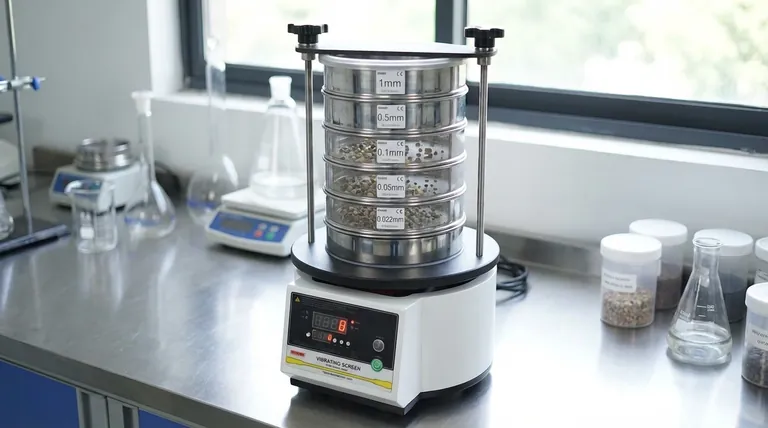
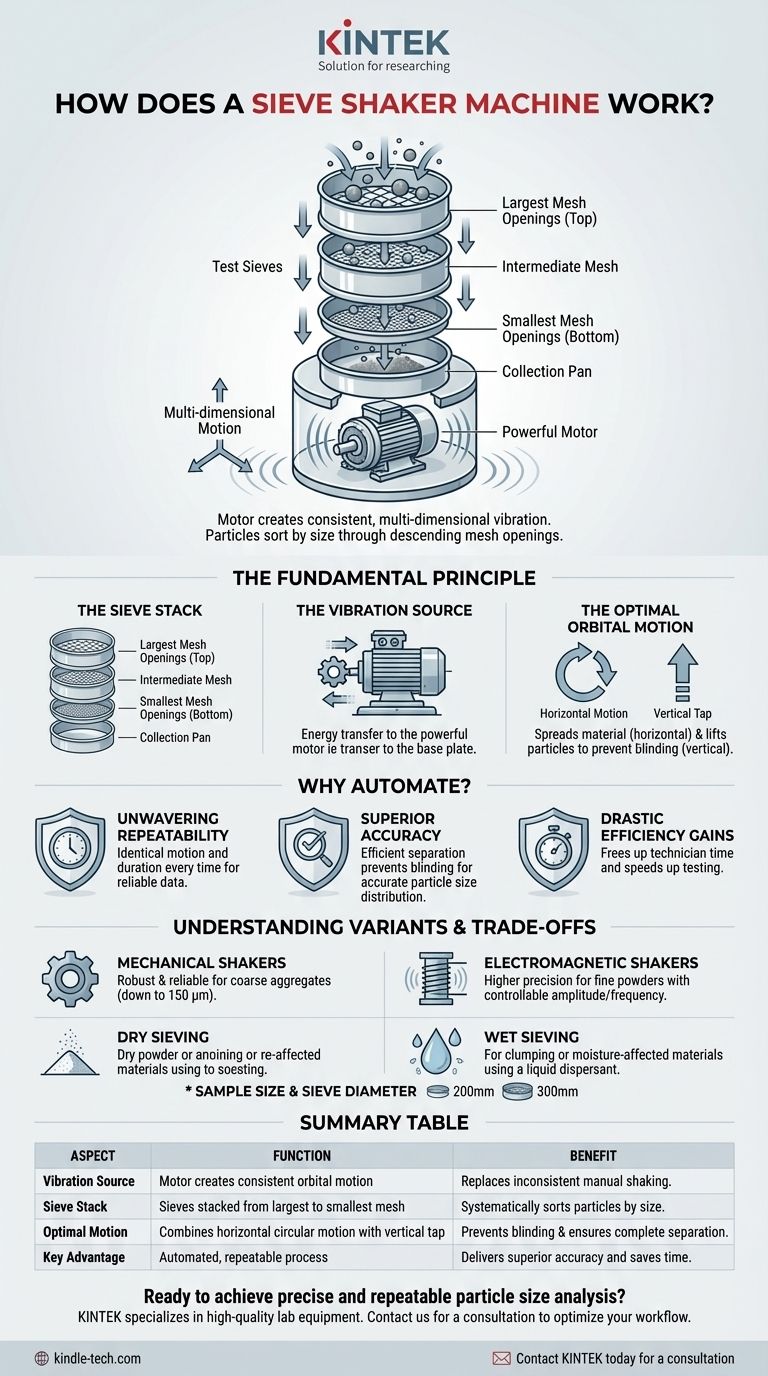
At its core, a sieve shaker machine works by using a motor to create consistent, multi-dimensional vibration. This vibration is transferred to a vertically stacked set of test sieves, which are arranged with the largest mesh openings at the top and the smallest at the bottom. As the material sample is agitated, particles smaller than a given sieve's openings pass through to the next level, effectively sorting the entire sample by size.
The fundamental challenge in particle analysis is achieving consistent and complete separation. A sieve shaker solves this by replacing inconsistent manual shaking with a controlled, automated orbital motion, ensuring every particle is tested against every sieve opening for highly accurate and repeatable results.

The Fundamental Principle: From Motion to Measurement
A sieve shaker’s effectiveness comes from its precise control over three key elements: the sieve arrangement, the power source, and the type of motion it generates.
The Sieve Stack
The process begins with a stack of test sieves. These are precision-woven mesh or perforated-plate screens held in a frame. They are arranged in descending order of aperture size, with the coarsest sieve on top and a solid collection pan at the very bottom.
The Vibration Source
A motor provides the force needed to agitate the sieve stack. This is the heart of the machine. The motor drives the base plate where the sieves are clamped, transferring energy throughout the stack.
The Optimal Orbital Motion
The most effective shakers do not just shake back and forth. They combine a circular, horizontal motion with a sharp vertical tap. This is often called orbital motion.
The horizontal movement spreads the material across the entire surface of the sieve, giving each particle a chance to find an opening. The vertical tap lifts the particles, preventing them from getting stuck (blinding the screen) and reorienting them for another pass at the mesh.
Why Automate? The Advantages Over Manual Sieving
While manual sieving is possible, a sieve shaker offers objective advantages that are critical for any professional lab or quality control process. It is not just about convenience; it is about the integrity of the data.
Unwavering Repeatability
A machine produces the exact same motion for the exact same duration, every single time. A human cannot. This consistency is the foundation of reliable quality control and comparative analysis.
Superior Accuracy
The controlled orbital motion is more efficient at particle separation than manual shaking. It systematically prevents particle blinding and ensures that particles are properly sorted, leading to a much more accurate determination of the sample's particle size distribution.
Drastic Efficiency Gains
Automated shakers free up technician time, reduce physical strain, and can often complete a test in a fraction of the time required for manual sieving.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Variants
Not all sieve shakers are the same. The primary differences lie in the driving mechanism and intended application, which present clear trade-offs.
Mechanical vs. Electromagnetic Shakers
Most standard sieve shakers use a conventional mechanical vibration motor. These are robust, reliable workhorses suitable for a wide range of materials, especially coarse aggregates down to about 150 µm.
For analyses requiring higher precision, particularly with very fine powders, electromagnetic shakers are superior. They use electromagnetic pulses to drive the motion, allowing for much finer control over amplitude and frequency, which is crucial for achieving accurate separation of smaller particles.
Dry Sieving vs. Wet Sieving
The standard method is dry sieving. However, some materials tend to agglomerate (clump together) due to static electricity or moisture. For these samples, wet sieving is an option.
In this process, a liquid (usually water) is used to disperse the particles and carry them through the sieves. This requires a shaker designed to handle liquids and a material that will not be adversely affected by the chosen fluid.
Sample Size and Sieve Diameter
Sieve shakers are designed for specific sieve diameters, most commonly 200mm (8 inches) and 300mm (12 inches). The choice depends directly on the volume of the sample being analyzed. Larger sample volumes require larger diameter sieves to ensure the material layer is not too thick for effective separation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Understanding how a sieve shaker works allows you to select the right tool for your specific analytical goal.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control for general or coarse materials: A standard mechanical shaker offers the best balance of performance, durability, and cost.
- If your primary focus is high-precision research with fine or low-density powders: An electromagnetic shaker will provide the superior control and accuracy your work demands.
- If you are working with materials that clump or hold a static charge: Ensure you select a model that is equipped for wet sieve analysis to guarantee proper particle dispersion.
By matching the machine's mechanism to your material's properties, you ensure the generation of accurate and trustworthy particle size data.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vibration Source | Motor creates consistent orbital motion | Replaces inconsistent manual shaking |
| Sieve Stack | Sieves stacked from largest to smallest mesh | Systematically sorts particles by size |
| Optimal Motion | Combines horizontal circular motion with vertical tap | Prevents blinding & ensures complete separation |
| Key Advantage | Automated, repeatable process | Delivers superior accuracy and saves time |
Ready to achieve precise and repeatable particle size analysis in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including robust mechanical and high-precision electromagnetic sieve shakers designed for your specific materials and applications. Our experts can help you select the perfect equipment to enhance your lab's efficiency and data integrity.
Contact KINTEL today for a consultation and let us help you optimize your particle analysis workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
People Also Ask
- What is the use of vibrating sieve machine? Achieve Precise Particle Size Analysis for Your Lab
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- What is the frequency of a sieve shaker? The Key to Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- What role does a laboratory vibrating sieve shaker play in the LiFePO4 powder processing workflow? Ensure Batch Quality



















