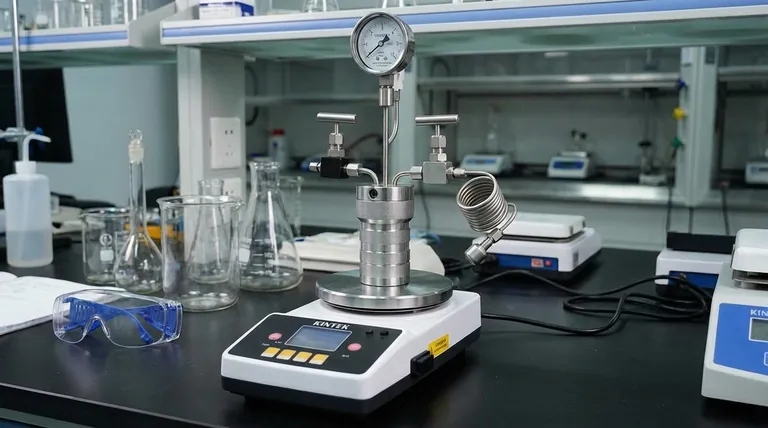
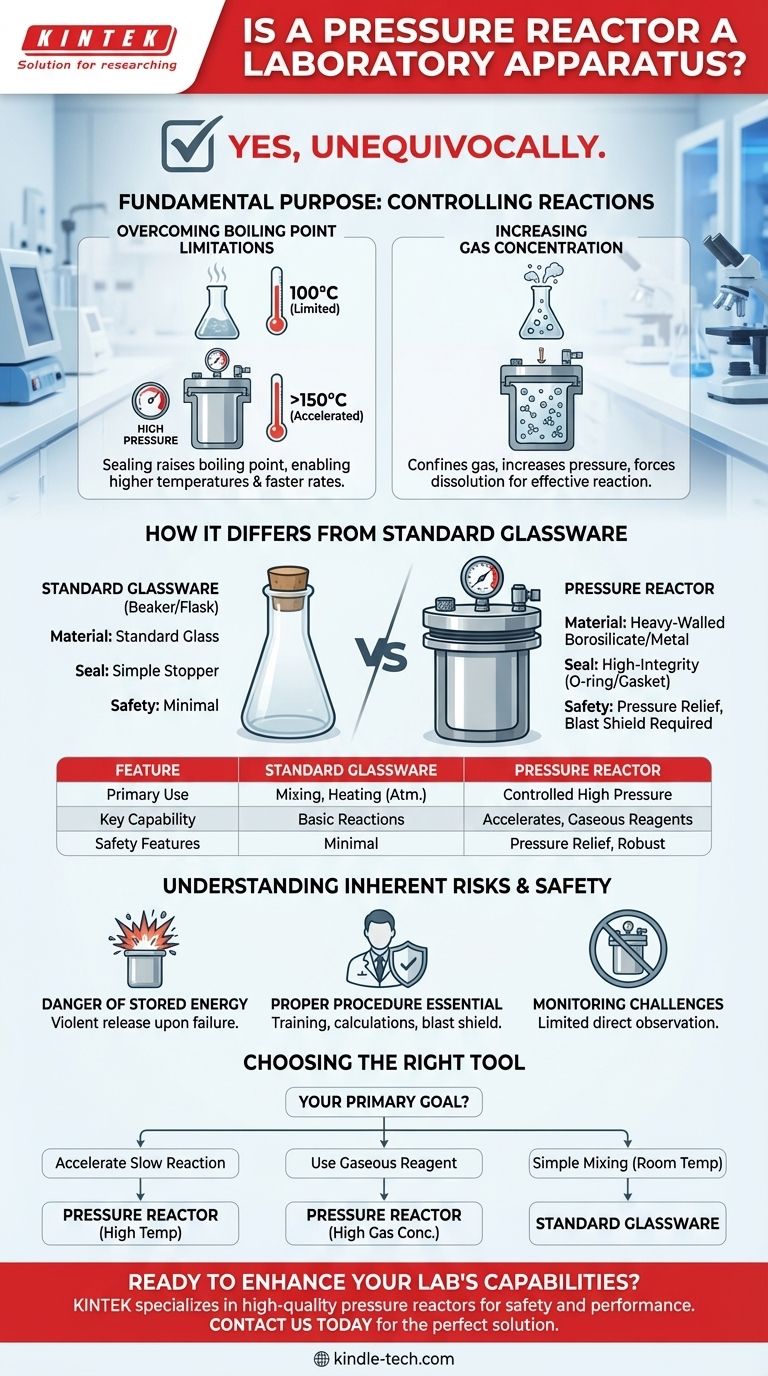
Yes, unequivocally. A pressure reactor is a specialized and essential piece of laboratory apparatus. Unlike common glassware like beakers or flasks, it is specifically engineered as a sealed vessel to safely conduct chemical reactions under conditions of elevated pressure, either generated by the reaction itself or applied from an external source.
The key function of a pressure reactor is to create a controlled, high-pressure environment. This allows chemists to manipulate reaction conditions in ways that are impossible at normal atmospheric pressure, fundamentally expanding the scope of what can be achieved in the lab.

The Fundamental Purpose of a Pressure Reactor
A pressure reactor, sometimes called a sealed tube or pressure tube, is not merely a container. It is an active tool for controlling the outcome of a chemical reaction. Its use is centered on a few core principles.
Overcoming Boiling Point Limitations
Many chemical reactions proceed very slowly at room temperature. Heating them is the most common way to speed them up.
However, a reaction's maximum temperature is limited by the boiling point of the solvent it's in. By sealing the vessel, the pressure builds, which in turn raises the solvent's boiling point.
This allows a reaction to be run at a much higher temperature than would be possible in an open flask, drastically accelerating reaction rates.
Increasing the Concentration of Gases
Many critical industrial and laboratory reactions require a reagent that is a gas at room temperature, such as hydrogen, oxygen, or carbon monoxide.
In an open flask, these gases have very low solubility in the reaction liquid. A pressure reactor confines the gas, increasing its pressure and forcing more of it to dissolve into the liquid phase. This high concentration makes the gas a more effective participant in the reaction.
How It Differs from Standard Glassware
While a simple sealed tube might look like a sturdy test tube, its design and function are fundamentally different from standard laboratory glassware.
Material and Construction
Pressure reactors are built to withstand force. They are typically made from heavy-walled borosilicate glass or robust metals like stainless steel or Hastelloy. This construction is essential to prevent catastrophic failure under pressure.
The Critical Importance of Sealing
An ordinary flask might use a simple stopper, but a pressure reactor requires a high-integrity seal. This is often achieved with a threaded cap and an O-ring or gasket designed to become tighter as internal pressure increases, ensuring the system remains safely contained.
Instrumentation and Safety Features
More advanced pressure reactors are sophisticated instruments. They often include integrated pressure gauges, thermometers, stirring mechanisms, and, most importantly, pressure-relief valves or rupture discs as a critical safety feature to prevent explosions.
Understanding the Inherent Risks
The power of a pressure reactor comes with significant responsibility and risk. It is one of the more dangerous pieces of equipment in a standard chemistry lab.
The Danger of Stored Energy
A pressurized system contains a large amount of stored energy. If the vessel were to fail, this energy would be released instantaneously and violently, creating an explosion that can propel shrapnel and spill hazardous chemicals.
The Need for Proper Procedure
Using a pressure reactor requires specialized training. Chemists must carefully calculate the potential pressure a reaction could generate and always work behind a blast shield. The vessel must be inspected for cracks or defects before every use.
Monitoring Challenges
Because the system is sealed, it can be difficult to observe the reaction directly or to add reagents partway through. This requires the chemist to have a much better upfront understanding of the reaction's behavior.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Goal
Selecting a pressure reactor means you need to manipulate the fundamental conditions of a reaction. For most simple tasks, standard glassware is the correct and safer choice.
- If your primary focus is to accelerate a slow reaction: A pressure reactor allows you to safely heat solvents well beyond their normal boiling points.
- If your primary focus is to use a gaseous reagent: A pressure reactor is essential for containing the gas and increasing its concentration in your reaction mixture.
- If your primary focus is simply mixing liquids at room temperature: A standard beaker or flask is the appropriate tool for the job.
Ultimately, a pressure reactor is a powerful laboratory instrument for pushing the boundaries of chemical reactions, enabling chemists to achieve results that would otherwise be out of reach.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Glassware | Pressure Reactor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Mixing, heating at atmospheric pressure | Reactions under controlled high pressure |
| Key Capability | Basic reactions | Accelerates reactions, uses gaseous reagents effectively |
| Safety Features | Minimal | Pressure-relief valves, robust construction, requires blast shield |
| Typical Materials | Standard glass | Heavy-walled borosilicate glass, stainless steel, Hastelloy |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with a reliable pressure reactor?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including robust pressure reactors designed for safety and performance. Whether you need to accelerate reaction rates or work with gaseous reagents, our solutions are tailored to meet your laboratory's specific needs.
Contact us today to find the perfect pressure reactor for your research and ensure your lab operates at the forefront of chemical innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a PTFE-lined hydrothermal autoclave in cys-CDs synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Carbon Dots
- Why are high-strength alloy tube reactors critical for HHIP? Ensuring Safety and Purity in High-Pressure Environments
- What is the advantage of using high-pressure hydrothermal reactors to treat biomass waste? Efficient Resource Recovery
- Why must SCWG reactors maintain a specific heating rate? Protect Your High-Pressure Vessels from Thermal Stress
- Why is a high-pressure hydrothermal synthesis autoclave necessary for MnO2 nanowires? Precision Catalyst Growth



















