At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a sophisticated process for creating ultra-thin, high-performance solid films from a gas. Precursor gases are introduced into a reaction chamber where they are heated, causing them to chemically react and decompose onto a substrate's surface. This reaction builds up the desired material, layer by layer, forming a new, solid coating.
The fundamental principle of CVD is not merely deposition, but a controlled chemical transformation. It turns specific gases into a solid material directly on a target surface, enabling the creation of materials with exceptional purity and structural integrity that would be impossible to form otherwise.
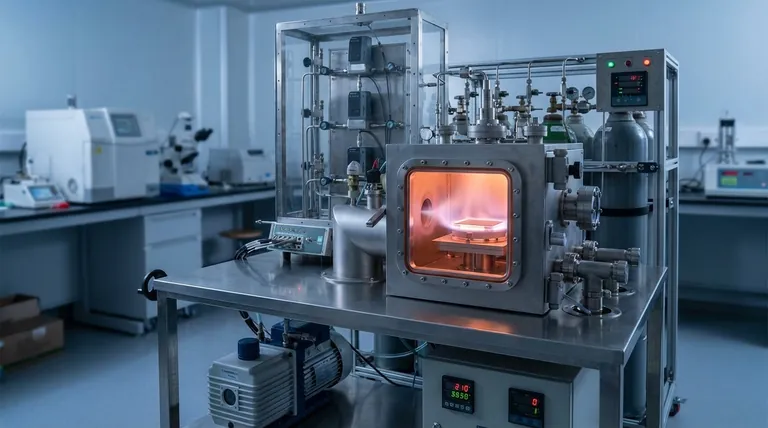

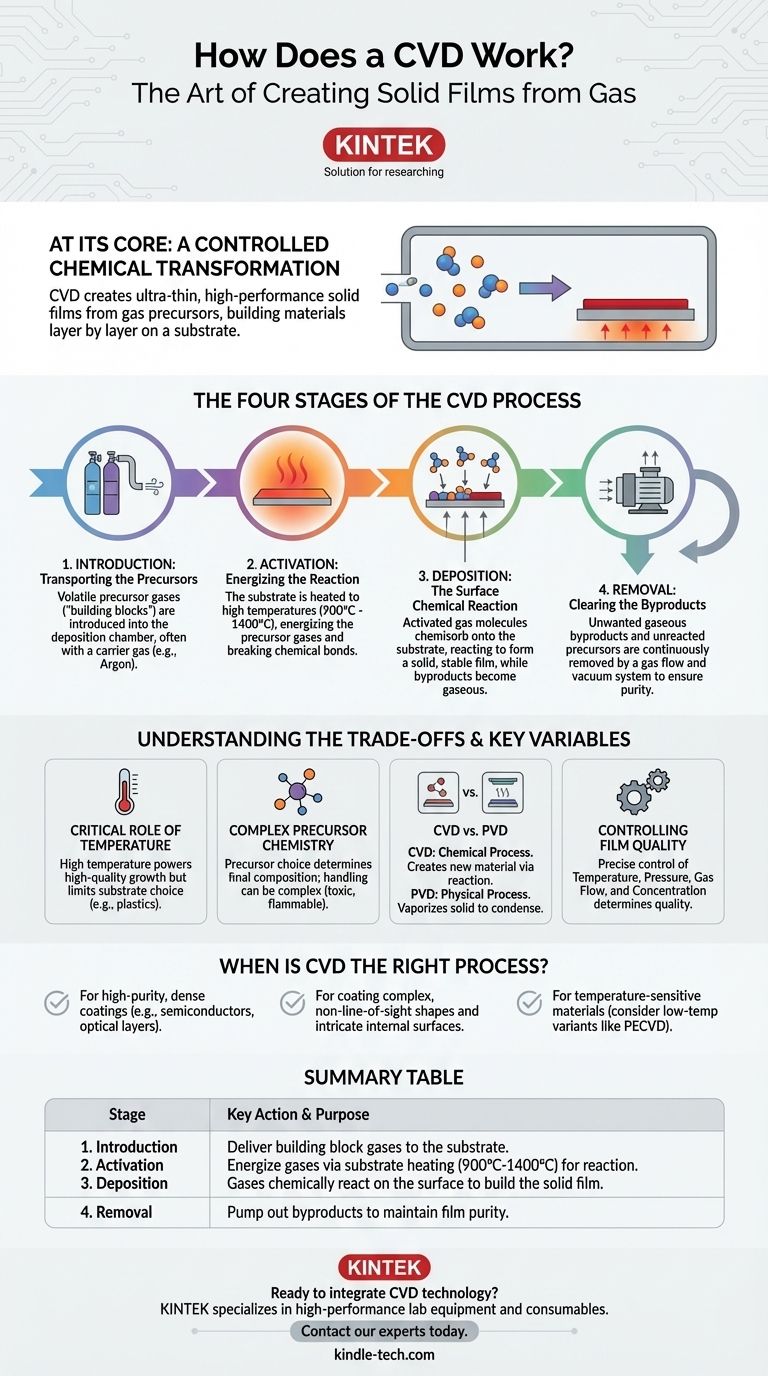
The Four Stages of the CVD Process
To understand how CVD works, it's best to break it down into a sequence of four distinct but interconnected stages. This entire process typically occurs under vacuum to ensure purity and control.
1. Introduction: Transporting the Precursors
The process begins by introducing one or more volatile precursor gases into the deposition chamber. These are the "building block" molecules that contain the elements needed for the final film.
These gases don't travel alone. They are often mixed with a carrier gas (like argon or nitrogen) that helps transport them uniformly towards the substrate, the material to be coated. This movement is governed by principles of diffusion and gas flow dynamics.
2. Activation: Energizing the Reaction
The precursor gases are stable at room temperature and need an input of energy to become reactive. The most common method is thermal activation.
The substrate is heated to a very high temperature, often between 900°C and 1400°C. When the precursor gases come into contact with or pass near this hot surface, the thermal energy breaks their chemical bonds, "activating" them for reaction.
3. Deposition: The Surface Chemical Reaction
This is the heart of the CVD process. The activated, unstable gas molecules adsorb onto the hot substrate surface in a process called chemisorption, forming strong chemical bonds.
Once on the surface, they undergo chemical reactions, either with other precursor molecules or by decomposing further. The desired element deposits onto the surface, forming a solid, stable film, while other elements become gaseous byproducts. The film grows atom by atom or molecule by molecule, resulting in a highly ordered, often crystalline, structure.
4. Removal: Clearing the Byproducts
The chemical reactions that form the solid film also generate unwanted gaseous byproducts.
These waste products, along with any unreacted precursor gas, are removed from the chamber by a continuous gas flow and the vacuum system. This constant removal is critical to prevent contamination of the film and to drive the chemical reaction forward.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Variables
While powerful, CVD is a process with specific requirements and limitations that dictate its use. Understanding these trade-offs is key to appreciating its role in manufacturing.
The Critical Role of Temperature
High temperature is the engine of most CVD processes. This provides the energy for high-quality film growth but also represents a major constraint. Many materials, such as plastics or certain electronic components, cannot withstand the extreme heat required, limiting the substrates that can be used.
Precursor Chemistry is Complex
The choice of precursor gas is paramount; it directly determines the composition of the final coating, whether it's an oxide, nitride, or a pure element like silicon. These gases can be toxic, flammable, or expensive, requiring complex and safe handling systems.
CVD vs. PVD: Chemical vs. Physical
CVD is often compared to Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). The key difference is that CVD is a chemical process, creating a new material via reaction. PVD is a physical process, akin to boiling a solid material into a vapor and letting it condense on a surface, with no chemical change. CVD films are often denser and more conformal.
Controlling Film Quality
The final quality of the coating—its thickness, uniformity, and purity—depends on the precise control of several variables. Temperature, pressure, gas flow rates, and precursor concentration must be meticulously managed to achieve the desired result.
When is CVD the Right Process?
Applying this knowledge requires knowing when CVD is the superior choice for a specific engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, dense coatings: CVD is the premier choice for creating semiconductor films, optical coatings, and hard protective layers (like titanium nitride) with exceptional structural quality.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-line-of-sight shapes: Because the precursors are gases, CVD can uniformly coat intricate internal surfaces and complex 3D objects where physical, line-of-sight methods would fail.
- If you are working with temperature-sensitive materials: Consider variants like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), which uses an electric field to activate the gases, allowing for deposition at much lower temperatures.
Ultimately, Chemical Vapor Deposition is a foundational technology that gives us precise control over matter at the atomic scale, making it indispensable for modern electronics and materials science.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Introduction | Precursor gases enter the chamber | Deliver building blocks to the substrate |
| 2. Activation | Substrate is heated (900°C-1400°C) | Energize gases for chemical reaction |
| 3. Deposition | Gases react on the substrate surface | Build the solid film layer by layer |
| 4. Removal | Byproduct gases are pumped out | Maintain film purity and process control |
Ready to integrate CVD technology into your lab workflow? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for materials science and semiconductor research. Our expertise ensures you have the right tools for precise temperature control, gas handling, and deposition processes. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and enhance your research capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods



















