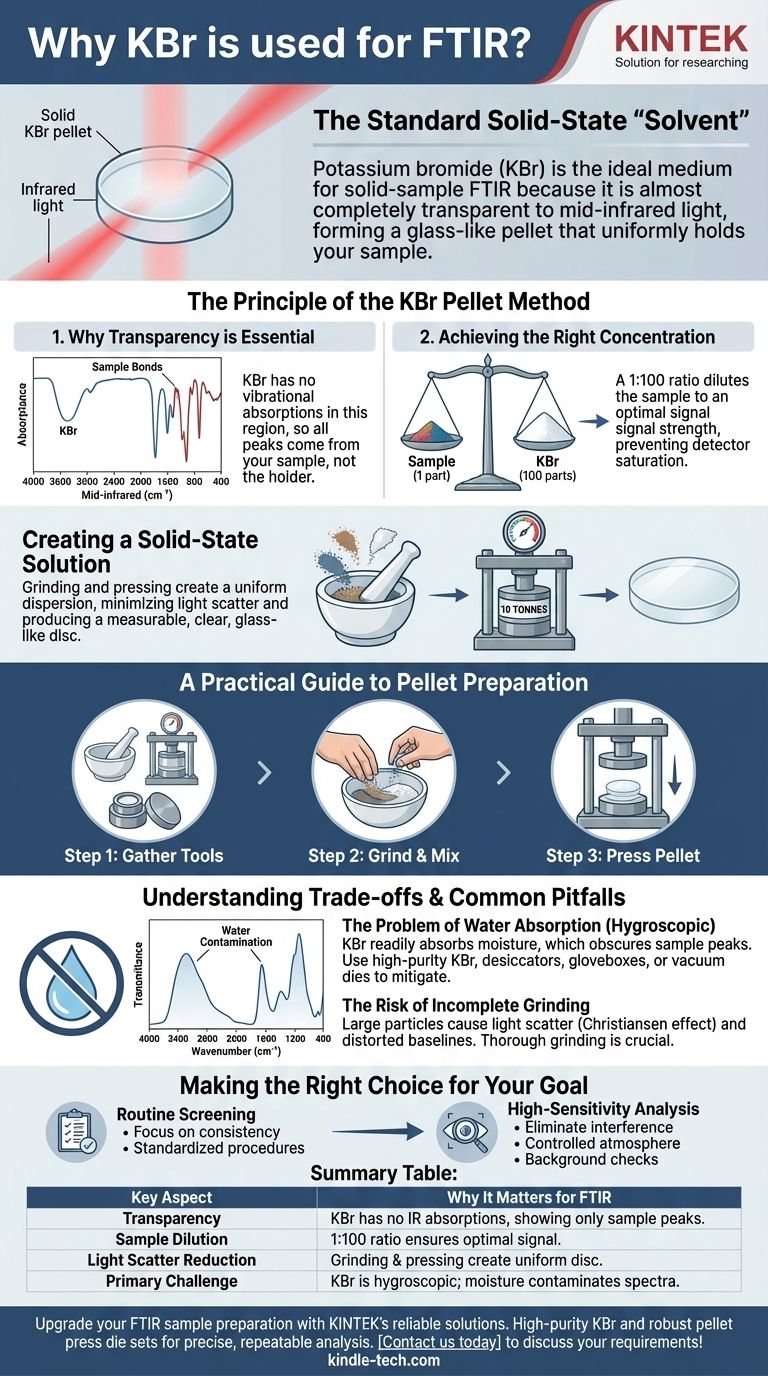
Potassium bromide (KBr) is the standard for solid-sample FTIR analysis for one primary reason: it is almost completely transparent to infrared light. This property allows it to act as an ideal solid-state "solvent," forming a pellet that holds your sample at the perfect dilution for measurement without interfering with the spectrum itself.
The core challenge of solid-state FTIR is not just holding the sample, but preparing it in a way that allows light to pass through uniformly. KBr solves this by creating a transparent matrix that disperses the sample, turning an opaque powder into a measurable, glass-like disc.

The Principle of the KBr Pellet Method
To get reliable data, your sample must be prepared in a non-absorbing matrix that allows infrared light to pass through it. The KBr pellet is the classic solution to this problem for solid samples.
Why Transparency is Essential
The goal of FTIR is to measure the light absorbed specifically by your sample's molecular bonds. KBr is used because it has no vibrational absorptions in the mid-infrared region (4000 cm⁻¹ to 400 cm⁻¹), which is the area of interest for most organic and inorganic analyses.
This means any absorption peaks you see in the final spectrum come from your sample, not the KBr holding it.
Achieving the Right Concentration
An FTIR signal must be strong enough to detect but not so strong that it completely blocks the light and saturates the detector.
Mixing a small amount of sample with a large amount of KBr—typically a 1:100 ratio—dilutes the sample perfectly. This ensures the resulting absorption bands are within the instrument's optimal detection range.
Creating a Solid-State Solution
Simply placing a solid powder in the beam path would scatter most of the light, producing unusable data.
By grinding the sample intimately with KBr powder and pressing it under high pressure, you create a uniform dispersion. The KBr forms a crystalline lattice that holds the finely-milled sample particles in place, minimizing light scatter and creating a clear, solid medium.
A Practical Guide to Pellet Preparation
The quality of your KBr pellet directly determines the quality of your spectrum. The process requires care and the right equipment.
Gathering the Right Tools
To prepare a high-quality pellet, you will need a hydraulic press and a pellet press die set.
You also need a pestle and mortar to grind the sample and KBr together. An agate mortar is highly recommended as it is non-porous and minimizes contamination.
The Grinding and Mixing Process
Weigh out your KBr and sample to achieve the desired 1:100 ratio (e.g., 1-2 mg of sample and 100-200 mg of KBr).
Grind them together thoroughly in the mortar until the mixture is a fine, homogenous powder. This step is critical for ensuring the sample is evenly dispersed throughout the pellet.
Pressing the Pellet
Place the mixture into the pellet die and apply pressure using a hydraulic press. A common rule of thumb is to apply a load of 10 tonnes for a standard 13 mm diameter die.
The goal is to produce a solid, clear, glass-like disc. A cloudy or cracked pellet indicates poor grinding, insufficient pressure, or moisture contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
While KBr is the industry standard, it is not without its challenges. Understanding its primary weakness is key to generating good data.
The Problem of Water Absorption
The single biggest issue with KBr is that it is hygroscopic—it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere.
Water has very strong, broad absorption bands in the infrared spectrum (around 3400 cm⁻¹ and 1640 cm⁻¹). If your KBr is "wet," these water peaks can obscure important features of your sample's spectrum.
Mitigating Moisture Contamination
Always use high-purity, spectroscopy-grade KBr and store it in a desiccator.
In humid environments, preparation should be done quickly. For sensitive measurements, grinding and pressing inside a glovebox with a dry atmosphere or using a specialized vacuum die is the best practice to eliminate water contamination.
The Risk of Incomplete Grinding
If sample particles are too large, they will scatter infrared light rather than absorb it. This phenomenon, known as the Christiansen effect, results in a distorted, sloping baseline and can make your spectral peaks difficult to interpret accurately.
Thorough grinding is the only way to prevent this and ensure a clean, flat baseline.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your preparation technique should be tailored to your analytical needs and laboratory environment.
- If your primary focus is routine screening: Focus on consistency. Use a pre-set sample-to-KBr ratio and a standardized grinding and pressing procedure to ensure your results are comparable from day to day.
- If your primary focus is high-sensitivity or quantitative analysis: Prioritize eliminating all interference. Prepare pellets in a controlled atmosphere (glovebox) and always run a background spectrum of a pure KBr pellet to check for water or other contaminants.
- If you are seeing broad, unwanted peaks around 3400 cm⁻¹ and 1640 cm⁻¹: Your pellet is contaminated with water. You must dry your KBr powder or improve your atmospheric controls during preparation.
By treating the KBr pellet not as a holder but as a critical optical component, you gain direct control over the quality and reliability of your spectral data.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Why It Matters for FTIR |
|---|---|
| Transparency | KBr has no IR absorptions, so spectrum shows only sample peaks. |
| Sample Dilution | 1:100 ratio ensures optimal signal strength for detection. |
| Light Scatter Reduction | Grinding and pressing create a uniform, glass-like disc. |
| Primary Challenge | KBr is hygroscopic; moisture can contaminate spectra. |
Upgrade your FTIR sample preparation with KINTEK's reliable solutions.
Struggling with inconsistent pellets or water contamination in your spectra? KINTEK specializes in high-purity spectroscopy-grade KBr and robust pellet press die sets designed for precise, repeatable FTIR analysis. Our equipment helps you achieve clear, glass-like pellets with minimal moisture interference, ensuring your data is accurate and reliable.
Whether you're performing routine screening or high-sensitivity quantitative analysis, KINTEK provides the lab equipment and consumables to meet your laboratory's needs.
Contact us today to discuss your FTIR requirements and discover how our products can enhance your analytical results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a laboratory drying oven in biomass pretreatment? Ensure Precise Analysis for Cassava & Maize
- What is the process of sputter coater? Achieve Superior Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What are the limitations of diamonds? Beyond the Myth of Perfection
- What is an alternative to a rotary vacuum evaporator? Find the Right Evaporation Technology for Your Lab
- Are biofuels cheaper to produce than fossil fuels? The True Cost of Green Energy Explained
- What tool is used for casting? The Essential Equipment for Metal Casting Explained
- What is the temperature of heat treatment? It Depends on Your Metal and Desired Properties
- What are the liquid products of pyrolysis? The Ultimate Guide to Bio-Oil Production



















