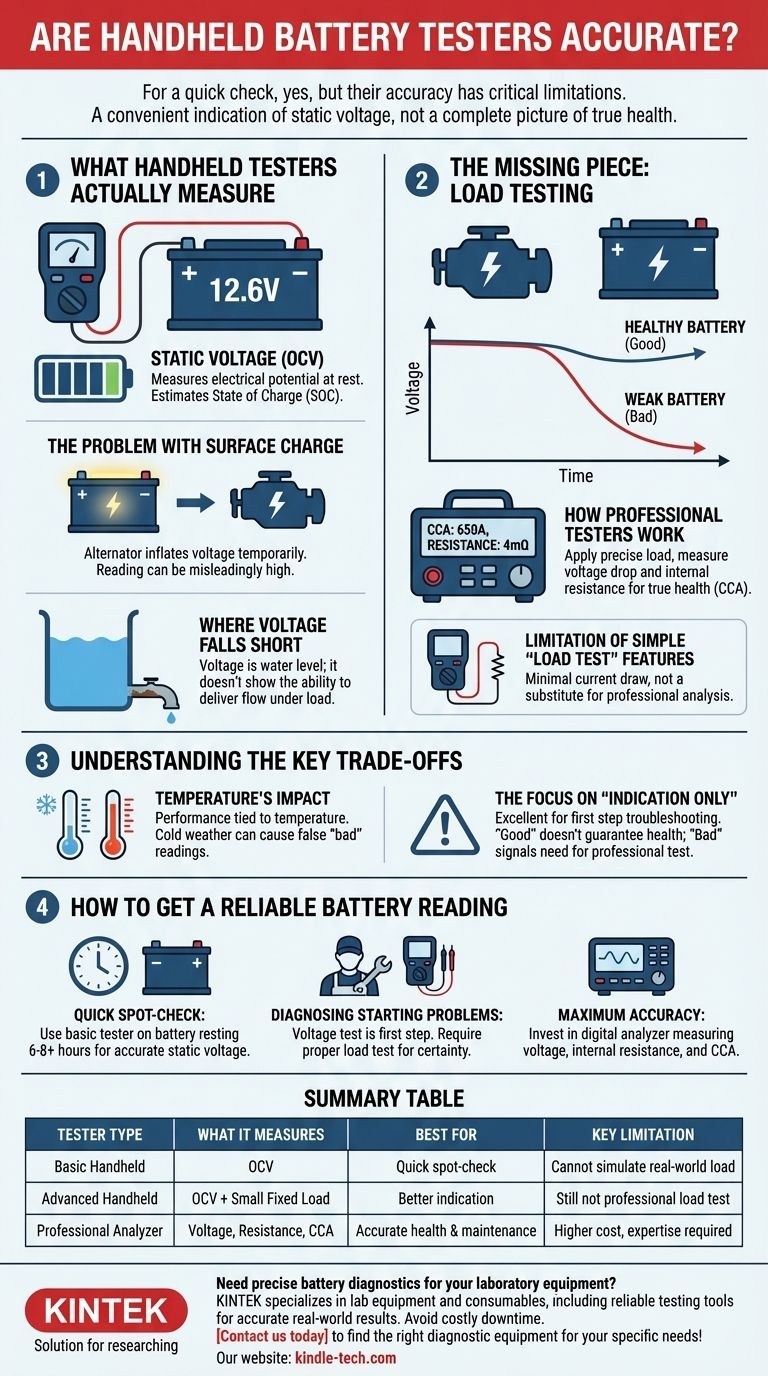
For a quick check, yes, but their accuracy has critical limitations. A handheld battery tester is designed to give you a fast, convenient indication of a battery's static voltage. While this is useful, it does not provide a complete picture of the battery's true health or its ability to perform under real-world conditions.
A handheld tester measures a battery's surface voltage, which is only one piece of the diagnostic puzzle. True battery health is determined by its ability to deliver sufficient current under load, a factor that most basic testers cannot accurately assess.

What Handheld Testers Actually Measure
The Concept of Static Voltage
Most simple, handheld battery testers measure Open-Circuit Voltage (OCV). This is the electrical potential of the battery when it is at rest and not connected to any significant load.
This reading is then used to estimate the battery's State of Charge (SOC). For example, a 12-volt lead-acid battery showing 12.6V or higher is considered fully charged, while 12.2V indicates it's at roughly 50%.
The Problem with Surface Charge
A battery's voltage can be misleading immediately after the engine has been running. The alternator creates a surface charge on the battery's internal plates, which can inflate the voltage reading for several hours.
A tester might read a "healthy" 12.7V on a battery with a high surface charge, but its true resting voltage could be much lower.
Where Voltage Falls Short
Voltage tells you how "full" the battery is, but it tells you nothing about its ability to deliver power.
Think of it like a water tank. Voltage is the water level, but it doesn't tell you the condition of the pipe at the bottom. A weak, aging battery is like a tank with a corroded and clogged pipe—the water level might be high, but it can't deliver a strong flow when you need it.
The Missing Piece: Load Testing
Why Load is Crucial
The single most important test of a car battery's health is its performance under load. This simulates the intense demand of an engine's starter motor.
A healthy battery's voltage will dip when a load is applied but will remain well within an acceptable range. A weak battery's voltage will plummet because its high internal resistance prevents it from delivering the required current.
How Professional Testers Work
Professional-grade diagnostic tools, often called electronic battery analyzers, do more than check voltage. They apply a precise, simulated load to the battery.
These devices measure the voltage drop along with the battery's internal resistance. This combination provides a definitive assessment of its Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) capability and overall health.
The Limitation of Simple "Load Test" Features
Some more advanced handheld testers include a "load test" function. However, this is typically a very small, fixed resistor that draws minimal current.
While this is better than a voltage-only test, it is not a substitute for the comprehensive analysis performed by a professional-grade tool.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Temperature's Impact
Battery performance is directly tied to temperature. A battery tested on a cold morning will show a lower voltage and deliver less power than the same battery tested on a warm afternoon.
Most basic testers do not account for ambient temperature, which can easily lead to a false "bad" reading in cold weather.
The Focus on "Indication Only"
As noted in professional guidance, these devices are best used for indication only. They are an excellent first step in troubleshooting.
A "good" reading is a positive sign, but it doesn't guarantee the battery is fine. A "bad" or "borderline" reading is a strong signal that you need a more thorough, professional test before replacing the battery.
How to Get a Reliable Battery Reading
To get the most value from any battery test and avoid a misdiagnosis, match your tool and method to your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is a quick spot-check: Use a basic handheld tester on a battery that has been resting for at least 6-8 hours to get a more accurate static voltage reading, free from surface charge.
- If your primary focus is diagnosing a starting problem: A voltage test is a good first step, but a "good" reading does not rule out the battery. You need a proper load test from a mechanic or a dedicated load tester to be certain.
- If your primary focus is maximum accuracy and preventative maintenance: Invest in a digital battery analyzer that measures not just voltage but also internal resistance and estimated Cold Cranking Amps (CCA).
Trusting your handheld tester for what it is—a helpful indicator, not a final verdict—is the key to making an informed decision.
Summary Table:
| Tester Type | What It Measures | Best For | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Handheld | Open-Circuit Voltage (OCV) | Quick spot-check of charge level | Cannot simulate real-world load conditions |
| Advanced Handheld | OCV + small fixed load | Better indication than voltage-only | Still not a substitute for professional load testing |
| Professional Analyzer | Voltage, internal resistance, CCA | Accurate health assessment and preventative maintenance | Higher cost, requires expertise |
Need precise battery diagnostics for your laboratory equipment? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including reliable testing tools that deliver accurate results under real-world conditions. Our solutions help laboratories maintain peak performance and avoid costly downtime. Contact us today to find the right diagnostic equipment for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Button Battery Case for Battery Lab Applications
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
People Also Ask
- Is there a way to test lithium batteries? Understand Voltage vs. True Health
- What is the function of CR2032 coin cell cases in the evaluation of LSLBO electrolyte? Optimize Battery Test Results
- What function does a CR2032 button cell case serve in testing solid-state sodium batteries? Optimize Your Lab Results
- How do you test a lithium battery to see if it's good? A Guide to Measuring Voltage, Capacity & Health
- What is the function of a 2032-type coin cell case in solid-state battery testing? Optimize Interfacial Connectivity



















