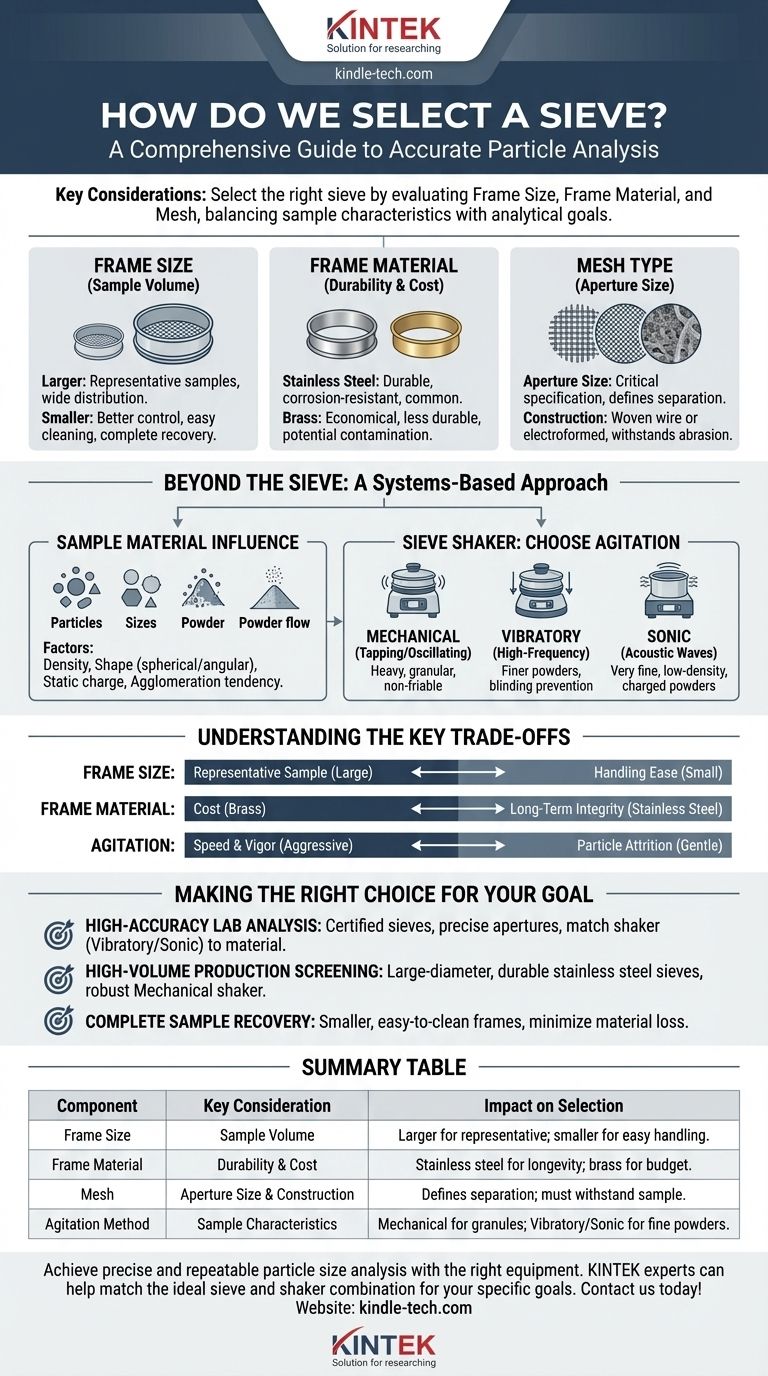
To select the right sieve, you must evaluate three primary components: the frame size, which dictates your sample volume; the frame material, which affects durability and cost; and the mesh, which performs the actual particle separation. The ideal choice balances the physical characteristics of your sample with the requirements of your analytical goal and the type of sieve shaker you use.
The most common mistake is choosing a sieve in isolation. A sieve is only one part of an integrated system. True accuracy and repeatability come from selecting a sieve, a sample size, and an agitation method that are all compatible with each other and appropriate for your material.

Deconstructing the Sieve: The Core Components
A test sieve seems simple, but its individual components have a significant impact on the quality and efficiency of your particle size analysis. Understanding each part is the first step toward making an informed decision.
Frame Size and Sample Volume
The diameter and height of the sieve frame determine the maximum volume of sample you can process effectively.
A larger frame allows for a larger, more statistically representative sample, which is critical for materials with a wide particle size distribution.
Conversely, smaller sieve frames offer better control over fine powders and are easier to clean, ensuring the complete recovery of valuable or small-volume specimens.
Frame Material and Durability
The frame provides a stable platform for the mesh and confines the material during agitation. The choice of material is a practical one.
Stainless steel is the most common choice, offering an excellent balance of durability, corrosion resistance, and cost.
Brass is a more economical option but is less durable and can wear over time, potentially contaminating your sample. It is best suited for less demanding applications.
Mesh Type and Aperture Size
The mesh is the functional heart of the sieve. The aperture size, or the size of the openings, is the most critical specification and directly defines the particle size you are separating.
Meshes can be made of woven wire or can be electroformed for extremely precise, microscopic openings. The material and construction must be able to withstand the abrasiveness of your sample and the stress of the shaking action without stretching or breaking.
Beyond the Sieve: A Systems-Based Approach
Selecting a sieve is not enough. You must consider how it integrates with your sample material and the sieve shaker to form a complete, functional system. The material you are analyzing dictates the equipment you need.
The Influence of Your Sample Material
The physical characteristics of your particles determine how they will behave during sieving.
Factors like particle density, shape (spherical vs. angular), static charge, and tendency to agglomerate will influence how easily they pass through the mesh. These traits will determine the most effective type of agitation needed.
The Sieve Shaker: Choosing the Right Agitation
A sieve shaker provides the energy needed to separate the particles. Different shakers are designed for different materials.
Mechanical shakers use a tapping and oscillating motion, which is effective for heavy, granular, or non-friable materials.
Vibratory shakers use a high-frequency vibration to fluidize the sample, making them ideal for finer powders and materials that might otherwise blind the mesh.
Sonic shakers use high-frequency acoustic waves to agitate particles, which is excellent for very fine, low-density, or electrostatically charged powders that are difficult to separate by other means.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Every choice in sieving involves a compromise. Being aware of these trade-offs allows you to optimize your process for what matters most: accurate and repeatable results.
Frame Size: Representative Sample vs. Handling Ease
A large sieve provides a more representative sample but can be heavy and difficult to clean thoroughly. A small sieve is easy to handle and clean for full sample recovery but may not provide a statistically valid sample for heterogeneous materials.
Frame Material: Cost vs. Long-Term Integrity
Brass frames are cheaper upfront but may deform or wear with heavy use, compromising sieve accuracy. Stainless steel costs more but provides superior durability and longevity, protecting the integrity of your results over thousands of cycles.
Agitation: Speed and Vigor vs. Particle Attrition
Aggressive agitation from a mechanical shaker can separate particles quickly, but it can also cause attrition—breaking down friable particles and skewing your results toward a finer distribution. Gentler methods like vibratory or sonic sieving preserve particle integrity but may take longer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final selection should be driven by the specific objective of your analysis. Use these guidelines to align your equipment with your goal.
- If your primary focus is high-accuracy lab analysis: Choose certified sieves with precise apertures, and match the shaker (often vibratory or sonic) to your specific material properties.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production screening: Opt for large-diameter, highly durable stainless steel sieves and a robust mechanical shaker designed for continuous operation.
- If your primary focus is complete sample recovery: Use smaller, easy-to-clean sieve frames to minimize material loss during transfer and cleaning.
By treating your sieve as part of an integrated system, you ensure that your particle separation process is not only efficient but fundamentally reliable.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Consideration | Impact on Selection |
|---|---|---|
| Frame Size | Sample Volume | Larger for representative samples; smaller for easy handling/recovery. |
| Frame Material | Durability & Cost | Stainless steel for longevity; brass for budget-friendly, less demanding uses. |
| Mesh | Aperture Size & Construction | Defines separation size; must withstand sample abrasiveness. |
| Agitation Method | Sample Characteristics | Mechanical for heavy granules; Vibratory/Sonic for fine, delicate powders. |
Achieve precise and repeatable particle size analysis with the right equipment.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including a comprehensive range of test sieves and sieve shakers. Our experts understand that accurate sieving depends on a perfectly matched system. We can help you select the ideal sieve and shaker combination for your specific material and analytical goals, whether you're focused on high-accuracy lab analysis, high-volume production screening, or complete sample recovery.
Let KINTEK equip your laboratory for success. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are standard sieves in pharmaceutical? Precision Instruments for Particle Size Control
- What are the advantages of using a sieve? Achieve Reliable, Low-Cost Particle Analysis
- What is the primary purpose of using laboratory standard sieves? Optimize Composting Pre-treatment for Pig Manure
- What is the process of sieve separation? A Guide to Precise Particle Size Analysis
- What precautions should be taken when doing a sieve analysis? Ensure Accurate Particle Size Data
- What are the standard test sieves for ASTM? Ensure Accuracy with ASTM E11 Compliant Sieves
- What is the size range for sieving? From 125mm Gravel to 20µm Powders
- How accurate is a test sieve? Ensure Reliable Particle Size Analysis



















