In short, a sputtering target is manufactured through advanced metallurgical processes like vacuum melting, casting, powder metallurgy, and precision machining. These methods are used to transform high-purity raw materials into a solid, dense, and uniform block. This finished block serves as the source material that is vaporized inside a vacuum chamber to create a thin film coating on a substrate.
The way a sputtering target is made is just as critical as the sputtering process itself. Its purity, density, and microstructure directly dictate the quality, performance, and consistency of the final thin film being deposited.
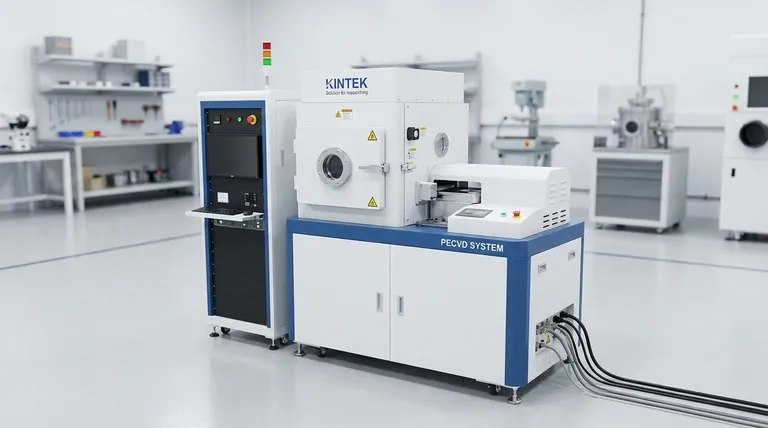

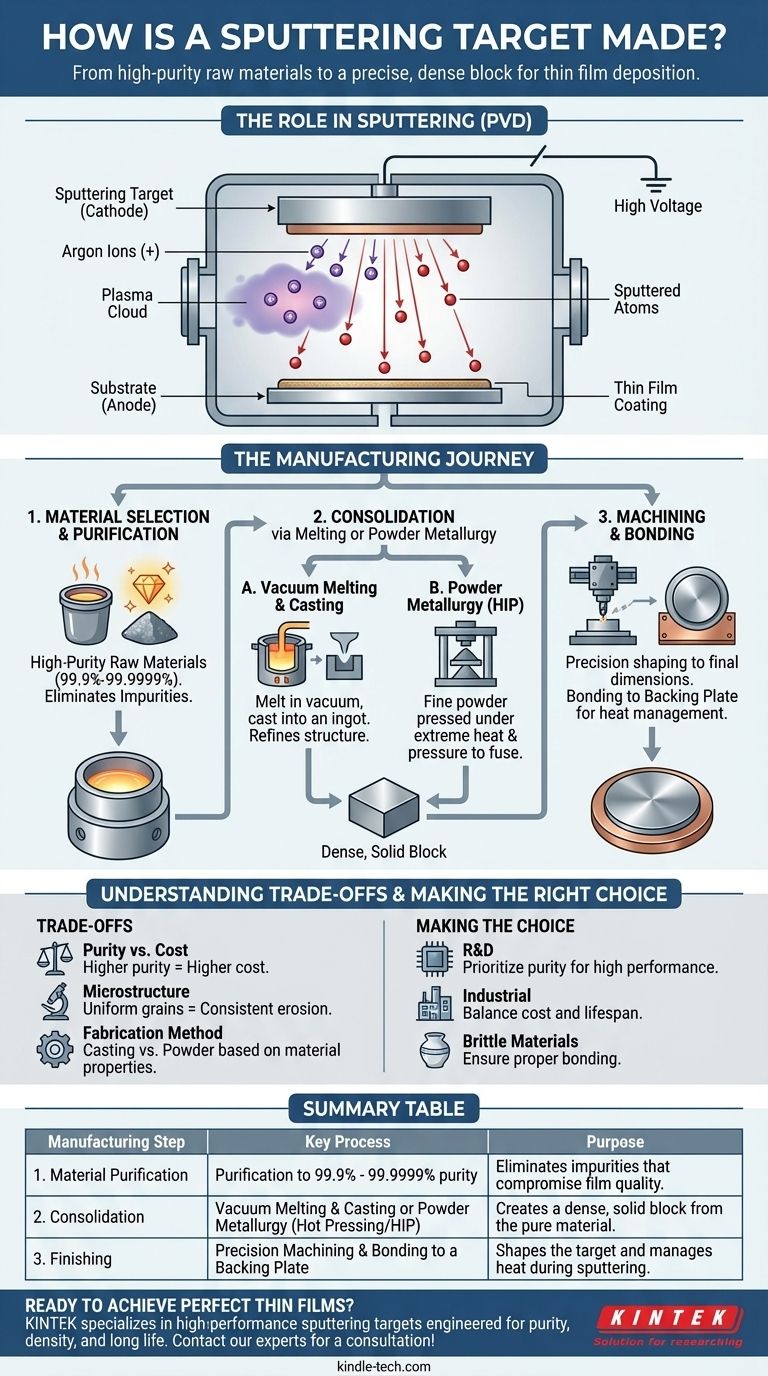
What is a Sputtering Target's Role?
A sputtering target is the "source" in a physical vapor deposition (PVD) process. Think of it as a solid block of the exact material you want to use for your coating.
The Source of the Coating
In the sputtering process, a vacuum chamber is filled with an inert gas like argon. A high negative voltage is applied to the target, which acts as a cathode.
This voltage creates a plasma, stripping electrons from the argon atoms and turning them into positively charged ions.
The Bombardment Process
These heavy argon ions are accelerated with immense force, slamming into the surface of the sputtering target.
This high-energy collision transfers momentum and knocks individual atoms or molecules off the target's surface, a process known as sputtering. These ejected particles then travel across the chamber and deposit onto a substrate (like glass, silicon, or plastic), building up a thin film layer by layer.
The Manufacturing Journey: From Raw Material to Target
Creating a target that can withstand this bombardment while providing a uniform stream of atoms requires a precise and controlled manufacturing process.
Step 1: Material Selection and Purification
The process begins with the highest purity raw materials possible (often 99.9% to 99.9999% pure). Impurities in the target will inevitably end up in your final film, potentially ruining its electrical, optical, or mechanical properties.
Step 2: Consolidation via Melting or Powder Metallurgy
The pure material must be consolidated into a dense, solid form. Two primary methods are used:
- Vacuum Melting & Casting: The material is melted in a vacuum or inert gas environment to prevent contamination. It is then cast into an ingot, which is often further processed through forging or rolling to refine its grain structure.
- Powder Metallurgy: For materials with very high melting points or for creating alloys, a fine powder of the material is pressed under extreme pressure and heat (a process called hot pressing or hot isostatic pressing - HIP) until the particles fuse into a solid, dense block.
Step 3: Machining and Bonding
The dense block is then precision machined into the final shape and dimensions required by the specific sputtering system (e.g., circular or rectangular).
Because targets get hot during sputtering, they are often bonded to a copper or aluminum "backing plate." This plate provides structural support and, more importantly, acts as a heat sink, drawing thermal energy away from the target to prevent it from cracking or melting.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of manufacturing method and material purity involves critical engineering compromises that directly impact cost and performance.
Purity vs. Cost
Achieving higher levels of purity is an expensive, energy-intensive process. A 99.999% pure target can be orders of magnitude more expensive than a 99.95% pure target. For non-critical applications, a lower-purity target may be sufficient and far more economical.
Microstructure and Grain Size
The internal grain structure of the target affects how uniformly it erodes. A target with a fine, uniform grain size will sputter more evenly and have a longer useful life. Coarse or non-uniform grains can lead to inconsistent deposition rates and premature target failure.
Fabrication Method and Material Properties
Casting generally produces very dense targets, but it's not suitable for all materials. Powder metallurgy can create targets from virtually any material but may result in slightly lower density compared to a cast target if not performed perfectly. This choice depends entirely on the material's fundamental properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal sputtering target depends entirely on the requirements of the final film.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge R&D (e.g., semiconductors, advanced optics): Prioritize the highest possible purity and a uniform, fine-grained microstructure to ensure repeatable and high-performance results.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial coating (e.g., architectural glass, decorative finishes): Balance the target's cost against its lifespan and the required purity to achieve the most economical process.
- If you are working with brittle materials (e.g., ceramics like ITO): Ensure the target is properly bonded to a backing plate to manage thermal stress and prevent cracking during sputtering.
Ultimately, the sputtering target is not just a piece of material; it is a highly engineered component designed for a single purpose: to be the perfect source for building a perfect thin film.
Summary Table:
| Manufacturing Step | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Material Purification | Purification to 99.9% - 99.9999% purity | Eliminates impurities that compromise film quality. |
| 2. Consolidation | Vacuum Melting & Casting or Powder Metallurgy (Hot Pressing/HIP) | Creates a dense, solid block from the pure material. |
| 3. Finishing | Precision Machining & Bonding to a Backing Plate | Shapes the target and manages heat during sputtering. |
Ready to Achieve Perfect Thin Films?
The quality of your sputtering target is the foundation of your deposition process. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including sputtering targets engineered for purity, density, and long life.
We help you:
- Select the right target for your application, balancing performance and cost-effectiveness.
- Ensure consistent results with targets designed for uniform erosion and reliable deposition.
- Optimize your entire sputtering process with expert support.
Don't let your target be the weak link. Whether you're in semiconductor R&D or large-scale industrial coating, contact our experts to find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
People Also Ask
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- What is the speed of PECVD? Achieve High-Speed, Low-Temperature Deposition for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials














