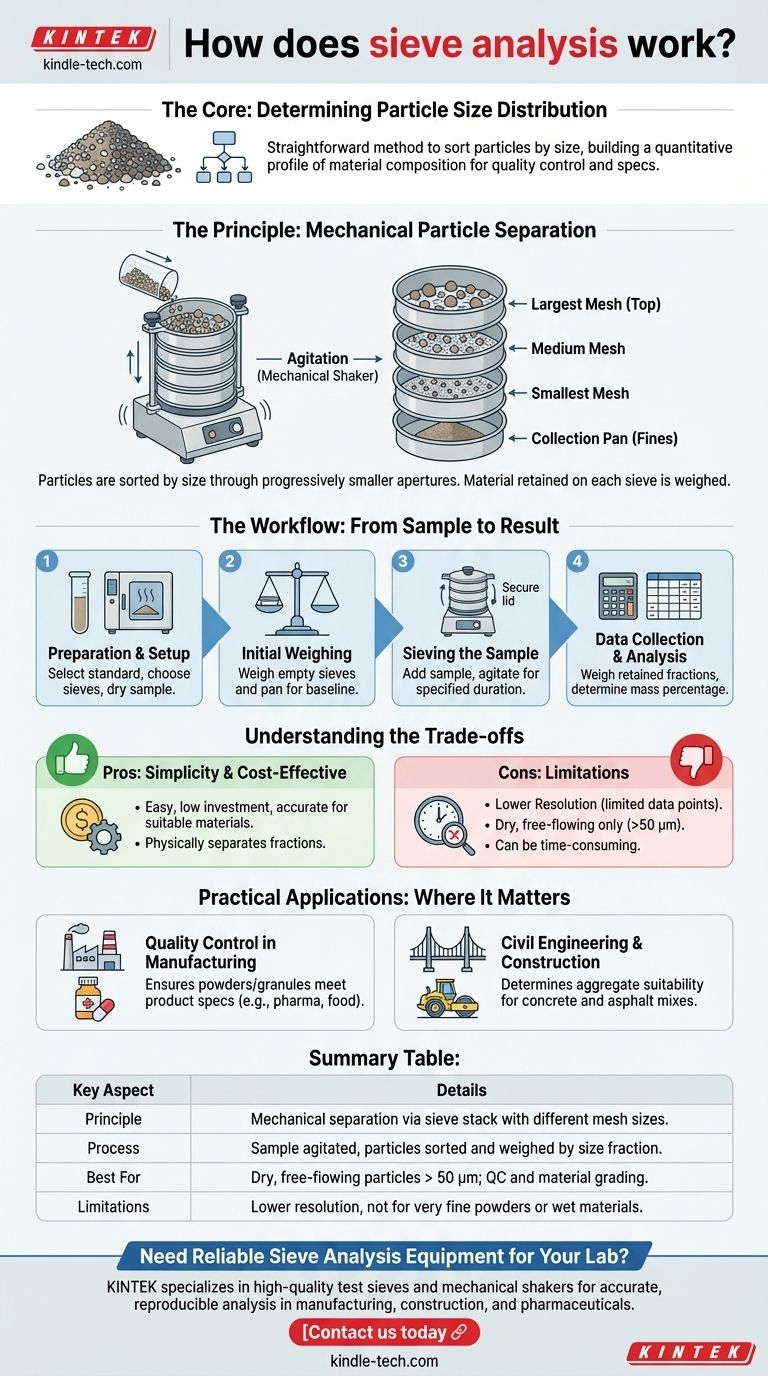
At its core, sieve analysis is a straightforward method for determining the particle size distribution of a granular material. It works by passing a sample through a stack of sieves with progressively smaller mesh openings. As the stack is agitated, particles are sorted by size, and by weighing the material retained on each sieve, you can build a quantitative profile of the material's composition.
The true value of sieve analysis lies not just in sorting particles, but in providing a cost-effective and highly reproducible method to translate a physical sample into critical data for quality control, material specification, and engineering design.

The Fundamental Principle: Mechanical Particle Separation
Sieve analysis operates on a simple, mechanical principle. It physically separates particles into different size ranges, offering a tangible look at the material's structure.
The Sieve Stack
A series of test sieves are stacked in order, with the sieve having the largest mesh openings at the top and the one with the smallest openings at the bottom. A solid collection pan is placed at the very bottom of the stack to collect the finest particles.
The Role of Agitation
A precisely weighed sample of the dry material is placed in the top sieve. The entire stack is then agitated, typically with a mechanical sieve shaker, for a set period. This motion allows particles to find their way through the apertures until they reach a sieve they are too large to pass through.
The End Result: A Size Distribution
After agitation, the material caught on each sieve represents a specific particle size fraction. The contents of each sieve are weighed, providing a data set that shows what percentage of the total sample mass falls within each size range.
The Sieve Analysis Workflow: From Sample to Result
The process is methodical, ensuring that the results are accurate and repeatable. It can be broken down into four distinct phases.
Phase 1: Preparation and Setup
Before any sieving begins, you must develop a method based on the material being tested. This involves selecting an appropriate standard (like ASTM or ISO), choosing the right sieve sizes for the stack, and preparing the sample, which often requires pre-drying it to ensure particles flow freely.
Phase 2: The Initial Weighing Process
Accuracy starts with a baseline. Each sieve in the stack, including the bottom pan, is weighed while empty and its mass is recorded. This is crucial for calculating the final mass of the retained fractions later.
Phase 3: Sieving the Sample
The prepared, weighed sample is added to the top sieve, the lid is secured, and the stack is placed in a sieve shaker. The shaker agitates the stack for a specified duration, ensuring consistent and thorough separation.
Phase 4: Data Collection and Analysis
After shaking is complete, each sieve is weighed again, this time with the retained particles. By subtracting the empty sieve weight from the final weight, you determine the mass of the material in each size fraction. These values are then often converted into percentages of the total sample mass.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While widely used, sieve analysis is not the right tool for every situation. Understanding its strengths and weaknesses is critical for proper application.
Key Advantage: Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
Sieve analysis is easy to perform, requires minimal investment in equipment, and provides accurate, reproducible results for suitable materials. A unique benefit is that it physically separates the size fractions, which can then be used for further analysis.
Key Limitation: Resolution
The number of data points you can obtain is limited by the number of sieves in your stack, which is typically a maximum of eight. This means your final particle size distribution is based on a relatively small number of size fractions, offering lower resolution than other methods.
Key Limitation: Material Constraints
The technique is only effective for dry, free-flowing particles. It also has a practical lower limit for measurement around 50 micrometers (µm); particles smaller than this are difficult to sieve accurately and may require alternative analysis methods like laser diffraction.
Key Limitation: Time Consumption
The entire process, especially the necessary sample drying and the multiple weighing steps, can be time-consuming compared to more modern, automated particle analysis techniques.
Practical Applications: Where Sieve Analysis Matters
This method is a cornerstone in industries where particle size directly impacts product performance, safety, and quality.
Quality Control in Manufacturing
Manufacturers use sieve analysis to provide a reliable check on particle size throughout a production line. It ensures that powders and granular materials meet the specifications required for the final product, from pharmaceuticals to food products.
Civil Engineering and Construction
The properties of aggregates are critical in construction. Sieve analysis is used to determine the suitability of sand, gravel, and crushed stone for use in concrete and asphalt mixes, ensuring the final material has the required strength and stability. It is also used to properly size screens for water production wells.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To decide if sieve analysis fits your needs, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control or material grading on a budget: Sieve analysis is an excellent, reliable choice due to its low cost and high reproducibility for known materials.
- If your primary focus is high-resolution data for R&D or analyzing very fine powders: You should consider alternative methods like laser diffraction, as sieve analysis will lack the necessary detail and cannot measure sub-50 µm particles.
Ultimately, understanding both its procedural simplicity and its inherent limitations is the key to effectively leveraging sieve analysis for material characterization.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Principle | Mechanical separation of particles using a stack of sieves with different mesh sizes. |
| Process | Sample is agitated on sieves; particles are sorted and weighed by size fraction. |
| Best For | Dry, free-flowing particles larger than 50 µm; ideal for quality control and material grading. |
| Limitations | Lower resolution than laser diffraction; not suitable for very fine powders or wet materials. |
Need Reliable Sieve Analysis Equipment for Your Lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including precision test sieves and mechanical sieve shakers. Whether you're in manufacturing, construction, or pharmaceuticals, our products ensure accurate, reproducible particle size analysis for your quality control needs.
Contact us today to find the perfect sieve analysis solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
People Also Ask
- What is the operating procedure of a sieve shaker? Master Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- What is powder sieving? A Guide to Accurate Particle Size Separation
- What are the different types of sieving machines? Choose the Right Motion for Your Material
- What are the applications of sieving machine? From Mining to Pharmaceuticals
- What are the components of a sieving machine? Unlock the Anatomy of Precision Particle Separation



















