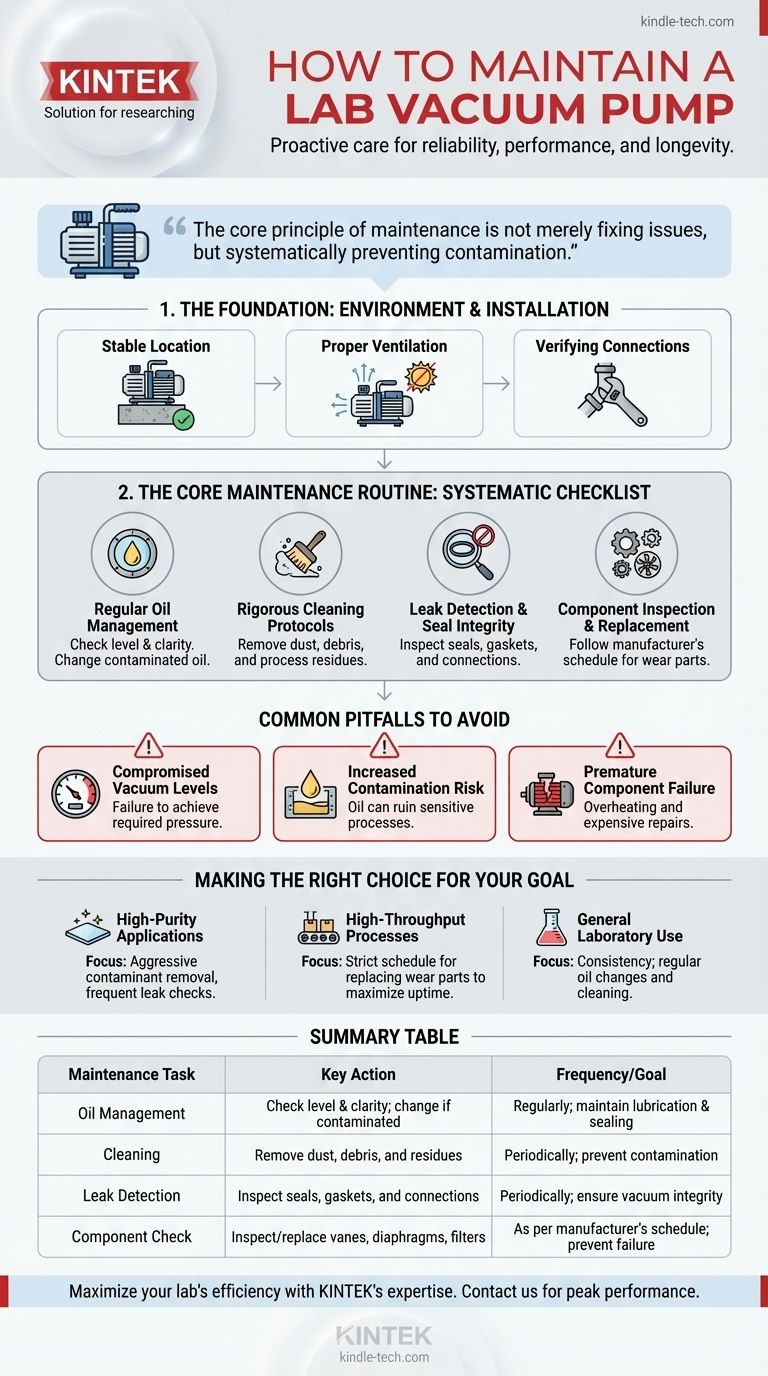
To properly maintain a lab vacuum pump, you must implement a routine schedule of checking and changing the oil, cleaning all components to remove contaminants, inspecting connections and seals for leaks, and replacing worn parts like vanes or diaphragms. This proactive approach ensures the pump operates at its specified vacuum level, provides reliable performance for your experiments, and extends its operational lifespan.
The core principle of vacuum pump maintenance is not merely fixing issues as they arise, but systematically preventing contamination. A consistent maintenance plan is the most critical factor in guaranteeing the safety, reliability, and long-term performance of your entire vacuum system.

The Foundation: Environment and Installation
Before considering a maintenance schedule, you must ensure the pump is set up for success. The physical environment and installation are the first line of defense against premature wear and failure.
Securing a Stable Location
A pump must be installed on a hard, flat, and stable foundation, such as a concrete floor or a sturdy steel frame. This minimizes vibration, which can loosen fittings and cause mechanical stress over time.
Ensure there is adequate space around the pump for proper airflow and to allow easy access for inspection and maintenance tasks.
Ensuring Proper Ventilation
Pumps generate heat and can emit oil vapor. Good ventilation is critical to dissipate this heat and prevent the buildup of fumes in the laboratory environment.
You should also protect the pump from direct sunlight and any potential liquid spills, which can damage electrical components and compromise safety.
Verifying Connections
Upon installation and periodically thereafter, check all pipeline connections and fittings. Even minor leaks at the connections will force the pump to work harder and prevent it from reaching its ultimate pressure.
The Core Maintenance Routine: A Systematic Checklist
A consistent schedule is the most effective way to manage pump health. While your manufacturer’s instructions are the ultimate authority, the following actions form the basis of nearly every maintenance plan.
Regular Oil Management (For Oil-Sealed Pumps)
The oil in a rotary vane pump serves as a lubricant, a sealant, and a coolant. Its condition is paramount.
You must regularly check the oil level and clarity. Contaminated, cloudy, or discolored oil has lost its effectiveness and must be changed immediately to prevent internal damage.
Rigorous Cleaning Protocols
Contaminants are the primary threat to a vacuum system. Dust, debris, and process residues must be managed proactively.
Keep the pump's exterior and the surrounding area clean. For the internal system, periodically clean the vacuum chamber and components according to the equipment's specific operating manual.
Leak Detection and Seal Integrity
Leaks are a common source of poor vacuum performance. Periodically inspect the sealing performance of the pump system.
Pay close attention to gaskets, O-rings, and connection points. Any worn or damaged seals should be replaced promptly to maintain vacuum integrity.
Component Inspection and Replacement
Mechanical parts wear down over time. It is essential to follow the manufacturer's recommended 'maintenance cycle'.
This includes inspecting and replacing consumable parts such as vanes, diaphragms, and filters before they fail catastrophically. Adhering to this schedule prevents unexpected downtime.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Neglecting maintenance has direct and often costly consequences. Understanding these risks reinforces the importance of a proactive approach.
Compromised Vacuum Levels
The most immediate effect of poor maintenance is a failure to achieve the required vacuum level. This can be due to contaminated oil, internal leaks, or worn-out vanes, all of which directly compromise experimental results.
Increased Contamination Risk
A poorly maintained pump can become a source of contamination itself. Oil backstreaming can introduce hydrocarbons into your vacuum chamber, ruining sensitive processes and samples.
Premature Component Failure
Operating a pump with old oil, minor leaks, or worn parts places excessive strain on the motor and mechanical components. This leads to overheating and ultimately results in expensive, premature failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your maintenance schedule should reflect the demands of your application. A "one-size-fits-all" approach is less effective than one tailored to your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is high-purity applications (e.g., surface science): Your top priority is aggressive contaminant removal and frequent leak checks.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput processes (e.g., industrial coating): Your top priority is adhering to a strict schedule for replacing wear parts to maximize uptime.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory use: Your top priority is consistency; establishing and following a regular schedule for oil changes and cleaning is key.
Ultimately, proactive maintenance is an investment in reliable, repeatable science.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Task | Key Action | Frequency/Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Management | Check level & clarity; change if contaminated | Regularly; maintain lubrication & sealing |
| Cleaning | Remove dust, debris, and residues | Periodically; prevent contamination |
| Leak Detection | Inspect seals, gaskets, and connections | Periodically; ensure vacuum integrity |
| Component Check | Inspect/replace vanes, diaphragms, filters | As per manufacturer's schedule; prevent failure |
Maximize your lab's efficiency and protect your investments with KINTEK's expertise.
Proper vacuum pump maintenance is critical for reliable results and long equipment life. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering the support and high-quality products you need to keep your vacuum systems running smoothly.
Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how we can help you maintain peak performance.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What are glass tubes used in chemistry lab? Essential Tools for Safe and Precise Experiments
- What is the compressive strength of fused quartz? >1.1 GPa, But It's the Other Properties That Matter
- What are the uses of quartz tube? Essential for High-Temperature, High-Purity Applications
- What is the role of zirconia grinding jars and balls in C_fiber/Si3N4? Achieve High-Purity Ceramic Composites
- Why use zirconia grinding jars and balls for LAGP electrolyte? Protect Purity and Performance
- What is the function of alumina tubes and alumina wool in a pyrolysis furnace? Optimize Your Biochar Production Quality
- What is a quartz tube used for? Mastering High-Temp, High-Purity Applications
- What are the impurities in quartz? Unlocking the Secrets of Color and Performance



















