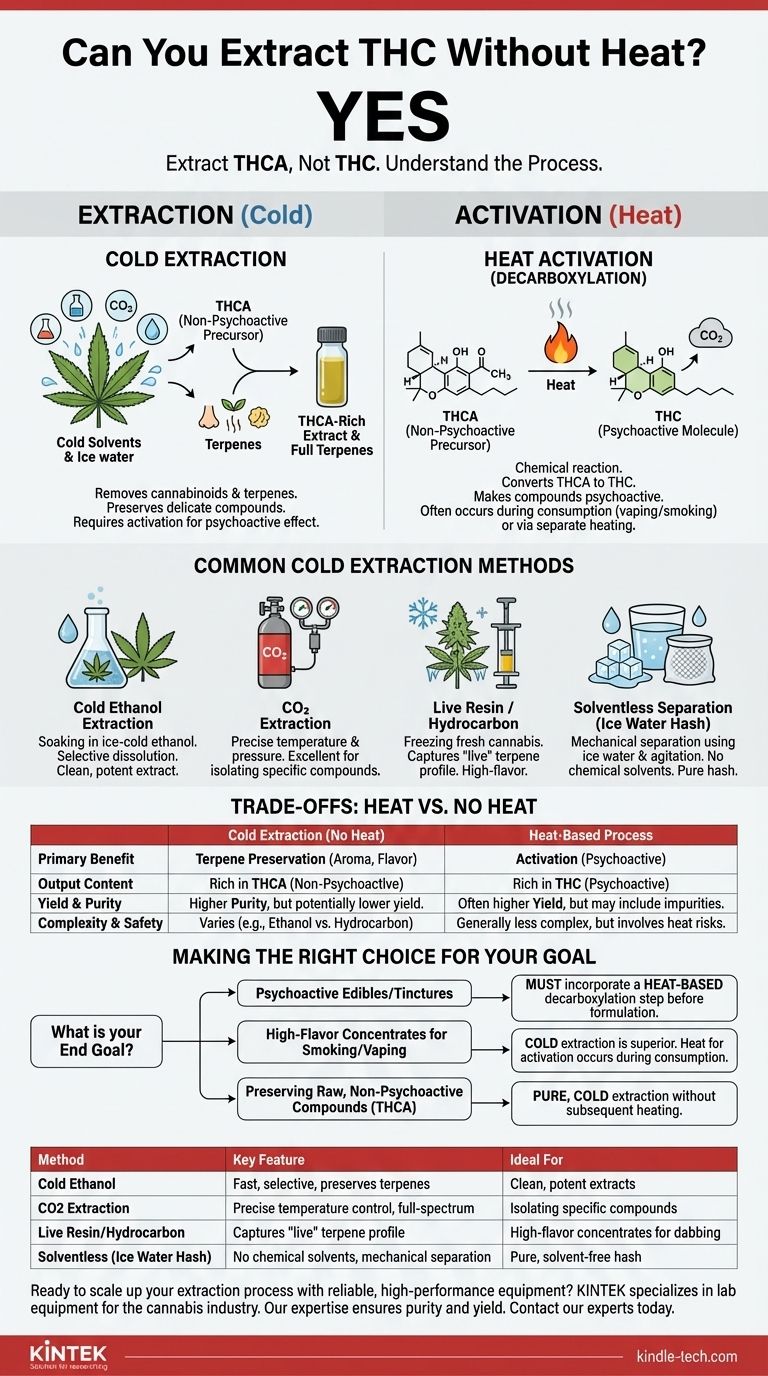
Yes, you can absolutely extract cannabinoids like THC from cannabis without using heat. In fact, many of the most advanced and high-quality extraction methods are performed at cold temperatures. However, it is critical to understand the difference between extracting a compound and activating it. Without heat, you are extracting THCA, the non-psychoactive precursor to the THC molecule.
The core principle to grasp is this: Extraction is the process of removing cannabinoids from the plant, while activation (decarboxylation) is the chemical reaction required to make them psychoactive. Cold extraction methods excel at preserving the plant's full profile, but the resulting product must still be heated later to achieve the desired effect.

Understanding the Core Chemistry: Extraction vs. Activation
To make an informed decision, you must first understand the two distinct processes at play. They are not interchangeable.
What is Extraction?
Extraction is essentially a washing process. A solvent (like ethanol, CO2, or butane) is used to dissolve the desirable compounds—cannabinoids and terpenes—from the cannabis plant material, separating them from the lipids, waxes, and cellulose.
The goal of extraction is to create a concentrated form of the plant's essential oils. This can be done at a wide range of temperatures.
The Critical Step: Decarboxylation
Raw cannabis does not contain significant amounts of psychoactive THC. Instead, it contains THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid), a non-psychoactive molecule with its own potential therapeutic benefits.
To become psychoactive, THCA must lose a carboxyl acid group (COOH). This chemical reaction is called decarboxylation, and it is triggered by heat. When you smoke or vaporize cannabis, you are performing decarboxylation instantly.
Common Methods for Cold Extraction
Cold extraction techniques are favored for their ability to preserve the most delicate compounds in the plant, particularly terpenes, which are responsible for the aroma and flavor of the final product.
Cold Ethanol Extraction
This method involves soaking cannabis in ice-cold ethanol for a very short period. The cold temperature makes the ethanol more selective, allowing it to dissolve cannabinoids and terpenes while leaving behind undesirable compounds like chlorophyll and waxes. The result is a clean, potent extract.
CO2 Extraction
Supercritical or subcritical CO2 extraction uses carbon dioxide under specific temperature and pressure to act as a solvent. Because the temperature can be precisely controlled and kept low, this method is excellent for isolating specific compounds and preserving the full spectrum of terpenes.
Live Resin/Hydrocarbon Extraction
"Live resin" is a prime example of cold extraction. It's made by freezing freshly harvested cannabis plants and then extracting them with a solvent like butane or propane at very low temperatures. This process captures the "live" terpene profile of the plant, which would otherwise be lost during drying and curing.
Solventless Separation
Methods like making ice water hash are not technically solvent-based extractions but are a form of cold mechanical separation. Agitating cannabis in ice water causes the cannabinoid-rich trichome heads to break off and be filtered through a series of mesh bags, resulting in a product called hash or bubble hash. This requires no chemical solvents at all.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Heat vs. No Heat
Choosing between a hot or cold process depends entirely on your end goal. Each approach comes with significant trade-offs.
Benefit of Cold Extraction: Terpene Preservation
This is the primary advantage of avoiding heat. Terpenes are highly volatile and begin to evaporate at relatively low temperatures. Cold extraction produces a concentrate that is far more aromatic, flavorful, and representative of the original plant.
The Decarboxylation Dilemma
The main "downside" of cold extraction is that the final product is rich in THCA, not THC. If you were to eat this extract, you would not experience a psychoactive effect. The psychoactivity is only "unlocked" when the extract is heated through dabbing, vaping, or smoking.
Yield and Purity
Heat can sometimes increase the total yield of an extraction by helping to break down cell walls. However, it often comes at the cost of purity, pulling in more fats, lipids, and chlorophyll. Modern cold techniques are highly efficient and prized for the purity they can achieve.
Safety and Complexity
Cold ethanol and solventless methods are relatively safe for at-home experimentation. However, hydrocarbon and CO2 extractions are industrial processes that require closed-loop systems, specialized equipment, and expert knowledge to manage the risks of flammable solvents or high pressures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision to use heat should be dictated by the intended use of the final product.
- If your primary focus is creating psychoactive edibles or tinctures: You must incorporate a heat-based decarboxylation step at some point before final formulation.
- If your primary focus is producing high-flavor concentrates for smoking or vaping: Cold extraction is the superior method, as the final act of consumption provides the necessary heat for activation.
- If your primary focus is preserving the raw, non-psychoactive compounds like THCA: A pure, cold extraction without any subsequent heating is precisely what you need.
Understanding this fundamental chemistry empowers you to create a product that is perfectly tailored to your specific objective.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Cold Ethanol | Fast, selective, preserves terpenes | Clean, potent extracts |
| CO2 Extraction | Precise temperature control, full-spectrum | Isolating specific compounds |
| Live Resin/Hydrocarbon | Captures "live" terpene profile | High-flavor concentrates for dabbing |
| Solventless (Ice Water Hash) | No chemical solvents, mechanical separation | Pure, solvent-free hash |
Ready to scale up your extraction process with reliable, high-performance equipment? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for the cannabis industry, from benchtop extractors to full-scale production systems. Our expertise ensures you get the purity and yield you need. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods



















