Yes, biomass is a well-established and versatile renewable source for producing energy. This process, known as bioenergy, involves converting organic materials—such as wood, agricultural crops, and waste—into heat, electricity, or liquid fuels. The method of conversion and the source of the biomass are critical factors that determine its efficiency and environmental impact.
While biomass is a viable renewable energy source, its practical effectiveness is not a simple matter. The choice of conversion technology and the sustainability of the biomass supply chain are what truly define its value and environmental footprint.
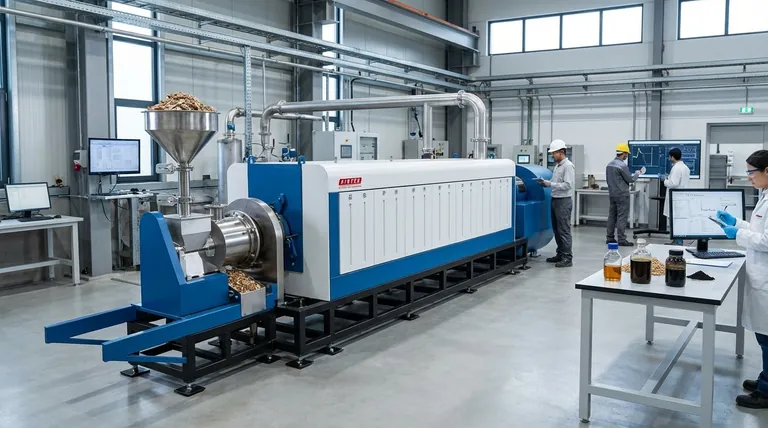

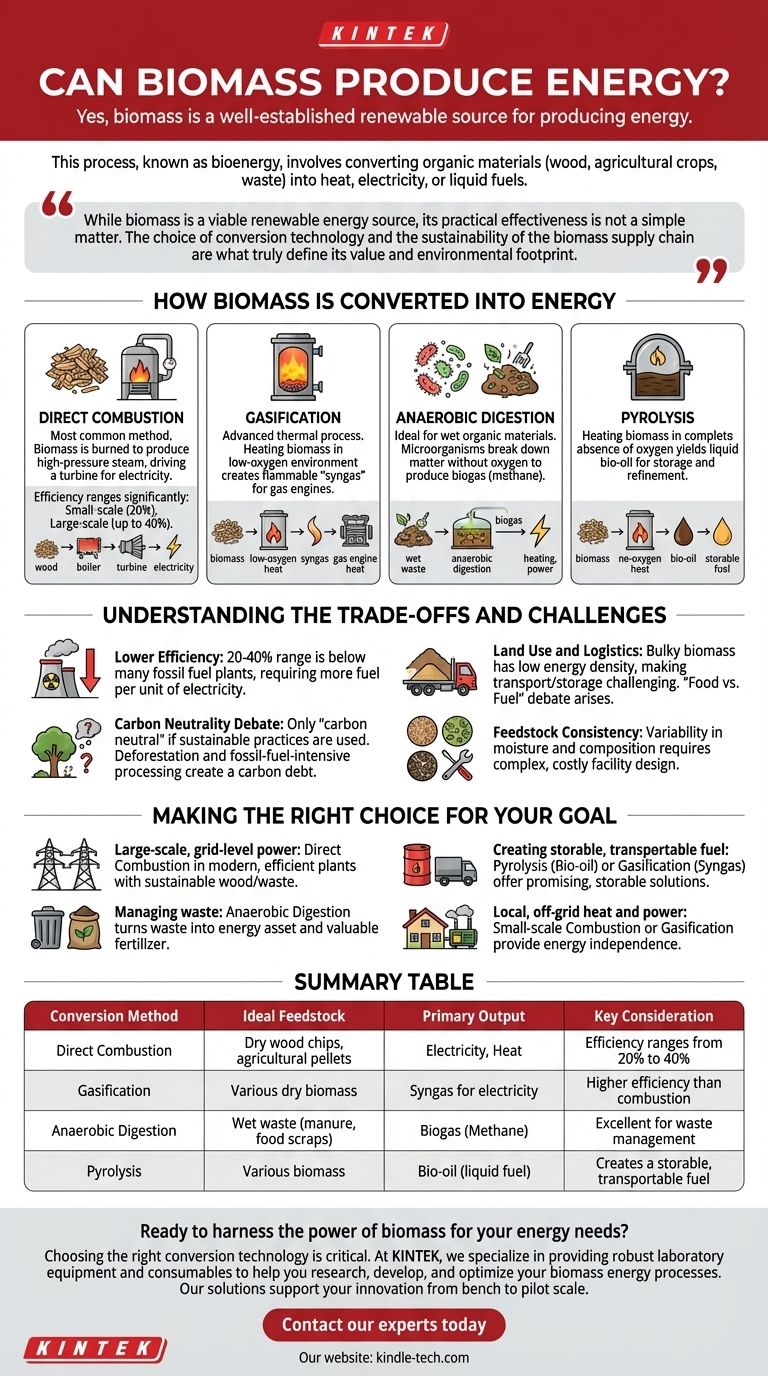
How Biomass Is Converted into Energy
The term "bioenergy" covers several distinct technological pathways. The most appropriate method depends on the type of biomass available and the desired energy output.
Direct Combustion
This is the most common and straightforward method. Biomass, typically dry material like wood chips or agricultural pellets, is burned in a boiler to produce high-pressure steam. This steam then drives a turbine connected to a generator to produce electricity.
The efficiency of direct combustion varies significantly. As noted, small-scale operations might only achieve 20% efficiency, while large, modern power plants can reach up to 40%. This means for every 100 units of energy stored in the biomass, only 20 to 40 units are converted into usable electricity.
Gasification
Gasification is a more advanced thermal process. It involves heating biomass in a low-oxygen environment, which converts it into a flammable gas mixture called "syngas." This syngas can then be burned in a gas engine or turbine to generate electricity with higher efficiency than direct combustion.
Anaerobic Digestion
This biological process is ideal for wet organic materials like animal manure, food scraps, and sewage sludge. Microorganisms break down the organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas—a mixture primarily composed of methane. This biogas can be used for heating or to run a generator for electricity.
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis involves heating biomass in the complete absence of oxygen. This process yields a liquid fuel known as bio-oil or pyrolysis oil. This oil can be stored, transported, and later refined or burned in a furnace or engine to generate heat or power.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While renewable, biomass energy is not without its complexities. A clear understanding of its limitations is crucial for any practical application.
The Reality of Conversion Efficiency
The 20-40% efficiency range for combustion places biomass power generation below many fossil fuel plants, which can exceed 60% efficiency with combined-cycle technology. This lower efficiency means more fuel is required per unit of electricity produced, which has implications for logistics, land use, and cost.
The Carbon Neutrality Debate
Biomass is often called "carbon neutral" because the carbon dioxide released during combustion is theoretically offset by the CO2 absorbed by the plants as they grew. However, this is a simplification.
If forests are clear-cut and not replanted, or if the transportation and processing of biomass are fossil-fuel-intensive, the overall process may not be carbon neutral. There is a "carbon debt" created when mature trees are harvested for energy, as it can take decades for new trees to re-absorb that same amount of carbon.
Land Use and Logistics
Biomass is bulky and has a lower energy density than fossil fuels, making transportation and storage a significant logistical and financial challenge. Furthermore, growing dedicated energy crops can compete with land needed for food production, a conflict often referred to as the "food vs. fuel" debate.
Feedstock Consistency
The moisture content, density, and chemical composition of biomass can vary widely. Power facilities must be designed to handle this variability, which adds complexity and cost compared to the highly consistent nature of natural gas or coal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use biomass for energy must be aligned with a specific objective, as no single approach fits all scenarios.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, grid-level power: Direct combustion in a modern, efficient plant using sustainably sourced wood residues or agricultural waste is the most proven path.
- If your primary focus is managing agricultural or municipal waste: Anaerobic digestion is an excellent solution to convert a waste liability into an energy asset, reducing landfill use and producing valuable fertilizer.
- If your primary focus is creating a storable, transportable fuel: Pyrolysis to produce bio-oil or gasification to produce syngas are promising technologies, though they often require higher initial investment.
- If your primary focus is local, off-grid heat and power: Small-scale combustion or gasification systems can provide energy independence, especially in rural areas with abundant agricultural or forest resources.
Ultimately, harnessing biomass effectively is about matching the right organic material with the right conversion technology to meet a specific energy need.
Summary Table:
| Conversion Method | Ideal Feedstock | Primary Output | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Combustion | Dry wood chips, agricultural pellets | Electricity, Heat | Efficiency ranges from 20% to 40% |
| Gasification | Various dry biomass | Syngas for electricity | Higher efficiency than combustion |
| Anaerobic Digestion | Wet waste (manure, food scraps) | Biogas (Methane) | Excellent for waste management |
| Pyrolysis | Various biomass | Bio-oil (liquid fuel) | Creates a storable, transportable fuel |
Ready to harness the power of biomass for your energy needs?
Choosing the right conversion technology is critical for efficiency and sustainability. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables to help you research, develop, and optimize your biomass energy processes. Whether you're exploring pyrolysis, gasification, or combustion, our solutions support your innovation from bench to pilot scale.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can equip your lab for success. Let's turn your organic materials into a valuable energy source together.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds



















