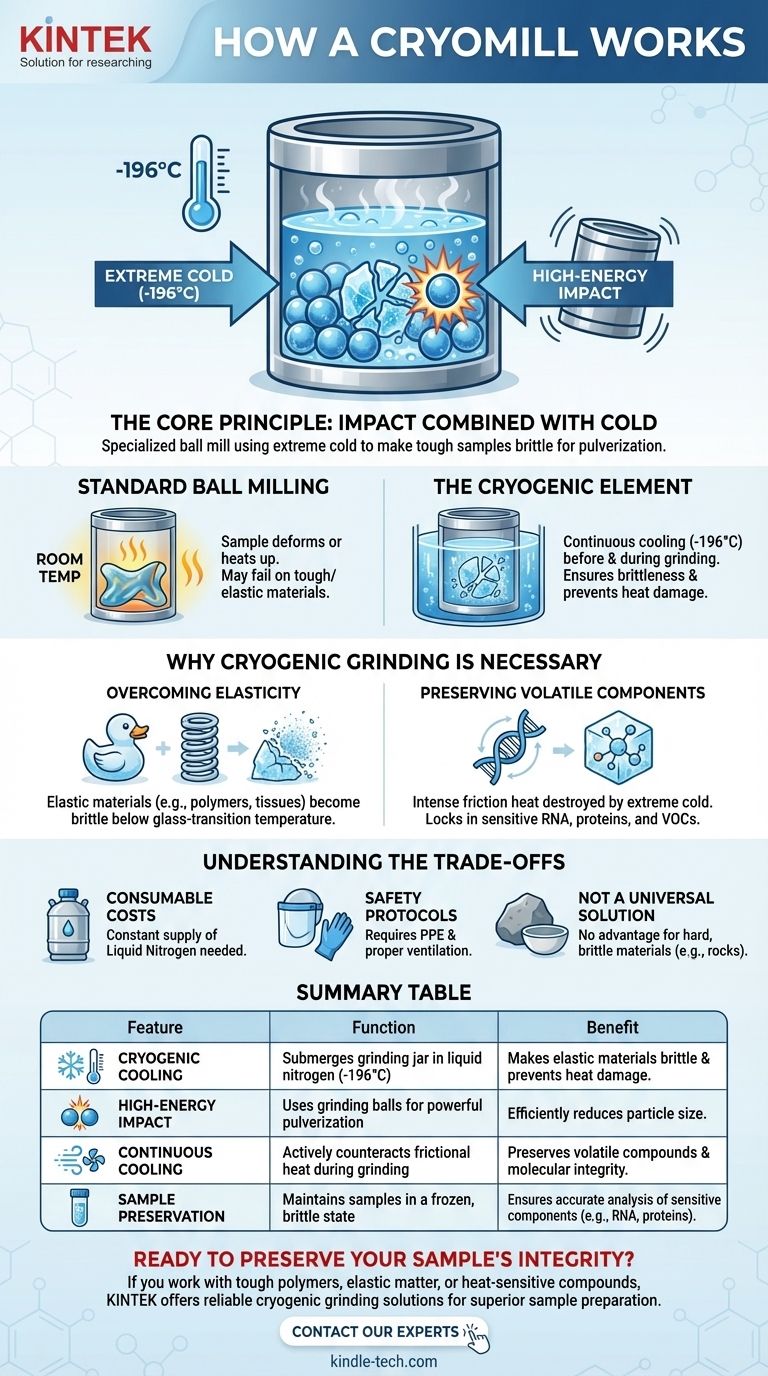
At its core, a CryoMill is a specialized ball mill that uses extreme cold to its advantage. It works by submerging a grinding jar in liquid nitrogen, which cools the sample and grinding balls to approximately -196°C. This cryogenic environment makes tough or heat-sensitive samples extremely brittle, allowing them to be pulverized into a fine powder by the high-energy impacts of the grinding balls.
The crucial innovation of the CryoMill is not just the grinding action, but its integrated and continuous cooling system. By actively counteracting the heat generated by friction, it ensures the sample remains frozen and brittle throughout the entire process, preserving its molecular integrity.
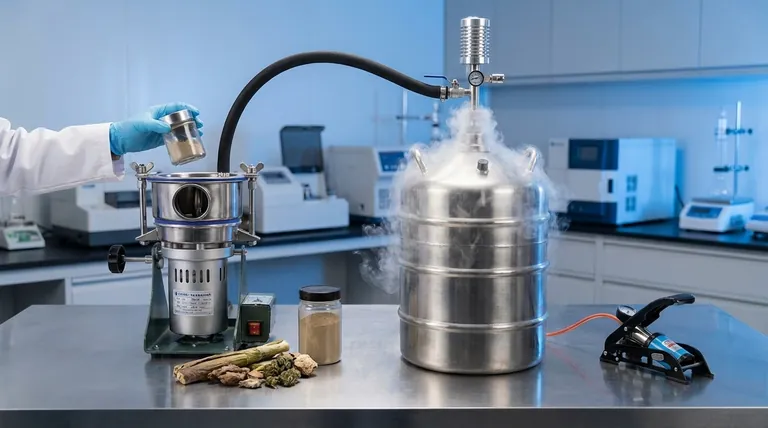

The Core Principle: Impact Combined with Cold
A CryoMill's effectiveness comes from merging two distinct physical processes: the brute force of ball milling and the transformative effect of cryogenic temperatures.
Standard Ball Milling Action
A conventional ball mill uses a jar filled with a sample and heavy grinding balls. The jar is shaken or tumbled at high speeds, causing the balls to collide with the sample at high energy. This impact force is what breaks the material down.
The Cryogenic Element
The CryoMill adds a critical layer to this process. The grinding jar is continuously bathed in liquid nitrogen before and during the grinding cycle. This serves two vital purposes that are impossible to achieve at room temperature.
Why Cryogenic Grinding is Necessary
The decision to use a CryoMill is driven by the specific nature of the sample. Standard milling can fail or even destroy materials that are either too tough or too delicate.
Overcoming Elasticity
Many materials, like plastics, polymers, and tough biological tissues, are elastic at room temperature. When struck by a grinding ball, they simply deform or heat up instead of shattering. By cooling them below their glass-transition temperature, the CryoMill transforms them into a hard, brittle state, making them easy to pulverize.
Preserving Volatile Components
The intense friction of milling generates significant heat. This heat can destroy or cause the loss of sensitive components, such as RNA, proteins, or volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in food and environmental samples. The extreme cold of the CryoMill locks these molecules in place, preventing thermal degradation and ensuring the resulting powder is a true representation of the original sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the CryoMill is a specialized instrument. Its benefits come with practical considerations that make it ideal for some tasks but unnecessary for others.
Consumable Costs
The primary trade-off is the need for a constant supply of liquid nitrogen. This introduces an ongoing operational cost that is absent in standard room-temperature mills.
Safety Protocols
Working with cryogenic fluids requires specific safety measures. Proper ventilation to prevent oxygen displacement and personal protective equipment (PPE) to guard against cold burns are mandatory.
Not a Universal Solution
For materials that are already hard and brittle at room temperature, such as rocks, minerals, or ceramics, the cryogenic component offers no significant advantage. A standard ball mill is often more straightforward and cost-effective for these applications.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing the right grinding method depends entirely on the nature of your sample and your analytical goals.
- If your primary focus is grinding tough, elastic materials (like polymers or plant matter): The CryoMill is the superior choice, as it induces the embrittlement necessary for effective pulverization.
- If your primary focus is preserving heat-sensitive molecules (like RNA or volatile compounds): The continuous cryogenic cooling is essential to prevent thermal degradation and ensure accurate downstream analysis.
- If your primary focus is simply particle size reduction of hard, stable materials (like ceramics): A standard room-temperature ball mill is the more practical and economical tool for the job.
By understanding the principle of cryogenic embrittlement, you can confidently select the precise tool to maintain the integrity of your unique sample.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Cryogenic Cooling | Submerges grinding jar in liquid nitrogen (-196°C) | Makes elastic materials brittle and prevents heat damage |
| High-Energy Impact | Uses grinding balls for powerful pulverization | Efficiently reduces particle size |
| Continuous Cooling | Actively counteracts frictional heat during grinding | Preserves volatile compounds and molecular integrity |
| Sample Preservation | Maintains samples in a frozen, brittle state | Ensures accurate analysis of sensitive components like RNA and proteins |
Ready to preserve your sample's integrity?
If you work with tough polymers, elastic plant matter, or heat-sensitive compounds like RNA and proteins, the CryoMill is the precise tool you need. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory equipment, including cryogenic grinding solutions, to help you achieve superior sample preparation and accurate analytical results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a CryoMill can enhance your research and protect your valuable samples.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Cryogenic Grinder Cryomill Cryogrinder with Liquid Nitrogen for Laboratory Use
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
People Also Ask
- What role do laboratory grinding and polishing systems play in nitriding? Ensure Superior Mirror-Finish & Ion Penetration
- What is cryogenic grinding of herbs? Preserve Flavor and Potency with Sub-Zero Milling
- What is a grinder used in labs? Essential for Homogeneous Sample Preparation & Analysis
- How does cryomilling work? Achieve Superior Nanostructures with Cryogenic Milling
- What is the role of a cryogenic grinder in PET recycling? Transform Waste into High-Reactive Micron Powders



















