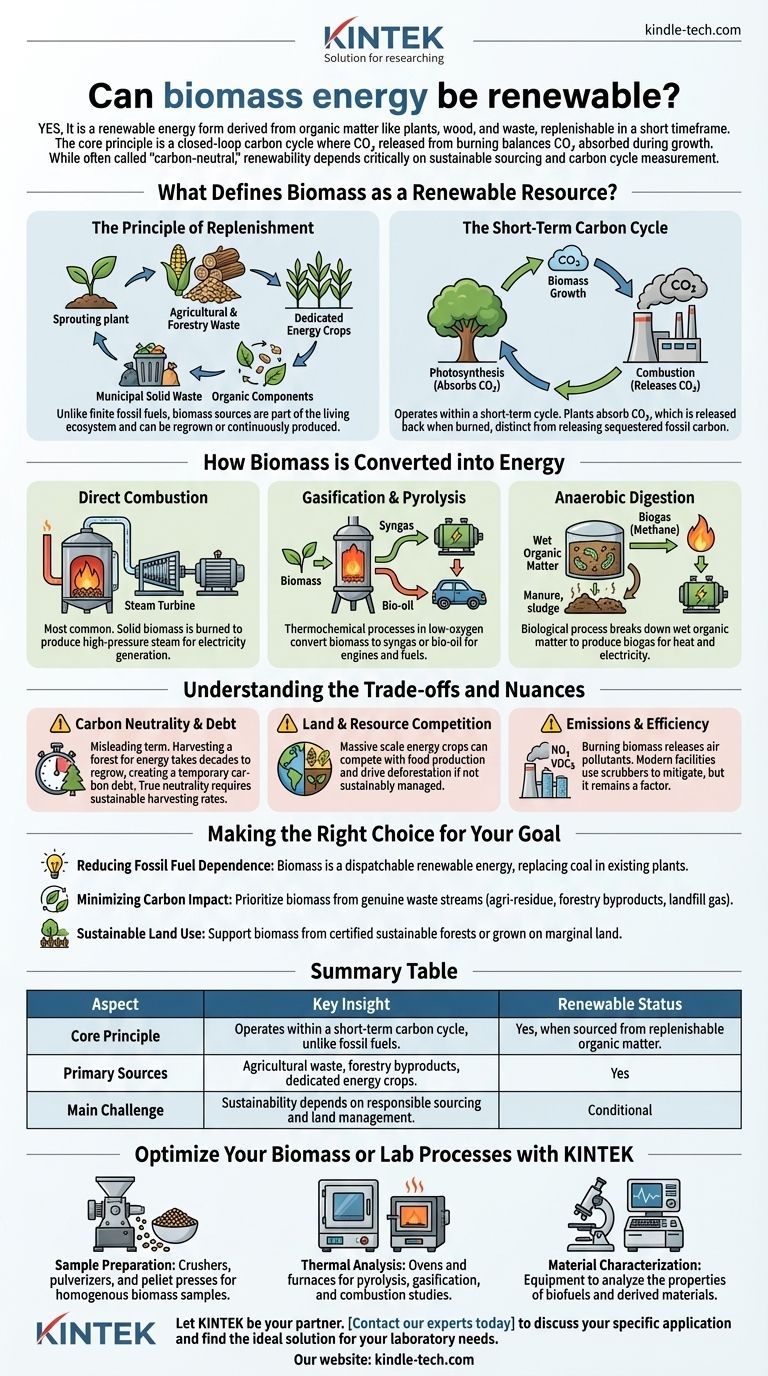
Yes, biomass energy is a form of renewable energy. It is classified as renewable because it is derived from organic matter, such as plants, wood, and waste, which can be regrown or replaced in a relatively short time frame. The core principle is that the carbon dioxide released when biomass is burned is balanced by the carbon dioxide absorbed by the plants during their growth, creating a closed-loop carbon cycle.
While often called "carbon-neutral," the true renewability of biomass energy is not absolute. It is critically dependent on the sustainability of its sourcing and the timescale over which the carbon cycle is measured.
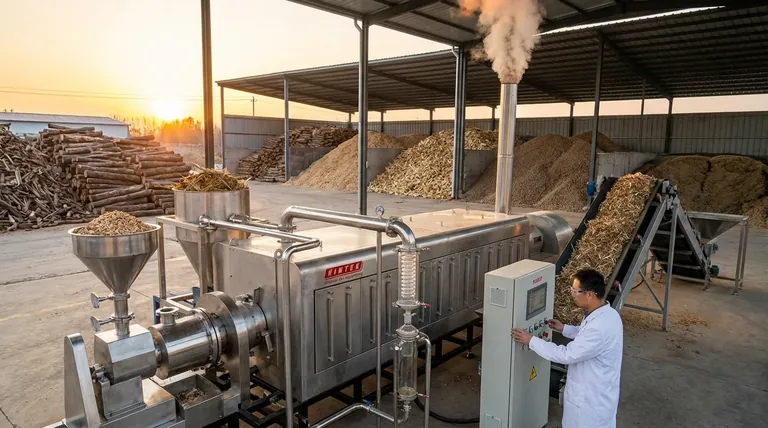

What Defines Biomass as a Renewable Resource?
The renewable status of biomass hinges on two core concepts: the ability to replenish the source material and the nature of its carbon cycle. This is what fundamentally separates it from fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas.
The Principle of Replenishment
Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and take millions of years to form, biomass sources are part of the living ecosystem. They can be regrown, cultivated, or are continuously produced as byproducts of human activity.
The main sources include agricultural and forestry waste, such as corn husks or sawdust, dedicated energy crops like switchgrass, and even the organic components of municipal solid waste.
The Short-Term Carbon Cycle
Biomass energy operates within a short-term carbon cycle. Plants absorb CO₂ from the atmosphere through photosynthesis as they grow. When this biomass is converted into energy, that same amount of CO₂ is released back into the atmosphere.
This process is fundamentally different from burning fossil fuels, which releases vast quantities of carbon that were sequestered underground millions of years ago, adding new carbon to the active atmospheric cycle.
How Biomass is Converted into Energy
Biomass is a versatile fuel that can be converted into usable energy through several methods. The chosen method depends on the type of biomass and the desired energy output.
Direct Combustion
This is the most common method. Solid biomass, such as wood chips or agricultural waste, is burned in a boiler to produce high-pressure steam. This steam then drives a turbine connected to a generator to produce electricity.
Gasification and Pyrolysis
These are thermochemical processes that heat biomass in low-oxygen environments. Instead of burning completely, the organic material converts into a synthesis gas (syngas) or bio-oil, which can then be used to power engines, generators, or be refined into transportation fuels.
Anaerobic Digestion
This biological process uses microorganisms to break down wet organic matter, like manure or sewage sludge, in the absence of oxygen. It produces a biogas (mostly methane) that can be burned to generate heat and electricity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
While renewable, biomass is not a perfect energy source. Its environmental benefit is highly conditional, and overlooking the trade-offs gives an incomplete picture.
The Question of "Carbon Neutrality"
The term "carbon-neutral" can be misleading. If a 50-year-old forest is clear-cut and burned for energy, it will take 50 years for a new forest to re-absorb that same amount of carbon. During that time, a significant "carbon debt" exists in the atmosphere.
True carbon neutrality is only achieved when the rate of biomass harvesting does not exceed the rate of regrowth. Using waste products that would decompose and release carbon anyway is the most beneficial approach.
Land and Resource Competition
Growing dedicated energy crops on a massive scale raises significant concerns. It can compete with land needed for food production, potentially impacting food prices and security. It can also drive deforestation or the conversion of natural habitats if not managed with strict sustainability guidelines.
Emissions and Efficiency
Burning biomass is not without emissions. It can release nitrogen oxides, volatile organic compounds, and particulate matter, which are air pollutants. While modern facilities use scrubbers and filters to mitigate this, it remains a factor to consider.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating biomass requires understanding its context. The "best" application depends entirely on the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is reducing fossil fuel dependence: Biomass is a valuable, dispatchable (on-demand) renewable energy source that can replace coal in existing power plants.
- If your primary focus is minimizing carbon impact: Prioritize biomass derived from genuine waste streams, such as agricultural residue, forestry byproducts, or landfill gas.
- If your primary focus is sustainable land use: Support policies that ensure biomass is sourced from certified sustainable forests or grown on marginal land not suitable for food crops.
Ultimately, the renewable credential of biomass is determined by how responsibly it is sourced, managed, and converted.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Renewable Status | Yes, when sourced from replenishable organic matter. |
| Core Principle | Operates within a short-term carbon cycle, unlike fossil fuels. |
| Primary Sources | Agricultural waste, forestry byproducts, dedicated energy crops. |
| Main Challenge | Sustainability depends on responsible sourcing and land management. |
Optimize Your Biomass or Lab Processes with KINTEK
Navigating the complexities of sustainable energy or precise material analysis requires reliable equipment. Whether you are researching biofuel conversion, characterizing biomass feedstocks, or developing new sustainable materials, KINTEK's high-quality lab equipment is engineered for accuracy and durability.
We provide solutions for:
- Sample Preparation: Crushers, pulverizers, and pellet presses for homogenous biomass samples.
- Thermal Analysis: Ovens and furnaces for pyrolysis, gasification, and combustion studies.
- Material Characterization: Equipment to analyze the properties of biofuels and derived materials.
Let KINTEK be your partner in achieving precise and reproducible results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the ideal solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products



















