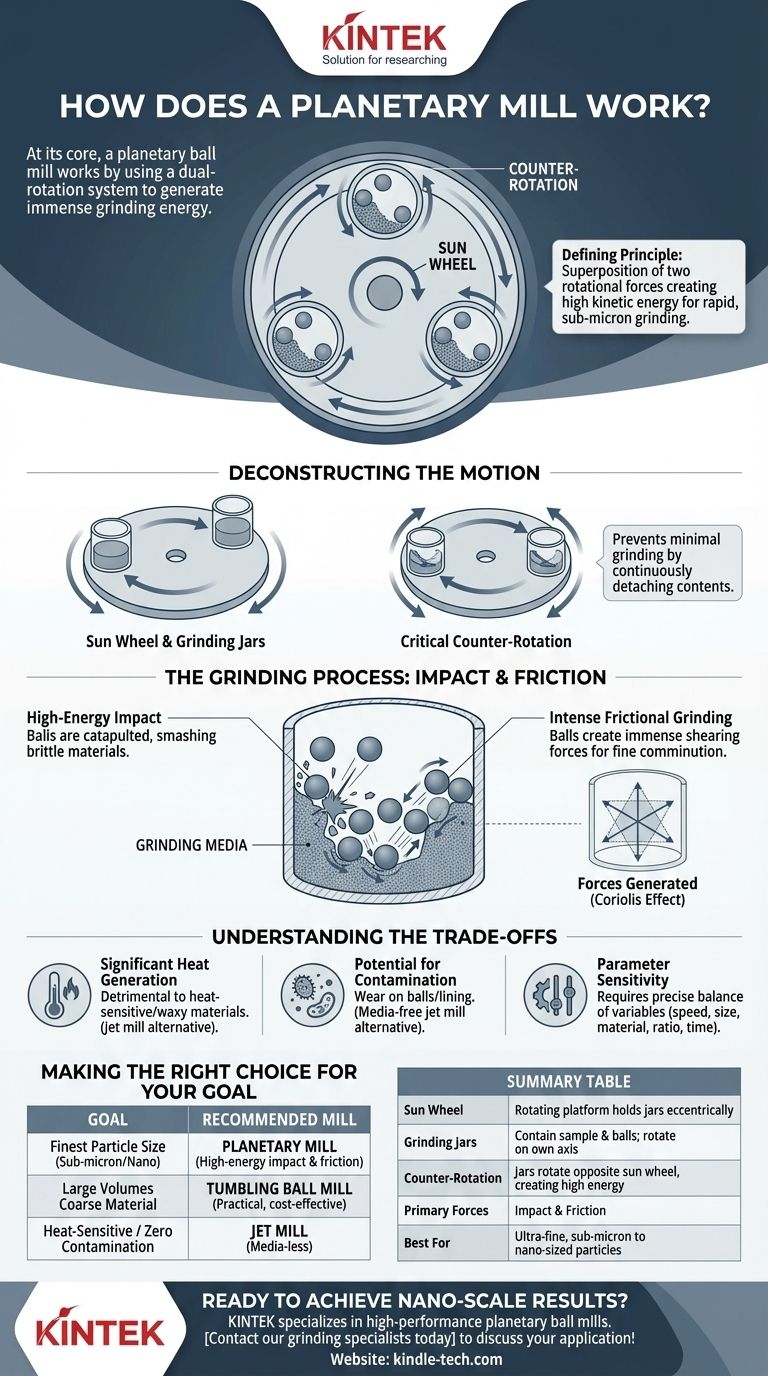
At its core, a planetary ball mill works by using a dual-rotation system to generate immense grinding energy. It consists of grinding jars mounted eccentrically on a larger rotating disk, called a sun wheel. Crucially, the grinding jars rotate on their own axis in the opposite direction to the sun wheel, creating a powerful combination of impact and friction forces that can pulverize materials to extremely fine sizes.
The defining principle of a planetary mill is the superposition of two rotational forces. This counter-rotation creates significantly higher kinetic energy than standard mills, enabling rapid and efficient grinding down to the sub-micron level.

Deconstructing the Planetary Motion
The unique effectiveness of a planetary mill comes from its complex and carefully engineered movement. Understanding the forces at play is key to understanding its power.
The Sun Wheel and Grinding Jars
The physical setup involves at least one grinding jar, which contains the sample material and grinding media (balls). This jar is positioned off-center on a larger, rotating platform known as the sun wheel.
The Critical Counter-Rotation
As the sun wheel rotates, it imparts a strong centrifugal force on the grinding jar. Simultaneously, a separate gearing system forces the grinding jar to rotate on its own axis but in the opposite direction.
This counter-rotation is the most important feature. It prevents the contents of the jar from simply being pinned to the outer wall by centrifugal force, which would result in minimal grinding.
How Forces are Generated
The interplay between these two opposing movements creates a powerful dynamic effect inside the jar, governed by the Coriolis effect.
The balls inside are subjected to two overlapping forces. First, the sun wheel's rotation throws them against the jar's outer wall. Then, the jar's counter-rotation causes them to continuously detach, accelerate, and fly across the jar's interior at extremely high speeds.
The Grinding Process: Impact and Friction
This complex motion translates into two distinct and highly efficient grinding mechanisms that occur simultaneously.
High-Energy Impact Events
The primary grinding action comes from impact. As the grinding balls are catapulted across the jar, they violently smash into the sample material and the opposite wall. This constant, high-energy bombardment is incredibly effective at breaking down brittle and hard materials.
Intense Frictional Grinding
The second mechanism is friction. As the grinding balls roll and slide against each other and the inner wall of the jar, they create immense shearing forces. This action is essential for the fine comminution of particles, polishing and blending them down to a uniform, sub-micron size.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the planetary mill's high-energy nature introduces specific considerations that are critical for achieving the right results.
Significant Heat Generation
The immense energy input from impact and friction is converted into heat. This can be detrimental to heat-sensitive or waxy materials, potentially altering their chemical structure. In contrast, a jet mill generates no attritional heat and is better suited for such samples.
Potential for Contamination
The high-impact nature of the process can cause microscopic wear on the grinding balls and the jar lining. Over time, this can introduce trace amounts of contamination into the sample. For applications requiring absolute purity, a media-free method like jet milling is superior.
Parameter Sensitivity
The final particle size is highly dependent on a precise balance of variables. Factors like the rotation speed, the size and material of the grinding balls, the ball-to-powder ratio, and the total grinding time must be carefully optimized to achieve the desired outcome.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct milling technique depends entirely on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is achieving the finest possible particle size (sub-micron/nano): The planetary mill's unparalleled high-energy impact and friction mechanism is the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is processing large volumes of coarse material without needing extreme fineness: A simpler, traditional tumbling ball mill is often more practical and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is grinding a heat-sensitive material or guaranteeing zero contamination: A media-less jet mill is the ideal solution.
By understanding the unique forces at play within a planetary mill, you can harness its power for advanced materials processing.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| Sun Wheel | Rotating platform that holds grinding jars eccentrically. |
| Grinding Jars | Contain sample and grinding balls; rotate on their own axis. |
| Counter-Rotation | Jars rotate opposite to the sun wheel, creating high-energy impacts. |
| Primary Forces | Impact (from ball collisions) and friction (from shearing action). |
| Best For | Achieving ultra-fine, sub-micron to nano-sized particles. |
Ready to achieve nano-scale results with your materials?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance planetary ball mills and other advanced lab equipment. Our experts can help you select the perfect mill to optimize your grinding process for maximum efficiency and particle size control.
Contact our grinding specialists today to discuss your application and get a personalized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of planetary ball mill? Key Drawbacks in Energy, Noise, and Wear
- Why is ball milling equipment required in Cold Sintering? Master Particle Refinement for Optimal Density
- How do stainless steel grinding jars and balls contribute to mechanical alloying? Optimize HEA Powder Synthesis
- What is the role of a ball mill in UHMWPE/DB composite prep? Achieve High-Energy Uniform Dispersion
- What is the function of a planetary ball mill in the preparation of high-entropy rare earth silicate multi-phase ceramics?
- What is ball mill method of size reduction? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control
- What role does the ball milling process play in RP-LYCB composite anodes? Essential Tips for Superior Battery Materials
- What is the role of a high-energy planetary ball mill in ODS alloy prep? Master Nano-Oxide Dispersion



















