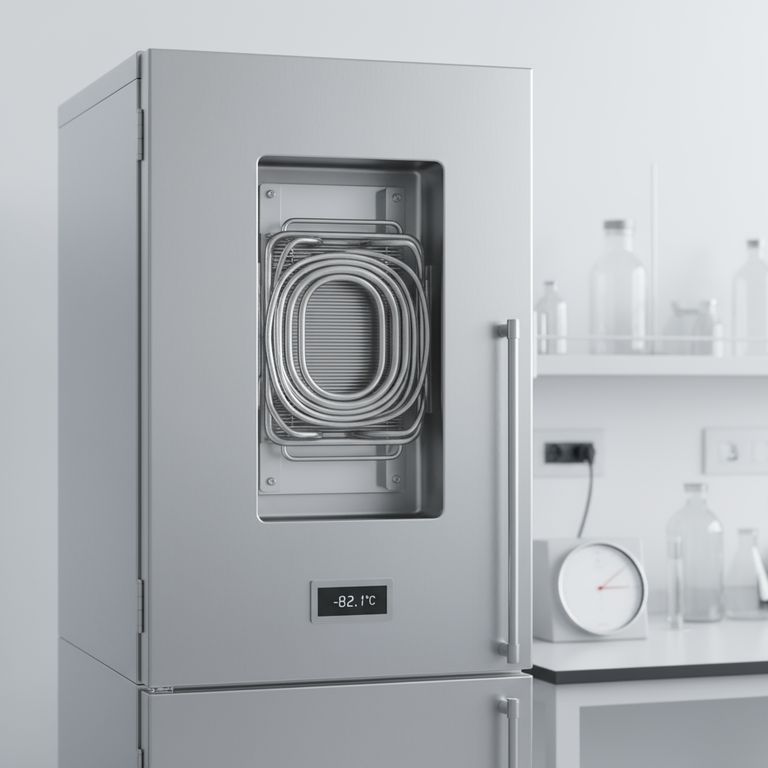
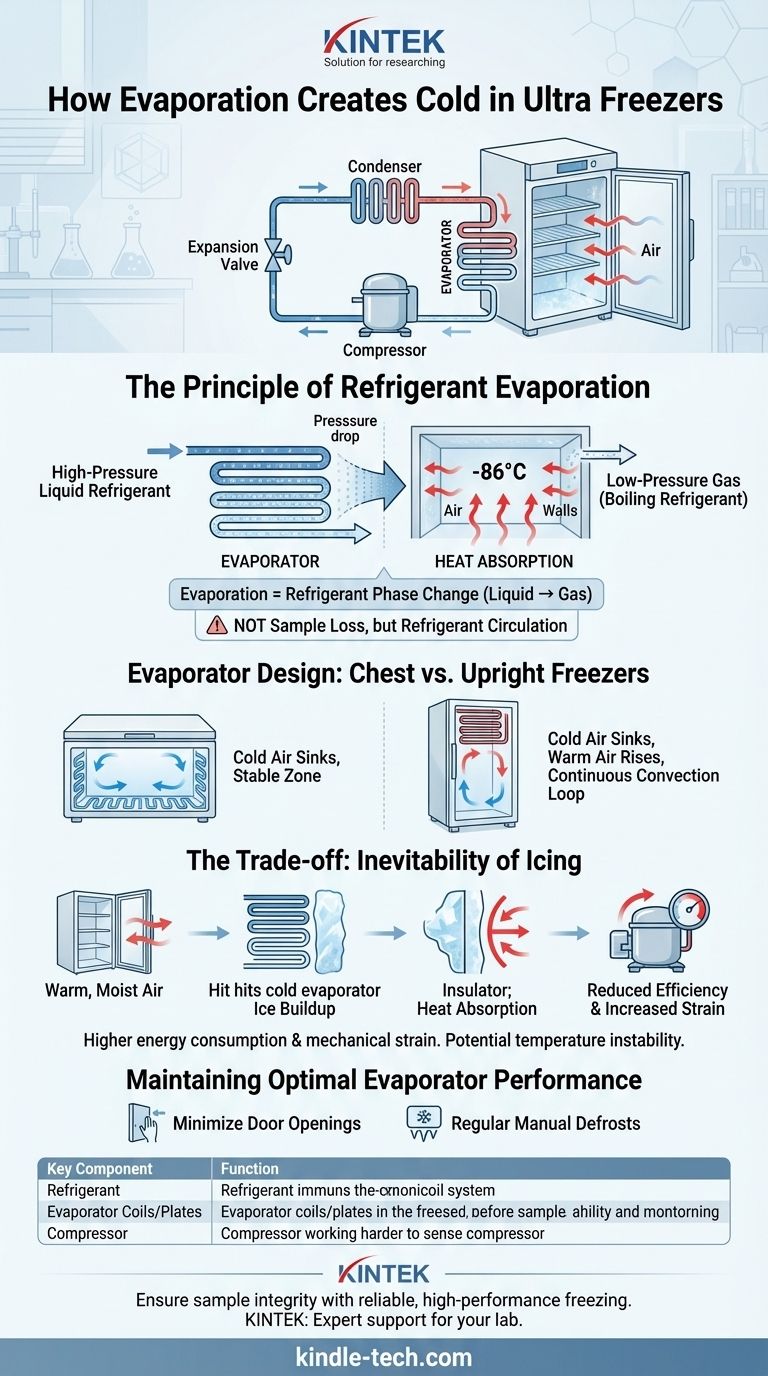
In an ultra-freezer, evaporation is the core process that creates cold. It does not refer to your samples disappearing, but to a specialized refrigerant changing from a liquid to a gas inside a sealed system of coils or plates. This phase change actively absorbs heat from the freezer's interior, lowering the temperature to as low as -86°C.
The term "evaporation" in refrigeration is technical jargon for the step in the cooling cycle where the refrigerant boils at an extremely low temperature. This process is the engine of heat removal, and understanding it is key to recognizing why issues like ice buildup can severely impact freezer performance.

The Principle of Refrigerant Evaporation
A Common Point of Confusion
First, it is critical to distinguish between two types of evaporation. The term in this context does not mean the loss of sample volume over time.
Instead, it refers exclusively to the refrigerant—a specialized fluid circulating within the freezer's closed cooling system.
How Evaporation Creates Cold
The cooling cycle relies on a simple principle of physics: when a liquid turns into a gas (evaporates), it must absorb energy from its surroundings.
A high-pressure liquid refrigerant is fed into a network of tubing inside the freezer chamber, known as the evaporator.
As the refrigerant enters the evaporator, its pressure is drastically lowered. This pressure drop causes its boiling point to plummet.
The refrigerant then boils and "evaporates" into a gas, even at extremely cold temperatures. To do this, it absorbs a massive amount of heat energy from the air and walls of the freezer chamber, making the interior intensely cold.
The Evaporator: Coils and Plates
The hardware where this process occurs is the evaporator, which takes the form of coils or steel plate heat exchangers.
These components are strategically placed inside the freezer to maximize contact with the interior air and walls, ensuring efficient removal of heat.
Evaporator Design: Chest vs. Upright Freezers
The physical layout of the evaporator coils is optimized based on the freezer's design to leverage natural air convection.
Chest Freezer Design
In a chest freezer, the evaporator coils are typically placed along the interior walls and the bottom of the unit.
Since cold air is dense and sinks, this placement ensures that the coldest surfaces are at the bottom and sides, creating a stable, uniform cold zone.
Upright Freezer Design
In an upright freezer, the coils run along the walls and the top of the chamber.
This design improves heat exchange efficiency as the coldest air at the top sinks, displacing warmer air upwards towards the coils to be cooled in a continuous convection loop.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The evaporator is the coldest point in the freezer, which makes it central to the system's primary weakness: ice formation.
The Inevitability of Icing
Every time the freezer door is opened, warm, moist air from the room rushes inside.
When this moisture comes into contact with the sub-zero evaporator coils, it freezes instantly, forming a layer of ice.
The Impact on Performance
This ice acts as an insulator. It creates a barrier between the refrigerant coils and the air inside the chamber.
As ice builds up, the evaporator becomes less effective at absorbing heat. The compressor must then run longer and work harder to maintain the target temperature.
Reduced Efficiency and Increased Strain
This inefficiency leads directly to higher energy consumption and increased mechanical strain on the compressor, which is often the most expensive component to fail.
Over time, excessive ice buildup can also cause temperature instability, putting valuable samples at risk.
Maintaining Optimal Evaporator Performance
Understanding that the evaporator's efficiency is directly tied to heat transfer gives you the power to maintain your unit's health and stability. Regular defrosting is not just cleaning; it is essential preventative maintenance.
- If your primary focus is sample integrity: Minimize door openings to prevent ice from forming on the evaporator, which is the key to maintaining stable, uniform temperatures.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and longevity: Perform regular manual defrosts as recommended by the manufacturer to remove insulating ice, which reduces compressor run-time and lowers operating costs.
By managing ice buildup on the evaporator, you directly control your freezer's performance and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Function in Evaporation Process |
|---|---|
| Refrigerant | Specialized fluid that boils at low pressure, absorbing heat as it changes from liquid to gas. |
| Evaporator Coils/Plates | The internal tubing where evaporation occurs, directly removing heat from the freezer chamber. |
| Compressor | Works with the evaporator; it must run harder if ice insulates the coils, reducing efficiency. |
Ensure your lab's critical samples are protected with reliable, high-performance freezing. Unstable temperatures or inefficient freezers can jeopardize research integrity and increase operational costs. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing ultra-freezers and expert support to maintain optimal conditions for your laboratory. Contact our team today to find the perfect freezing solution for your specific needs and maximize your freezer's performance and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 158L Precision Vertical Ultra Low Freezer for Laboratory Applications
- 708L Ultra Low Temperature Freezer High Performance Laboratory Freezer
- 28L Compact Upright Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Laboratory
- 58L Precision Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Upright Freezer for Critical Sample Storage
- 508L Advanced Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Critical Laboratory Storage
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are commonly stored in ultra low temperature freezers? Preserving Cells, Vaccines & Biomolecules
- How is temperature controlled in ultra low temperature freezers? A Guide to Stable -80°C Storage
- What are the different types of ultra-low temperature freezers available? Choose the Right ULT Freezer for Your Lab
- What is convection-based cooling in ultra-low temperature freezers? Achieve Superior Temperature Stability for Your Samples
- How should frost be removed from Ultra-Low Temperature Freezers? Protect Your Samples and Equipment



















