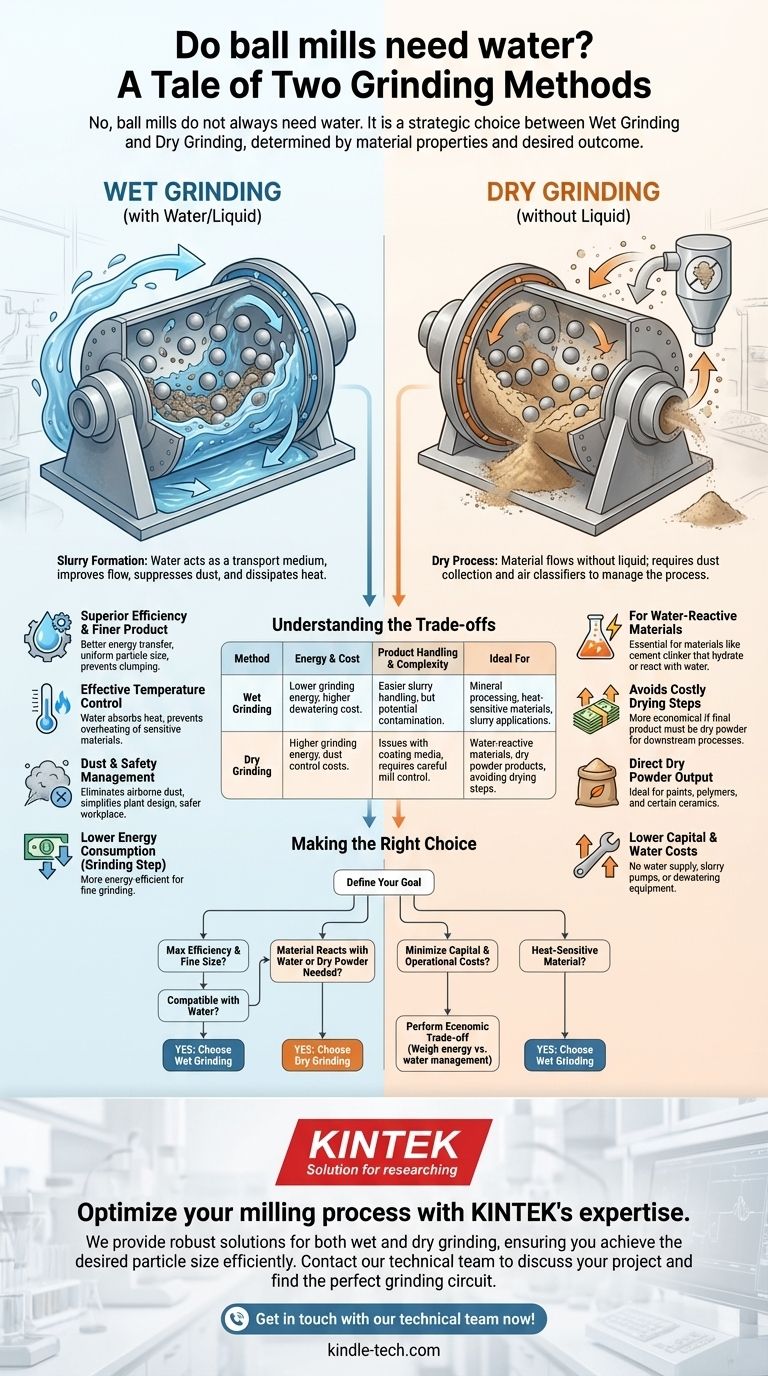
No, ball mills do not always need water. The decision to use water is a fundamental choice between two distinct operational modes: wet grinding and dry grinding. While many industrial applications use wet grinding for its efficiency, dry grinding is essential for materials that are water-sensitive or when the final product must be a dry powder.
The choice between adding water (wet grinding) or not (dry grinding) is not determined by the mill itself, but by the material's properties, the desired final particle size, and the requirements of the downstream process. Each method has significant and distinct operational trade-offs.

The Core Distinction: Wet vs. Dry Grinding
A ball mill's function is to reduce the size of materials through impact and attrition. How the material flows inside the mill is critical, and this is where the choice to use a liquid medium like water comes into play.
What is Wet Grinding?
In wet grinding, water (or another liquid) is added to the material to form a slurry. This slurry is then fed into the ball mill.
The water is not just a passive ingredient; it serves several critical functions. It acts as a transport medium, improves the flow of material, suppresses dust, and helps to dissipate the heat generated during the grinding process.
What is Dry Grinding?
In dry grinding, the material is processed without the addition of any liquid. The material must be sufficiently dry to flow properly inside the mill.
This method is necessary when the material cannot be exposed to water. It often requires specialized equipment like air classifiers and dust collection systems to manage the process effectively.
Why Choose Wet Grinding?
For many industries, particularly mineral processing, wet grinding is the default choice due to its significant advantages in efficiency and product quality.
Superior Efficiency and Finer Product
The slurry environment in wet grinding promotes more efficient energy transfer from the grinding media (the balls) to the material particles.
This process typically produces a finer and more uniform particle size distribution compared to dry grinding. The liquid prevents fine particles from clumping together or coating the grinding media, ensuring consistent grinding action.
Effective Temperature Control
Grinding generates a significant amount of heat through friction and impact. As noted in general mill operation, managing this heat is crucial.
Water is an excellent coolant, absorbing this thermal energy and preventing the material from overheating. This is vital for heat-sensitive materials whose chemical or physical properties could be altered by high temperatures.
Dust and Safety Management
Wet grinding completely eliminates the generation of airborne dust, a major operational and health hazard in dry milling operations.
This simplifies plant design, reduces the need for expensive dust collection systems, and creates a safer working environment.
When is Dry Grinding Necessary?
Despite the efficiencies of wet grinding, dry grinding is the only viable option in several key scenarios.
For Water-Reactive Materials
The most common reason for choosing dry grinding is material chemistry. Materials like cement clinker would hydrate and set if ground with water.
Similarly, certain chemicals or metals that react or oxidize in the presence of water must be ground in a dry state.
To Avoid Costly Drying Steps
If the final product must be a dry powder for subsequent processes (e.g., for use in paints, polymers, or certain ceramics), dry grinding is often more economical.
Wet grinding would require an additional, energy-intensive dewatering and drying stage, which can represent a significant portion of the total processing cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between wet and dry grinding is a decision based on balancing efficiency, cost, and final product requirements.
The Cost of Water vs. The Cost of Air
Wet grinding introduces costs for water supply, slurry pumping, and downstream dewatering. However, it generally consumes less energy per ton of product for the grinding step itself.
Dry grinding avoids water-related costs but requires significant investment in dust control and air handling systems. It is also typically less energy-efficient, leading to higher power consumption and greater wear on the mill's liner and grinding media.
Product Handling and Contamination
A slurry is often easier to pump and transport around a plant than a dry powder.
However, the use of water introduces a potential source of contamination, which can be a concern in high-purity applications like pharmaceuticals or specialty electronics.
Operational Complexity
Dry grinding can suffer from issues where fine material coats the grinding media and mill liner, drastically reducing grinding efficiency. This requires careful control of mill conditions.
Wet grinding is generally more forgiving and stable, but managing slurry density and rheology adds its own layer of process control complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use water is a strategic one that defines your entire milling circuit. Base your choice on your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum efficiency and achieving a very fine particle size: Wet grinding is almost always the superior technical choice, assuming your material is compatible with water.
- If your material reacts with water or must be a dry powder for the next step: Dry grinding is your only option, and the system must be designed to manage heat and dust.
- If your primary focus is minimizing capital and operational costs: You must perform a careful economic trade-off. Weigh the high energy and dust control costs of dry grinding against the dewatering and water management costs of wet grinding.
- If your material is sensitive to high temperatures: Wet grinding offers invaluable process control by providing a built-in cooling mechanism.
Understanding whether to use water is the first step toward designing an efficient and effective size-reduction process.
Summary Table:
| Grinding Method | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Wet Grinding | Uses water to form a slurry. Higher efficiency, finer particles, better cooling, dust-free. | Mineral processing, heat-sensitive materials, when a slurry is acceptable. |
| Dry Grinding | No liquid added. Requires dust collection. Less energy-efficient for fine grinding. | Water-reactive materials (e.g., cement), when a dry powder is required for the final product. |
Optimize your milling process with KINTEK's expertise.
Choosing between wet and dry grinding is a critical decision that impacts your product quality, operational costs, and safety. As a specialist in laboratory equipment and consumables, KINTEK can help you select the right ball mill and configure the perfect grinding circuit for your specific material and requirements.
We provide robust solutions for both wet and dry grinding applications, ensuring you achieve the desired particle size efficiently and reliably.
Contact us today to discuss your project and let our experts guide you to the most efficient and cost-effective milling solution.
Get in touch with our technical team now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of ball milling? A Versatile Tool for Material Synthesis and Modification
- Why use ball milling for NMC cathode materials? Achieve Precision Particle Sizing for Composite Cathodes
- Why is a laboratory ball mill used in Co-Ni catalyst research? Optimize CO2 Conversion with Precise Milling
- How does a high-energy planetary ball mill facilitate the synthesis of sulfide glassy electrolytes? Achieve Amorphization
- What is the key role of a planetary ball mill for IZO targets? Achieve Atomic-Level Uniformity in Material Preparation



















