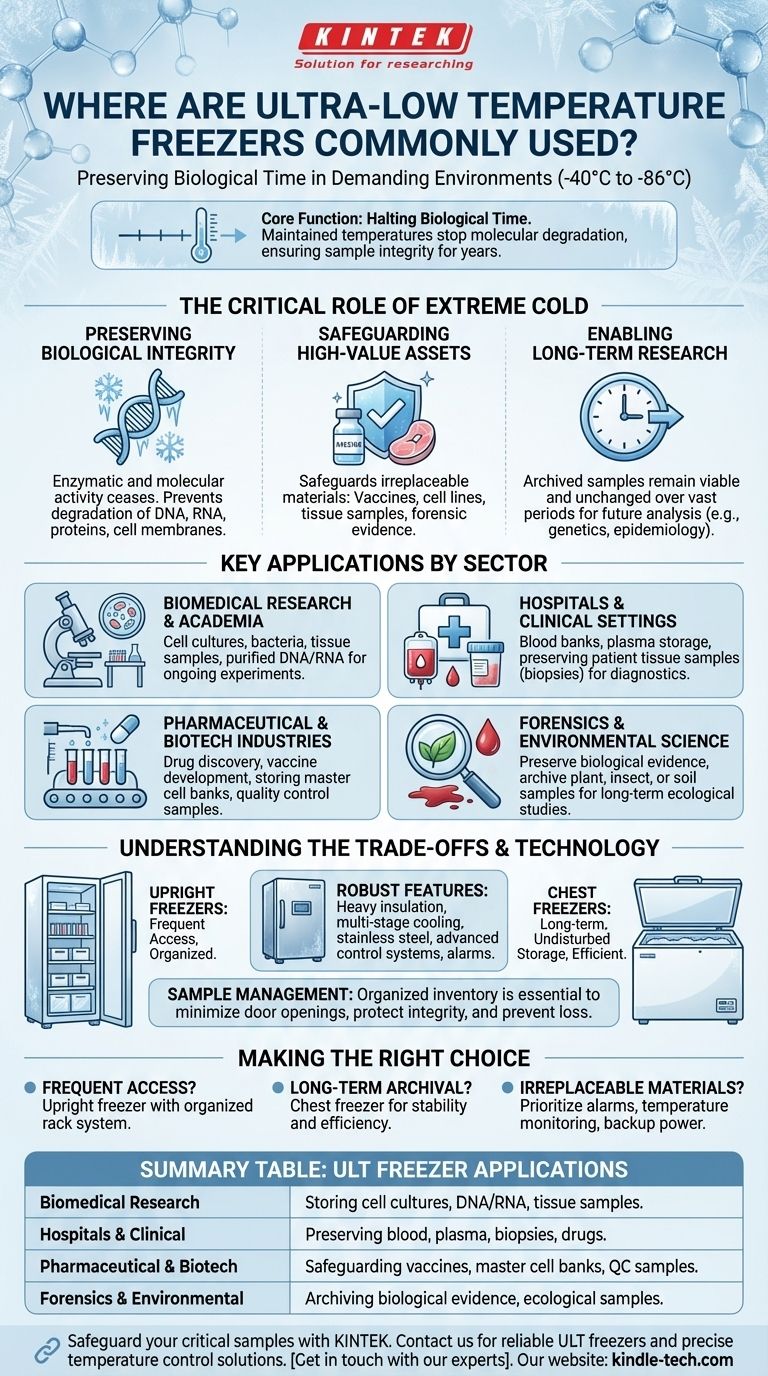
Ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezers are most commonly used in demanding medical, research, and scientific environments. You will find them in research institutes, hospitals, blood banks, pharmaceutical labs, and biotechnology companies where the long-term preservation of sensitive biological materials is critical.
The core function of a ULT freezer isn't just cold storage; it's about halting biological time. By maintaining temperatures between -40°C and -86°C, these units effectively stop the molecular degradation of invaluable samples, ensuring their integrity for years or even decades.

The Critical Role of Extreme Cold
Standard freezers are insufficient for long-term scientific and medical storage. The function of a ULT freezer goes far beyond simple cooling; it is a tool for preservation at the molecular level.
Preserving Biological Integrity
At ultra-low temperatures, nearly all enzymatic and molecular activity ceases. This prevents the degradation of delicate structures like DNA, RNA, proteins, and cell membranes, which would otherwise break down over time.
Safeguarding High-Value Assets
The materials stored in ULT freezers often represent years of research, critical patient diagnostics, or the foundation of new pharmaceuticals. These freezers safeguard irreplaceable assets such as vaccines, cell lines, tissue samples, and forensic evidence.
Enabling Long-Term Research
Many scientific studies, particularly in genetics and epidemiology, require samples to be stored for decades to allow for future analysis. ULT freezers provide the stable environment necessary to ensure these archived samples remain viable and unchanged over vast periods.
Key Applications by Sector
While the principle of preservation is universal, the specific application of ULT freezers varies significantly depending on the field.
In Biomedical Research and Academia
University labs and research institutes use ULT freezers to store a vast array of materials. This includes cell cultures, bacteria, tissue samples, and purified DNA/RNA for ongoing and future experiments in fields like molecular biology and genetics.
In Hospitals and Clinical Settings
Hospitals rely on these freezers for blood banks, plasma storage, and preserving patient tissue samples (biopsies) for diagnostic purposes. They are also crucial for storing specialized drugs and reagents that require extreme cold.
In Pharmaceutical and Biotech Industries
For pharmaceutical and biotech companies, ULT freezers are essential for the entire product lifecycle. They are used in drug discovery, vaccine development, and for storing master cell banks and quality control samples.
In Forensics and Environmental Science
Forensic labs use ULT freezers to preserve biological evidence, such as tissue and blood, preventing DNA degradation. Environmental researchers use them to archive plant, insect, or soil samples for long-term ecological studies.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Technology
Choosing and operating a ULT freezer involves understanding its design and operational requirements. It is not a standard appliance but a piece of critical laboratory infrastructure.
Upright vs. Chest Freezers
The two primary designs serve different needs. Upright freezers offer easy, organized access with shelving, making them ideal for frequently used samples. Chest freezers are better for long-term, undisturbed storage, as they lose less cold air when opened and maintain temperature more efficiently.
Robust Construction and Features
These freezers are built with heavy insulation and powerful, multi-stage cooling systems. Key features include stainless steel interiors for cleanliness, tightly sealed doors, and sophisticated control systems with audible and visual alarms to alert staff to any temperature fluctuations.
The Importance of Sample Management
A fully loaded ULT freezer can hold thousands of individual, high-value samples. An organized inventory system is not just a convenience; it is essential to minimize door opening times, protect sample integrity, and prevent the loss of critical materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a ULT freezer and which model to choose depends entirely on the application and the nature of the materials being stored.
- If your primary focus is frequent access in a busy lab: An upright freezer with a well-organized rack system is the most efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is long-term archival of critical assets: A chest freezer provides superior temperature stability and energy efficiency for undisturbed storage.
- If your primary focus is storing irreplaceable materials: Prioritize a unit with robust alarm systems, temperature monitoring, and a reliable backup power plan.
Ultimately, a ULT freezer is an investment in the long-term integrity and future value of your most critical biological materials.
Summary Table:
| Sector | Primary Use of ULT Freezers |
|---|---|
| Biomedical Research | Storing cell cultures, DNA/RNA, tissue samples for experiments. |
| Hospitals & Clinical | Preserving blood, plasma, biopsies, and temperature-sensitive drugs. |
| Pharmaceutical & Biotech | Safeguarding vaccines, master cell banks, and quality control samples. |
| Forensics & Environmental Science | Archiving biological evidence and ecological samples for long-term study. |
Safeguard your critical samples with the right ultra-low temperature freezer. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing reliable lab equipment, including ULT freezers, to meet the demanding needs of research, clinical, and biotech laboratories. Our expertise ensures you get the precise temperature control and sample integrity your work demands. Contact us today to find the perfect preservation solution for your lab's unique requirements. Get in touch with our experts
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 158L Precision Vertical Ultra Low Freezer for Laboratory Applications
- 938L Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Advanced Laboratory Storage
- 808L Precision Laboratory Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer
- 108L Vertical Ultra Low Temperature ULT Freezer
- 408L Advanced Vertical Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Critical Research Material Preservation
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of ultra-low temperature freezers available? Choose the Right ULT Freezer for Your Lab
- Why are ULT freezers considered vital equipment in labs? Ensuring Uncompromised Sample Integrity for Critical Research
- What is the purpose of ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezers? Preserve Critical Biological Samples
- How are advancements in compressor technology and refrigerant fluids improving ULT freezers? Boost Efficiency & Cut Costs
- How should frost be removed from Ultra-Low Temperature Freezers? Protect Your Samples and Equipment



















