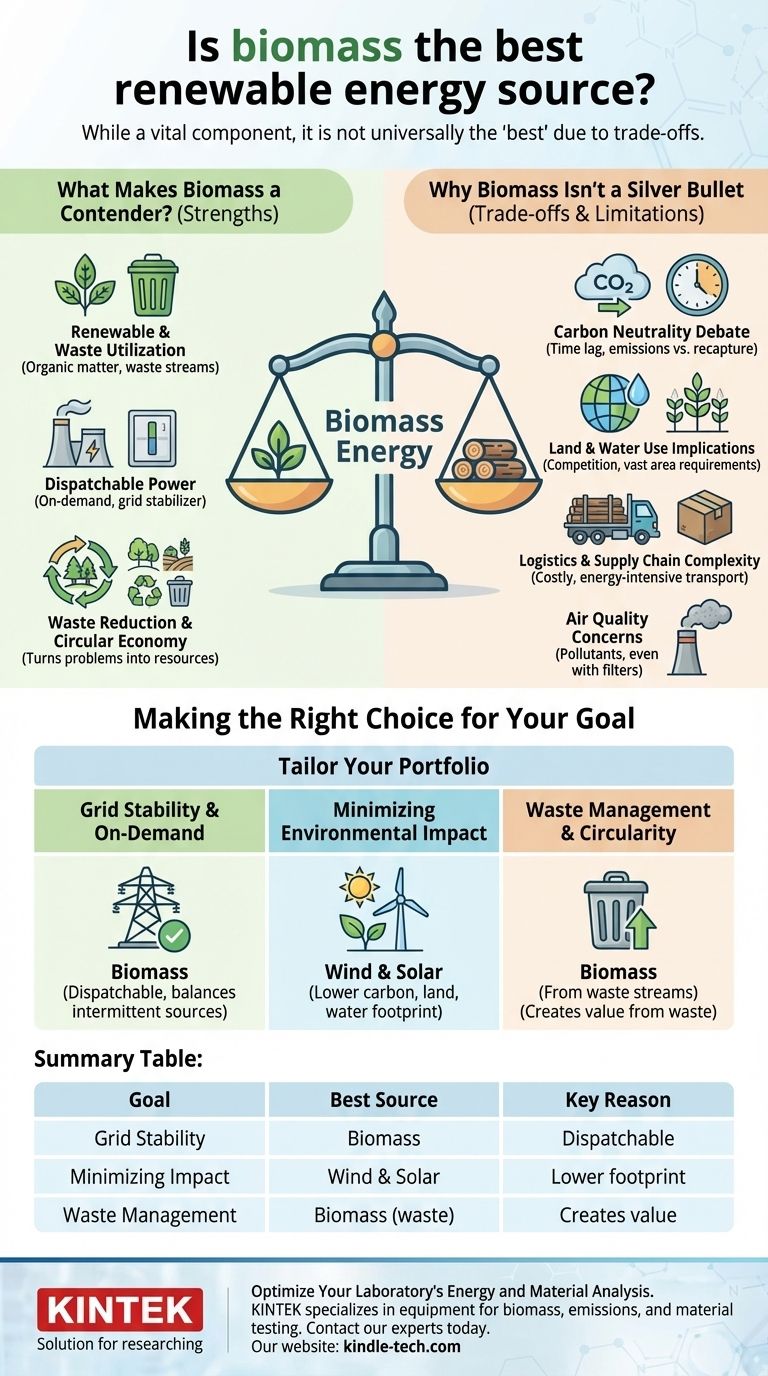
While biomass is a vital component of the renewable energy landscape, it is not universally the "best" source. Its primary advantage is providing consistent, on-demand power, a feature many other renewables lack. However, its suitability is highly dependent on specific goals, as it comes with significant environmental and logistical trade-offs not associated with sources like solar or wind.
The core issue is one of trade-offs. Biomass offers reliability and the ability to use waste streams, but it raises complex questions about carbon emissions, land use, and air quality that must be carefully weighed against other renewable options.

What Makes Biomass a Contender?
Biomass energy is derived from organic matter. Understanding its strengths is key to seeing where it fits in a modern energy grid.
A Renewable Source from Organic Matter
Biomass includes a wide range of materials, such as wood, dedicated energy crops, and organic wastes from agriculture, forestry, and municipalities.
By converting this organic matter into electricity or heat, it serves as a direct, renewable substitute for fossil fuels.
The Key Advantage: Dispatchable Power
Unlike solar or wind which are "intermittent" (only producing when the sun shines or wind blows), biomass power is dispatchable. This means it can be turned on and off on demand.
This reliability makes it exceptionally valuable for stabilizing the power grid, providing energy during peak demand or when intermittent sources are unavailable. It acts like a rechargeable battery for the entire grid.
Waste Reduction and the Circular Economy
Utilizing waste streams—like agricultural residue, forest debris, or municipal organic waste—to generate energy is a major benefit.
This approach turns a potential disposal problem into a valuable resource, supporting the principles of a circular economy.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Biomass Isn't a Silver Bullet
True technical analysis requires an objective look at the limitations. The case for biomass becomes complicated when considering its environmental footprint and logistical demands.
The Carbon Neutrality Debate
The claim that biomass is carbon neutral is a point of significant debate. The idea is that the CO2 released during combustion is offset by the CO2 absorbed by the plants as they grew.
However, this cycle can take decades, especially for forests. There is a critical time lag between when the carbon is released and when it is fully recaptured, meaning biomass can contribute to near-term warming.
Land and Water Use Implications
Growing dedicated energy crops can compete with agriculture for fertile land and fresh water, potentially impacting food security and prices.
While using waste avoids this issue, large-scale biomass operations often require vast land areas for cultivation, harvesting, and processing.
Logistics and Supply Chain Complexity
Biomass is bulky and has a lower energy density than fossil fuels. This makes transportation from the source (forests, farms) to the power plant costly and energy-intensive.
An efficient and sustainable supply chain is a major logistical challenge that must be overcome for a biomass project to be viable.
Air Quality Concerns
Burning any organic material, including biomass, releases air pollutants like particulates and nitrogen oxides.
While modern plants use advanced filters, these emissions can still impact local air quality, a disadvantage not present with wind, solar, or hydropower.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" renewable energy source is not a single technology but a diverse portfolio tailored to specific needs. Use these points to guide your decision-making.
- If your primary focus is grid stability and on-demand power: Biomass is a leading renewable candidate because it is dispatchable and can balance the intermittency of solar and wind.
- If your primary focus is minimizing environmental impact: Wind and solar generally offer a lower carbon, land, and water footprint per unit of energy produced, provided land is sited responsibly.
- If your primary focus is waste management and circularity: Using agricultural, forestry, or municipal organic waste for biomass energy is an excellent way to create value from materials that would otherwise be discarded.
Ultimately, the most resilient and sustainable energy strategy involves integrating multiple renewable sources, leveraging the unique strengths of each.
Summary Table:
| Goal | Best Renewable Energy Source | Key Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Stability & On-Demand Power | Biomass | Dispatchable; balances intermittent solar/wind |
| Minimizing Environmental Impact | Wind & Solar | Lower carbon, land, and water footprint |
| Waste Management & Circularity | Biomass (from waste streams) | Creates value from agricultural/forestry/municipal waste |
Optimize Your Laboratory's Energy and Material Analysis
Choosing the right energy source requires precise data. KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables needed to analyze biomass feedstocks, monitor emissions, and test material properties for your renewable energy projects. From sample preparation to advanced analytical instruments, our solutions help you make data-driven decisions for a sustainable future.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time



