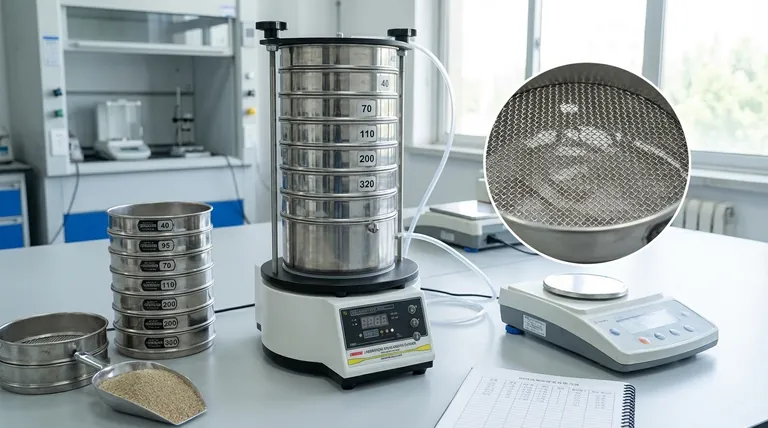
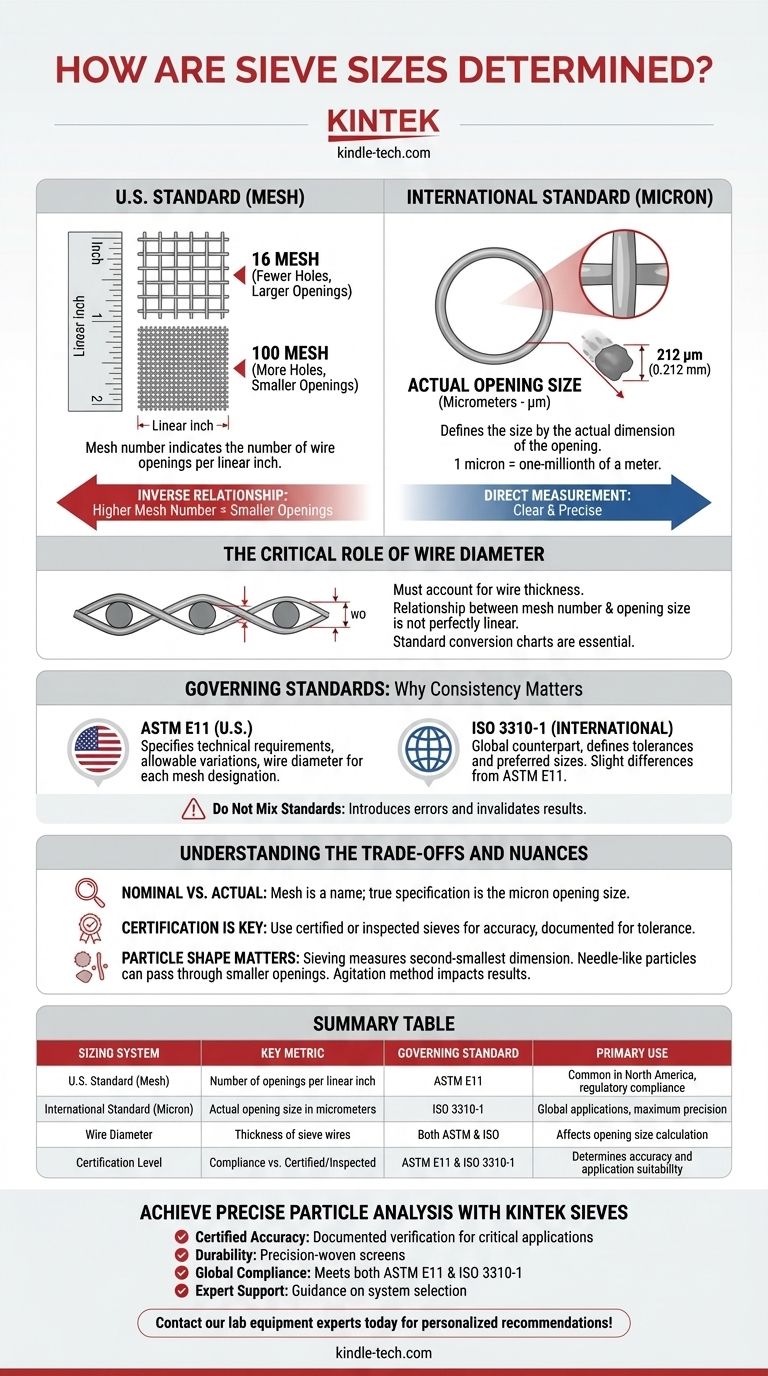
At its core, a sieve's size is determined by one of two standardized measurements. The most common system in the United States uses a "mesh" number, which indicates the number of wire openings per linear inch. The international standard, and the more precise method, defines the size by the actual dimension of the opening, typically measured in micrometers (microns) or millimeters.
The central principle to grasp is an inverse relationship: as the mesh number increases, the number of holes per inch goes up, meaning the individual holes—and the particles that can pass through them—become progressively smaller.

The Two Core Sizing Systems
To properly select and use a sieve, you must first understand the two primary ways its size is designated. These systems are governed by strict international standards to ensure results are repeatable and comparable across different labs and industries.
Understanding Sieve Mesh (The U.S. Standard)
The mesh number is a nominal designation based on the number of openings in the sieve screen across one linear inch.
Imagine a simple screen door. If it had 16 openings per inch, it would be a "16 mesh" screen. A sieve with 100 openings packed into that same inch would be a "100 mesh" sieve, with much finer holes.
This system is governed by the ASTM E11 standard in North America. A higher mesh number always signifies smaller openings for finer particle separation.
Understanding Microns (The International Standard)
The more direct and globally recognized method is to state the actual opening size. This is typically measured in micrometers (µm), also known as microns.
One micron is one-millionth of a meter. This system provides a direct, unambiguous measurement of the particle size that will be retained or passed by the sieve.
This method is central to the ISO 3310-1 standard. For example, a "212 micron" sieve has openings that are precisely 0.212 millimeters wide.
The Critical Role of Wire Diameter
You cannot simply calculate the opening size from the mesh number alone because you must account for the thickness of the wires themselves.
As the mesh number increases, the wire diameter used to create the mesh also changes. This is why a standard conversion chart is essential; the relationship between mesh number and opening size is not perfectly linear.
The Governing Standards: Why Consistency Matters
The entire purpose of sieving for particle analysis is to produce reliable, reproducible data. This is only possible when the equipment is manufactured to a verifiable standard.
ASTM E11 (The U.S. Standard)
This standard, set by ASTM International, specifies the technical requirements for test sieves. It defines the permissible variations in opening size, the wire diameter for each mesh designation, and the inspection framework.
ISO 3310-1 (The International Standard)
This is the global counterpart from the International Organization for Standardization. While the principles are nearly identical to ASTM E11, the specific tolerances and lists of preferred standard sizes can differ slightly.
Why You Must Adhere to a Single Standard
Mixing sieves certified under different standards (e.g., using an ASTM sieve in a stack of ISO sieves) can introduce small but significant errors. For quality control or scientific research, this can invalidate your results.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
While the system is standardized, there are practical considerations and common points of confusion to be aware of.
Nominal vs. Actual Opening Size
Remember that the mesh number is a name, not a precise measurement. The true specification is the nominal opening size in microns or millimeters and its allowable tolerance, as defined by the standard.
Sieve Certification is Key
For any application where accuracy is critical, you must use certified sieves. A "Compliance" sieve is manufactured to meet the standard, but a "Certified" or "Inspected" sieve has been optically measured to prove and document that its openings are within the required tolerance.
Particle Shape Matters
Sieving only measures a particle's second-smallest dimension. Long, needle-like particles may pass through an opening that is smaller than their total length. The method of agitation (tapping, shaking, ultrasonic) also significantly impacts results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's requirements will determine which system and certification level you should use.
- If your primary focus is U.S. regulatory compliance or existing procedures: Use ASTM E11 certified sieves and refer to them by their standard mesh designation.
- If your primary focus is international collaboration or maximum precision: Use ISO 3310-1 certified sieves and specify the required opening size in microns.
- If your primary focus is process consistency over absolute accuracy: Ensure all sieves in your process are from the same manufacturer and standard, even if they are only "Compliance" grade.
Understanding how these standards define a sieve's size is the first step toward accurate and repeatable particle analysis.
Summary Table:
| Sizing System | Key Metric | Governing Standard | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| U.S. Standard (Mesh) | Number of openings per linear inch | ASTM E11 | Common in North America, regulatory compliance |
| International Standard (Micron) | Actual opening size in micrometers | ISO 3310-1 | Global applications, maximum precision |
| Wire Diameter | Thickness of sieve wires | Both ASTM & ISO | Affects opening size calculation |
| Certification Level | Compliance vs. Certified/Inspected | ASTM E11 & ISO 3310-1 | Determines accuracy and application suitability |
Achieve Precise Particle Analysis with KINTEK Sieves
Struggling with inconsistent particle size results? Your sieve standards matter. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality laboratory sieves that meet both ASTM E11 and ISO 3310-1 specifications, ensuring your particle analysis is accurate, repeatable, and compliant.
Why choose KINTEK for your sieving needs?
- Certified Accuracy: Our inspected sieves come with documented verification for critical applications
- Durability: Precision-woven screens withstand rigorous use without deformation
- Global Compliance: Perfect for both North American and international standards
- Expert Support: Get guidance on selecting the right sieve system for your specific application
Ready to improve your particle analysis accuracy? Contact our lab equipment experts today for personalized recommendations and see how KINTEK's sieves can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is a standardized sieving system necessary for elephant grass research? Ensure Reliable Sample Consistency
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution



















