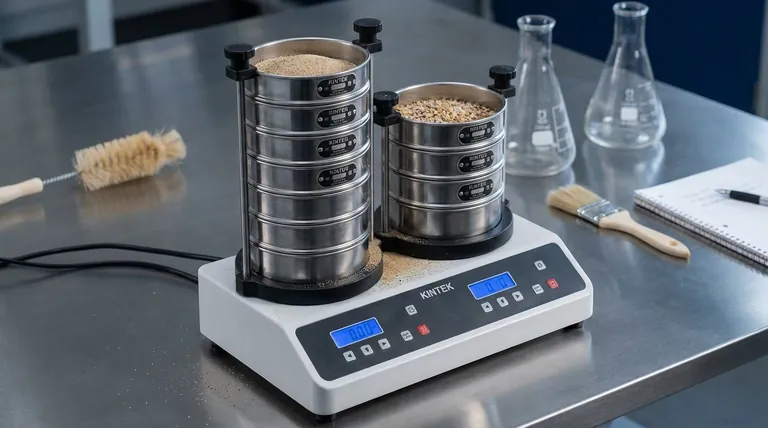
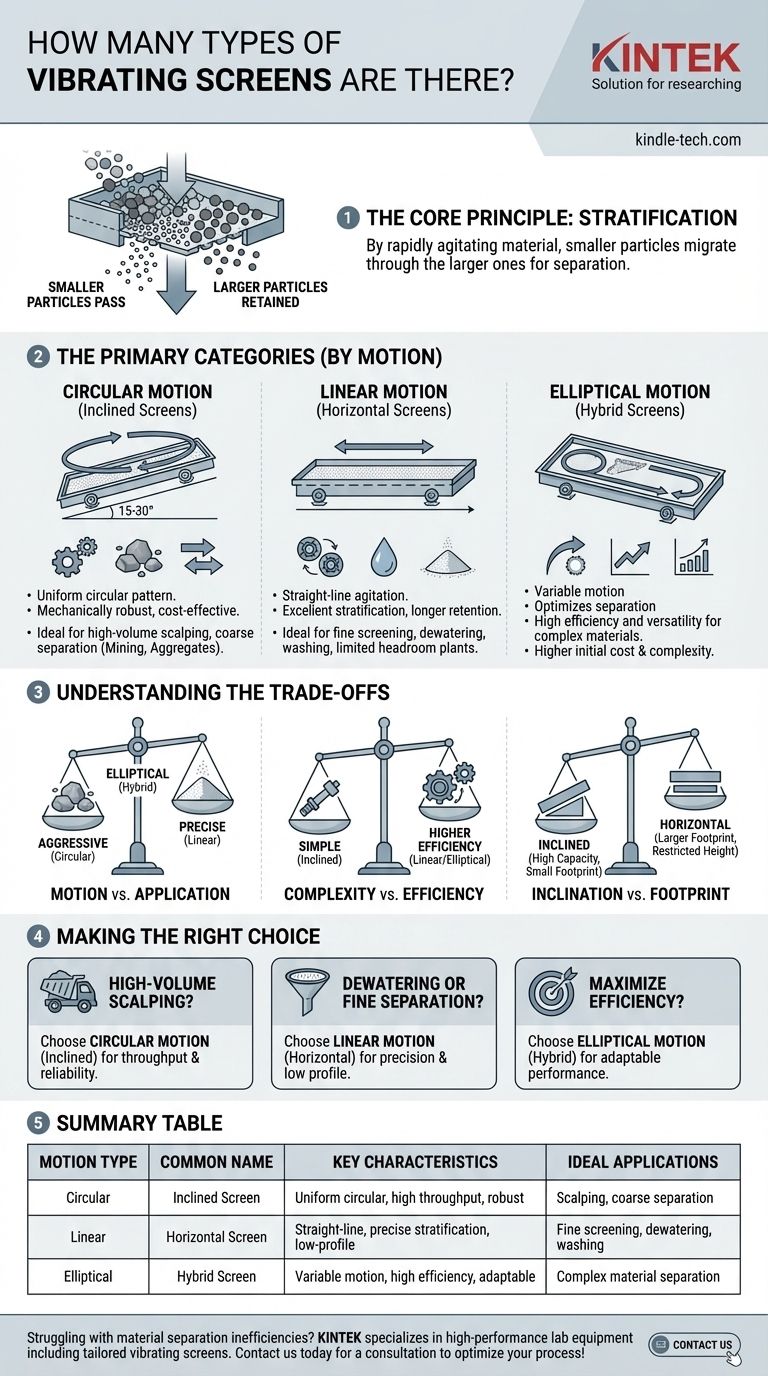
While there is no single, definitive number, the most useful way to classify vibrating screens is by their distinct motion characteristics. The industry primarily categorizes them into three fundamental types based on the path the screen media travels: circular, linear, and elliptical. Understanding these motions is the key to selecting the right equipment for a specific material and application.
The "type" of a vibrating screen isn't just a label; it describes the specific motion it uses to separate material. This motion—whether circular, linear, or a hybrid—directly determines the screen's efficiency, capacity, and ideal application.

The Core Principle: How Vibrating Screens Work
A vibrating screen operates on a simple but powerful principle: stratification. By rapidly agitating a bed of mixed material, the screen causes smaller particles to migrate down through the larger ones.
This allows the smaller particles to pass through the screen openings (apertures), while the larger particles are retained and conveyed toward the discharge end. The specific pattern of this vibration is what defines the screen's type and performance.
The Primary Categories of Vibrating Screens (By Motion)
The mechanics that generate the vibration dictate how the screen behaves and what it excels at. Each motion pattern offers a distinct advantage.
Circular Motion Vibrating Screens
These are often called inclined screens because they are typically installed at an angle of 15-30 degrees. The entire screen body moves in a uniform circular or "hula-hoop" pattern.
This motion is generated by a simple eccentric shaft, making these screens mechanically robust, cost-effective, and easy to maintain. The combination of vibration and gravity effectively moves material down the screen deck.
They are the workhorses of the industry, ideal for high-volume scalping (removing oversized material) and coarse separations in applications like mining and aggregate production.
Linear Motion Vibrating Screens
Often referred to as horizontal screens, these units use a pair of counter-rotating motors or a geared exciter to produce a straight-line, back-and-forth motion.
This linear agitation lifts material up and forward with each stroke, creating a conveying action even on a horizontal or slightly inclined deck. This provides excellent material stratification and longer retention time on the screen surface.
They excel at fine screening, dewatering, and washing applications where precision and efficiency are more critical than raw throughput. Their horizontal profile is also a major advantage in plants with limited headroom.
Elliptical Motion Vibrating Screens
These screens represent a more advanced, hybrid approach. The motion is intentionally varied along the length of the screen deck to optimize the separation process.
Typically, the motion is more aggressive and circular at the feed end to quickly stratify the material bed. It then transitions to a more gentle, linear, or elliptical motion at the discharge end to improve near-size particle screening efficiency.
This adaptability makes them highly efficient and versatile, but they are also more mechanically complex and carry a higher initial cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a screen is not just about picking a type; it's about balancing performance, cost, and operational constraints.
Motion vs. Application
The fundamental trade-off is between the aggressive, high-throughput action of a circular motion screen and the precise, efficient separation of a linear motion screen. Elliptical screens attempt to provide the best of both but at a higher cost.
Complexity vs. Efficiency
A simple inclined screen with a single eccentric shaft is robust and has lower maintenance costs. However, a linear or elliptical screen, with its more complex drive system, can deliver significantly higher screening efficiency for difficult-to-separate materials.
Inclination vs. Footprint
Inclined screens use gravity to their advantage, achieving high capacity within a relatively small machine footprint. Horizontal (linear motion) screens require a larger screening area to achieve the same capacity but are indispensable when vertical space is restricted.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be driven by the specific goal of your screening process.
- If your primary focus is high-volume scalping or coarse separation in a rugged environment: A circular motion (inclined) screen offers the best combination of throughput, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is dewatering, fine material separation, or working within a height-restricted plant: A linear motion (horizontal) screen provides the necessary precision and low-profile design.
- If your primary focus is maximizing efficiency across a complex feed of material and budget is less of a concern: An elliptical motion screen delivers superior, adaptable performance for challenging applications.
Ultimately, selecting the correct vibrating screen begins with a clear understanding of how its fundamental motion solves your specific separation challenge.
Summary Table:
| Motion Type | Common Name | Key Characteristics | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circular | Inclined Screen | Uniform circular motion, high throughput, robust & cost-effective | Scalping, coarse separation (mining, aggregates) |
| Linear | Horizontal Screen | Straight-line motion, precise stratification, horizontal/low-profile design | Fine screening, dewatering, washing, height-restricted plants |
| Elliptical | Hybrid Screen | Variable motion (aggressive at feed end, gentle at discharge), high efficiency | Complex material separation, efficiency-focused applications |
Struggling with material separation inefficiencies? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including vibrating screens tailored to your specific laboratory needs. Whether you require robust circular motion for high throughput or precise linear motion for fine screening, our experts will help you select the ideal solution to enhance your lab's productivity and accuracy. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can optimize your screening process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- How do laboratory constant temperature shakers ensure material uniformity? Optimize Bimetallic Nanocatalyst Synthesis
- What is the role of a laboratory shaker in silane sol preparation? Master Uniform Aramid Fabric Coating
- Why use a laboratory crushing and sieving system for rice husks? Optimize Hydrolysis for 1mm Particle Size
- What are the precautions of sieve shaker? Ensure Accurate Particle Analysis & Protect Your Equipment
- What is the function of a benchtop shaker in zirconium extraction? Achieve Rapid Chemical Equilibrium Efficiency
- What is the role of a sieving system in wet depithing? Optimize Sugarcane Bagasse Cellulose Extraction
- How long should sieve shaker be run for? Find Your Optimal Sieving Time for Accurate Results
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity



















